Difference between revisions of "Protein coding sequences/Reporters"
m |
|||
| (18 intermediate revisions by 6 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | {{Catalog/MainLinks}} | ||
[[Protein coding sequences|< Back to Protein coding sequences]] | [[Protein coding sequences|< Back to Protein coding sequences]] | ||
{{:{{PAGENAME}}/Overview}} | {{:{{PAGENAME}}/Overview}} | ||
| + | __TOC__ | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
<style> | <style> | ||
| Line 10: | Line 12: | ||
</style> | </style> | ||
</html> | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Chromoproteins== | ||
| + | [[Image:UUChromo.jpg|400px|left]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chromoproteins are often responsible for coloration in corals or sea anemones. The expressed pigment can be seen by the naked eye and without any external tool, making them very useful as reporter proteins. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Chromoproteins and fluorescent proteins can have some overlap. Generally, fluorescent proteins appear white or clear to the naked eye, but some have the property of showing pigmentation also. One such protein is <partinfo>BBa_E1010</partinfo>. | ||
| + | |||
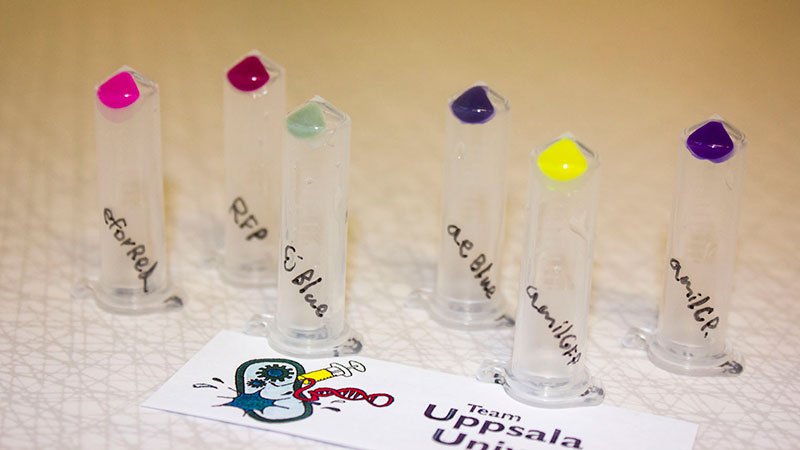
| + | '''2012 Uppsala University:''' | ||
| + | The Uppsala University team created a chromoprotein collection as part of their project in 2012. Here are pellets of bacteria expressing chromoproteins eforRed (<partinfo>BBa_K592012</partinfo>), RFP (<partinfo>BBa_E1010</partinfo>), cjBlue (<partinfo>BBa_K592011</partinfo>), aeBlue (<partinfo>BBa_K864401</partinfo>), amilGFP (<partinfo>BBa_K592010</partinfo>) and amilCP (<partinfo>BBa_K592009</partinfo>). | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | To add parts to this table use the category: '''//cds/reporter/chromoprotein''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | <parttable>Chromoproteins</parttable> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==IP-Free Fluorescent proteins== | ||
| + | [[Image:DNA2.0_Four_protein_Screen_Shot_2014-02-05_at_4.57.24_PM.png|400px|left]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | These parts were created by DNA 2.0 as part of their IP-Free series of fluorescent and chromogenic proteins. They are available to use under the BioBrick Public Agreement. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To add parts to this table, make sure to add the category: //legal/ip-free. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <parttable>ip_free_fluorescent_proteins</parttable> | ||
==Fluorescent proteins== | ==Fluorescent proteins== | ||
| − | Fluorescence can be readily quantified using a microscope, plate reader or flow cytometer equipped to excite the fluorescent protein with the appropriate wavelength of light. Since | + | {| |
| + | |[[Image:GFP.jpg|thumb|center|100px|GFP visualized under UV light.]] | ||
| + | | Fluorescent proteins are convenient ways to visualize or quantify the output of a device or part. Many different fluorescent proteins are available from the Registry. The first fluorescent protein to be cloned and the most commonly used fluorescent protein is '''green fluorescent protein (GFP)'''. GFP was cloned from jellyfish. Based on GFP, several investigators generated mutations that altered the spectral properties of GFP resulting in '''yellow fluorescent protein (YFP)''' and '''cyan fluorescent protein (CFP)'''. | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |[[Image:RFP.jpg|thumb|center|100px|RFP visualized in white light.]] | ||
| + | |'''Red fluorescent protein (RFP)''', shown on the left, was isolated from coral. Note that the colonies appear red to the naked eye as well as fluoresce red. RFP is unrelated to the GFP family of fluorescent proteins. Several derivatives of RFP have been generated including '''mOrange''' and '''mCherry'''. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | Fluorescence can be readily quantified using a microscope, plate reader or flow cytometer equipped to excite the fluorescent protein with the appropriate wavelength of light. Since several different fluorescent proteins are available, multiple gene expression measurements can be made in parallel. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To include a part in this table, include the categories "//function/reporter/fluorescence" and set the part type to Coding under the Hard Information tab of the part. | ||
<parttable>fluorescent_reporter_protein_coding_sequence</parttable> | <parttable>fluorescent_reporter_protein_coding_sequence</parttable> | ||
| − | <!-- To include a part in this table, include the categories "// | + | <!-- To include a part in this table, include the categories "//function/reporter/fluorescence" and set the part type to Coding under the Hard Information tab of the part. --> |
==Luciferases== | ==Luciferases== | ||
Luminescence can be readily quantified using a plate reader or luminescence counter. Luciferases are especially well-suited for measuring low levels of gene expression because cells tend to have little to no background luminescence in the absence of a luciferase. | Luminescence can be readily quantified using a plate reader or luminescence counter. Luciferases are especially well-suited for measuring low levels of gene expression because cells tend to have little to no background luminescence in the absence of a luciferase. | ||
| − | |||
<parttable>luciferase_reporter_protein_coding_sequence</parttable> | <parttable>luciferase_reporter_protein_coding_sequence</parttable> | ||
| − | <!-- To include a part in this table, include the categories "// | + | <!-- To include a part in this table, include the categories "//function/reporter/light" and set the part type to Coding under the Hard Information tab of the part. --> |
==Enzymes that produce colored substrates== | ==Enzymes that produce colored substrates== | ||
Enzymes that produce colored substrates can be quantified using spectrophotometers or other instruments that can take absorbance measurements including plate readers. Like luciferases, enzymes like β-galactosidase are good for measuring low levels of gene expression because they tend to amplify low signals. | Enzymes that produce colored substrates can be quantified using spectrophotometers or other instruments that can take absorbance measurements including plate readers. Like luciferases, enzymes like β-galactosidase are good for measuring low levels of gene expression because they tend to amplify low signals. | ||
| − | |||
<parttable>color_reporter_protein_coding_sequence</parttable> | <parttable>color_reporter_protein_coding_sequence</parttable> | ||
| − | <!-- To include a part in this table, include the categories "// | + | <!-- To include a part in this table, include the categories "//function/reporter/color" and set the part type to Coding under the Hard Information tab of the part. --> |
==Miscellaneous== | ==Miscellaneous== | ||
| − | |||
<parttable>other_reporter_protein_coding_sequence</parttable> | <parttable>other_reporter_protein_coding_sequence</parttable> | ||
| − | + | <!-- To include a part in this table, include the categories "//function/reporter" and none of the above categories set the part type to Coding under the Hard Information tab of the part. --> | |
| − | <!-- To include a part in this table, include the categories "// | + | |
==References== | ==References== | ||
| Line 42: | Line 76: | ||
| − | + | __NOEDITSECTION__ | |
Latest revision as of 21:22, 20 January 2016
< Back to Protein coding sequences
Introduction to Reporters
What are reporters? Why call them reporters and not fluorescent proteins, beta-galactosidase/Xgal assays or pigments? The answer is that in synthetic biology, they are often used as a mechanism to display information. If you design a biosensor system that is sensitive to substrate A, you ideally want a way of displaying these results without needing an additional assay. Using a reporter protein is a great way of achieving this property.
Reporter protein coding sequences encode proteins whose presence in the cell or organism is readily observed. For example, fluorescent proteins cause a cell to fluoresce when excited with light of a particular wavelength, luciferases cause a cell to catalyze a reaction that produces light, and enzymes such as beta-galactosidase convert a substrate to a colored product. Reporters are frequently used to quantify the strength or activity of upstream gene expression parts such as promoters and ribosome binding sites. Reporters, when fused in frame to other protein coding sequences, can also be used to identify where a protein is located in a cell or organism.
There are several different ways to measure or quantify a reporter depending on the particular reporter and what kind of characterization data is desired. Generally speaking, microscopy is useful for obtaining both spatial and temporal information on reporter activity, particularly at the single cell level. Flow cytometers are best suited for measuring the distribution in reporter activity across a large population of cells. Plate readers are generally best for taking population average measurements of many different samples over time.
Some iGEM teams have excellent projects that create new reporters, or make great use of existing ones. Please see the tables below for fluorescent proteins, chromoproteins, luciferase proteins and enzymes that produce colored substrates in the Registry.
Contents
Chromoproteins
Chromoproteins are often responsible for coloration in corals or sea anemones. The expressed pigment can be seen by the naked eye and without any external tool, making them very useful as reporter proteins.
Chromoproteins and fluorescent proteins can have some overlap. Generally, fluorescent proteins appear white or clear to the naked eye, but some have the property of showing pigmentation also. One such protein is BBa_E1010.
2012 Uppsala University: The Uppsala University team created a chromoprotein collection as part of their project in 2012. Here are pellets of bacteria expressing chromoproteins eforRed (BBa_K592012), RFP (BBa_E1010), cjBlue (BBa_K592011), aeBlue (BBa_K864401), amilGFP (BBa_K592010) and amilCP (BBa_K592009).
To add parts to this table use the category: //cds/reporter/chromoprotein
| Name | Description | Type | Created by | length | uses | seq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_K592009 | amilCP, blue chromoprotein | Coding | Lei Sun | 669 | 99 | . . . attgcacgcaaacctgtggtcgcctaataa |
| BBa_K592010 | amilGFP, yellow chromoprotein | Coding | Lei Sun | 699 | 27 | . . . catgttaaccctttgaaggttaaataataa |
| BBa_K592011 | cjBlue, green chromoprotein | Coding | Antonio Ascue Avalos | 702 | 14 | . . . tgcccgagcaaacttggtcataattaataa |
| BBa_K592012 | eforRed, red chromoprotein | Coding | Lei Sun | 681 | 22 | . . . catttctcaccgctgccgaaggctctccca |
| BBa_K864401 | aeBlue blue chromoprotein | Coding | Erik Lundin | 699 | 8 | . . . gcaccgagtaaattagggcatcactaataa |
| BBa_K1122007 | AmilCP (BBa_K592009) compatible with Genabler assembly | Coding | Lina Gasiūnaitė | 685 | . . . cacgcaaacctgtggtcgccgcctgaagag | |
| BBa_K1033902 | meffBlue, blue chromoprotein | Coding | Erik Gullberg | 669 | 1 | . . . atcgcacgcaagccggtggtcgcctaataa |
| BBa_K1033906 | tsPurple, purple chromoprotein | Coding | Sabri Jamal | 690 | 17 | . . . agcgatgtgccggaaaaagcgacgtaataa |
| BBa_K1033916 | amajLime, yellow-green chromoprotein | Coding | Sabri Jamal | 693 | 10 | . . . cacatcacctcggtcgtgccgttctaataa |
| BBa_K1033919 | gfasPurple, purple chromoprotein | Coding | Sabri Jamal | 669 | 5 | . . . atcgcgcgcaaatcggtggttgcctaataa |
| BBa_K1033910 | fwYellow, yellow chromoprotein | Coding | Sabri Jamal | 714 | 11 | . . . gcagttgacctggagacgtaccgttaataa |
| BBa_K1023005 | eforRed | Coding | Michiel Karrenbelt | 687 | . . . tcccctctcccgaaggctctcccgtaataa | |
| BBa_K1033932 | spisPink, pink chromoprotein | Coding | Erik Lundin | 678 | 5 | . . . gctgttgcccgtgtgctggaagtgtaataa |
| BBa_K1033933 | asPink, pink chromoprotein | Coding | Erik Lundin | 702 | 6 | . . . gcaccgagcaagctgggtcataattaataa |
| BBa_K1399000 | RFP from Discosoma striata (coral) with AAV-ssrA degradation tag | Coding | Anna Stikane | 714 | . . . gacgaaaactacgctgctgctgtttaataa | |
| BBa_K1399001 | RFP from Discosoma striata (coral) with LVA-ssrA degradation tag | Coding | Anna Stikane | 714 | 2 | . . . gacgaaaactacgctttagtagcttaataa |
| BBa_K1399002 | RFP from Discosoma striata (coral) with LAA-ssrA degradation tag (wt) | Coding | Anna Stikane | 714 | 1 | . . . gacgaaaactacgctctggctgcttaataa |
| BBa_K1399003 | RFP from Discosoma striata (coral) with DAS-ssrA degradation tag | Coding | Anna Stikane | 714 | 1 | . . . gacgaaaactacgctgacgcttcttaataa |
| BBa_K1824017 | AeBlue blue chromoprotein | Coding | Zhe Yang | 699 | . . . gcaccgagtaaattagggcatcactaataa | |
| BBa_K1680006 | Fluorescent protein dronpa | Coding | Katharina Sporbeck | 669 | . . . gctcactctgaattgccaagacaagctaag | |
| BBa_K1824019 | AeBlue blue chromoprotein with aav tag | Coding | Zhe Yang | 738 | . . . gacgaaaactacgctgcagcagtttaataa | |
| BBa_K1680017 | Cre-Dronpa Fusion | Coding | Nicolai von K�gelgen | 1728 | . . . gctcactctgaattgccaagacaagctaag | |
| BBa_K1680018 | Cre-Dronpa fusion | Coding | Nicolai von K�gelgen | 1746 | . . . gctcactctgaattgccaagacaagctaag | |
| BBa_K1680019 | Cre-dronpa fusion | Coding | Nicolai von Kuegelgen | 1764 | . . . gctcactctgaattgccaagacaagctaag | |
| BBa_K1680020 | Cre-dronpa fusion | Coding | Nicolai von Kuegelgen | 1782 | . . . gctcactctgaattgccaagacaagctaag | |
| BBa_K1680021 | Dronpa caged Cre with NLS | Coding | Nicolai von Kuegelgen | 2433 | . . . gctcactctgaattgccaagacaagctaag | |
| BBa_K1680022 | Dronpa caged Cre with NLS | Coding | Nicolai von Kuegelgen | 2451 | . . . gctcactctgaattgccaagacaagctaag | |
| BBa_K1680023 | Dronpa caged Cre with NLS | Coding | Nicolai von Kuegelgen | 2469 | . . . gctcactctgaattgccaagacaagctaag | |
| BBa_K1680024 | Dronpa caged Cre with NLS | Coding | Nicolai von Kuegelgen | 2487 | . . . gctcactctgaattgccaagacaagctaag | |
| BBa_K1886004 | sll1472 ccaS | Coding | Lejian Jiang | 2733 | . . . aaacgctataaccatttgcctcgagcttag | |
| BBa_K2656018 | amilCP Coding Sequence | Coding | Adri�n Requena Guti�rrez, Carolina Ropero | 670 | 2 | . . . attgcacgcaaacctgtggtcgcctaataa |
| BBa_K5527001 | amilCP purple, Purple chromoprotein | Coding | Otto Isaksson | 669 | -1 | . . . attgcacgcaaacctgtggtcgcctaataa |
| BBa_K5527002 | amilCP yellow, Yellow chromoprotein | Coding | Otto Isaksson | 669 | -1 | . . . attgcacgcaaacctgtggtcgcctaataa |
| BBa_K5527003 | amilCP light purple, Light purple chromoprotein | Coding | Otto Isaksson | 669 | -1 | . . . attgcacgcaaacctgtggtcgcctaataa |
| BBa_K1484000 | AsPink chromoprotein in GoldenGate standard | Coding | Virginie Rutten | 721 | . . . gctgggtcataattaataagctttgagacc | |
| BBa_K1484001 | tsPurple chromoprotein in GoldenGate standard | Coding | Virginie Rutten | 709 | . . . ggaaaaagcgacgtaataagctttgagacc | |
| BBa_K1484002 | AmajLime chromoprotein in BBa and MoClo standard | Coding | Virginia Rutten | 711 | . . . cggtcgtgccgttctaataactttgagacc | |
| BBa_K1484003 | AeBlue chromoprotein in BBa and MoClo standard | Coding | ---- | 724 | . . . agggcatcactaataaaggtaggtcttcgt | |
| BBa_K1484004 | AmilGFP chromoprotein in BBa and MoClo standard | Coding | Virginia Rutten | 724 | . . . gaaggttaaataataaaggtaggtcttcgt | |
| BBa_K1484005 | AmilCP chromoprotein in BBa and MoClo standard | Coding | Virginia Rutten | 706 | . . . gccgaaggctctcccaaggtaggtcttcgt | |
| BBa_K1484006 | EforRed chromoprotein in BBa and MoClo standard | Coding | Virginia Rutten | 706 | . . . gccgaaggctctcccaaggtaggtcttcgt | |
| BBa_K1484007 | cjBlue chromoprotein in BBa and MoClo standard | Coding | Virginia Rutten | 724 | . . . acttggtcataattaaaggtaggtcttcgt | |
| BBa_K1484008 | AeBlue0034 chromoprotein in BBa and MoClo standard | Coding | Virginia Rutten | 758 | . . . agggcatcactaataaaggtaggtcttcgt | |
| BBa_K1362461 | **highly** engineered mutant of red fluorescent protein from Discosoma striata (coral) with barcode | Coding | Constantin Ahlmann-Eltze, Charlotte Bunne, Magdalena Büscher, Jan Gleixner, Max Horn, Anna Huhn, Nils Klughammer, Jakob Kreft, Elisabeth Schäfer, Carolin Schmelas, Silvan Schmitz, Max Waldha | 706 | 3 | . . . aataacgatgatagtgctagtgtagatcgc |
| BBa_K1685005 | aeBlue | Coding | ITB_Indonesia 2015 | 699 | 2 | . . . gcaccgagtaaactgggtcatcactaataa |
| BBa_K2669002 | AmilCP: Codon Optimized basic part | Coding | Elin Ramstr�m | 675 | 2 | . . . atcgcgcgcaagccggttgtcgcttgataa |
| BBa_K3892006 | EforRed | Coding | iGEM21_Linkoping_Sweden | 687 | -1 | . . . ttctcaccgctgccgaaggctctcccataa |
IP-Free Fluorescent proteins
These parts were created by DNA 2.0 as part of their IP-Free series of fluorescent and chromogenic proteins. They are available to use under the BioBrick Public Agreement.
To add parts to this table, make sure to add the category: //legal/ip-free.
| Name | Description | Type | Created by | length | uses | seq |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_J97000 | IP-Free EiraCFP (Cyan Fluorescent Protein) | Reporter | Drew Endy | 699 | . . . gtgaaagcggttgatctggacacgtatcag | |
| BBa_J97003 | IP-Free TannenRFP (Red Fluorescent Protein) | Reporter | Drew Endy | 678 | 1 | . . . aagcacttcaccgtcgacgttaaagaaacg |
| BBa_J97001 | P-Free JuniperGFP (Green Fluorescent Protein) | Reporter | Drew Endy | 702 | 7 | . . . atcaaagcagtggacctggagacgtatcgc |
| BBa_J97002 | IP-Free BlazeYFP (Yellow Fluorescent Protein) | Reporter | Drew Endy | 708 | . . . caaaaagcagtggacctggagacgtatcgc |
Fluorescent proteins
| Fluorescent proteins are convenient ways to visualize or quantify the output of a device or part. Many different fluorescent proteins are available from the Registry. The first fluorescent protein to be cloned and the most commonly used fluorescent protein is green fluorescent protein (GFP). GFP was cloned from jellyfish. Based on GFP, several investigators generated mutations that altered the spectral properties of GFP resulting in yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) and cyan fluorescent protein (CFP). | |
| Red fluorescent protein (RFP), shown on the left, was isolated from coral. Note that the colonies appear red to the naked eye as well as fluoresce red. RFP is unrelated to the GFP family of fluorescent proteins. Several derivatives of RFP have been generated including mOrange and mCherry. |
Fluorescence can be readily quantified using a microscope, plate reader or flow cytometer equipped to excite the fluorescent protein with the appropriate wavelength of light. Since several different fluorescent proteins are available, multiple gene expression measurements can be made in parallel.
To include a part in this table, include the categories "//function/reporter/fluorescence" and set the part type to Coding under the Hard Information tab of the part.
| Name | Protein | Description | Tag | Direction | Fluorescent Color | Emission | Excitation | Length | Status | Uses |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_E0030 | EYFP | enhanced yellow fluorescent protein derived from A. victoria GFP | None | Forward | Yellow | 527 | 514 | 723 | In stock | 140 |
| BBa_E0020 | ECFP | engineered cyan fluorescent protein derived from A. victoria GFP | None | Forward | Cyan | 476 | 439 | 723 | In stock | 95 |
| BBa_E1010 | mRFP1 | **highly** engineered mutant of red fluorescent protein from Discosoma striata (coral) | None | Forward | Red | 607 | 584 | 706 | In stock | 593 |
| BBa_E0040 | GFPmut3b | green fluorescent protein derived from jellyfish Aequeora victoria wild-type GFP (SwissProt: P42212 | None | Forward | Green | 511 | 501 | 720 | In stock | 875 |
| BBa_E2050 | mOrange | derivative of mRFP1, yeast-optimized | None | Orange | 562 | 548 | 769 | In stock | 15 | |
| BBa_J52021 | dnTraf6-linker-GFP | Green | 1446 | In stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_J52026 | dnMyD88-linker-GFP | Green | 1155 | In stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_I715022 | Amino Portion of RFP | Red | 462 | In stock | 2 | |||||
| BBa_I715023 | Carboxyl portion of RFP | Red | 220 | In stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_I712028 | CherryNLS - synthetic construct monomeric red fluorescent protein with nuclear localization sequence | Forward | Red | 733 | In stock | 8 | ||||
| BBa_K125500 | GFP fusion brick | Forward | Green | 718 | In stock | 13 | ||||
| BBa_K165005 | Venus YFP, yeast optimized for fusion | Forward | Yellow | 744 | In stock | 2 | ||||
| BBa_K082003 | GFP | GFP(+LVA) | Green | 756 | In stock | 31 | ||||
| BBa_K156009 | OFP (orange fluorescent protein) | Forward | Orange | 864 | In stock | 1 | ||||
| BBa_K156010 | SBFP2 (strongly enhanced blue fluorescent protein) | Blue | 720 | In stock | 9 | |||||
| BBa_K294055 | GFPmut3b | GFP RFP Hybrid | None | Green | 511 | 501 | 720 | In stock | 3 | |
| BBa_K283005 | lpp_ompA_eGFP_streptavidin | 1533 | In stock | 1 | ||||||
| BBa_K157043 | CFP | 732 | In stock | 1 | ||||||
| BBa_K411207 | Green Fluorescent Protein with LVA tag (GFPLVA) | Green | 753 | In stock | 2 | |||||
| BBa_K648013 | GFP with Standard 25 Prefix/Suffix | Green | 735 | In stock | 13 | |||||
| BBa_K525306 | Fusion Protein of S-Layer SgsE and mCerulean | Blue | 3129 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K592100 | Blue Fluorescent Protein (mTagBFP) | Blue | 705 | In stock | 41 | |||||
| BBa_K592101 | Yellow Fluorescent Protein (YFP) | Yellow | 720 | In stock | 5 | |||||
| BBa_K864100 | Super Yellow Fluorescent Protein 2 (SYFP2) | Yellow | 723 | In stock | 8 | |||||
| BBa_K1122005 | dsRED (BBa_E1010) compatible with Genabler assembly | Red | 697 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1122006 | mCherry (BBa_J06504) compatible with Genabler assembly | Red | 730 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1122008 | mTagBFP (BBa_K592100) compatible with Genabler assembly | Blue | 721 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1033916 | amajLime, yellow-green chromoprotein | Yellow, Green | 693 | In stock | 10 | |||||
| BBa_K1184000 | KillerRed | Red | 723 | In stock | 5 | |||||
| BBa_K1159301 | Super Yellow Fluorescent Protein 2 (SYFP2) in RFC[25] | Yellow | 714 | In stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_K1159302 | Enhanced Cyan Fluorescent Protein (eCFP) in RFC[25] | Cyan | 714 | In stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_K1093002 | sfCFP | Cyan | 720 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1093003 | sfBFP N-terminal | Blue | 645 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1093004 | sfCFP N-terminal | Cyan | 645 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1093017 | mCherry C-terminal | Red | 243 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1399000 | mRFP1 | RFP from Discosoma striata (coral) with AAV-ssrA degradation tag | SsrA-AAV | Forward | Red | 607 | 584 | 714 | In stock | |
| BBa_K1399001 | mRFP1 | RFP from Discosoma striata (coral) with LVA-ssrA degradation tag | SsrA-LVA degradation tag | Forward | Red | 607 | 584 | 714 | In stock | 2 |
| BBa_K1399002 | mRFP1 | RFP from Discosoma striata (coral) with LAA-ssrA degradation tag (wt) | SsrA-LAA degradation tag | Forward | Red | 607 | 584 | 714 | In stock | 1 |
| BBa_K1399003 | mRFP1 | RFP from Discosoma striata (coral) with DAS-ssrA degradation tag | SsrA-DAS degradation tag | Forward | Red | 607 | 584 | 714 | In stock | 1 |
| BBa_K1399005 | GFPmut3b | GFP (mut3b) with AAV-ssrA degradation tag | SsrA-AAV degradation tag | Forward | Green | 511 | 501 | 753 | In stock | 4 |
| BBa_K1399004 | GFPmut3b | GFP (mut3b) with LVA-ssrA degradation tag | SsrA-LVA degradation tag | Forward | Green | 511 | 501 | 753 | In stock | 8 |
| BBa_K1399006 | GFPmut3b | GFP (mut3b) with LAA-ssrA degradation tag | SsrA-LAA degradation tag | Forward | Green | 511 | 501 | 753 | In stock | 2 |
| BBa_K1399007 | GFPmut3b | GFP (mut3b) with SsrA-DAS+2 degradation tag | SsrA-DAS+2 degradation tag | Forward | Green | 511 | 501 | 759 | In stock | 4 |
| BBa_K1399008 | GFPmut3b | GFP (mut3b) with DAS-ssrA degradation tag | SsrA-DAS degradation tag | Forward | Green | 511 | 501 | 753 | In stock | 2 |
| BBa_K1351021 | Monomeric Red Fluorescent Protein from Discosoma striata | Red | 675 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1323009 | DsRed (RFP) Coding Sequence | Red | 678 | In stock | 4 | |||||
| BBa_K1323010 | YFP Coding Sequence | Yellow | 720 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1510017 | red florescence protein RFC23 | Red | 703 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1486056 | CxpR & Split IFP1.4 [Cterm + Cterm][2] | Forward | Infrared | 3742 | In stock | |||||
| BBa_K1321337 | sfGFP in Freiburg format (RFC 25) | Green | 711 | In stock | 27 | |||||
| BBa_K1418030 | SYFP2 | Yellow | 723 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1418040 | CFP | Cyan | 723 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1418041 | CFP(ns) | Cyan | 717 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1740000 | Dronpa 145N ORF (E. coli optimized) | Green | 672 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1615089 | mRFP RFC25 | Red | 675 | In stock | 11 | |||||
| BBa_K1742002 | Dronpa 145N | Green | 693 | In stock | 3 | |||||
| BBa_K1789003 | GFP1(with termination codon) | Green | 474 | In stock | 12 | |||||
| BBa_K1789004 | GFP2 | Green | 249 | In stock | 7 | |||||
| BBa_K1680006 | Fluorescent protein dronpa | Green | 669 | In stock | ||||||
| BBa_K1673010 | Partially UV-Resistant RFP | Red | 678 | In stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_K1673101 | UV-Resistant RFP | Red | 678 | In stock | 2 | |||||
| BBa_K1673102 | UV Mutation Optimized RFP (Improved Expression) | Red | 681 | In stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_K1673103 | UV Mutation Maximizied RFP | Red | 678 | In stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_K106000 | GFP, AarI BD part | Forward | Green | 714 | It's complicated | |||||
| BBa_K106004 | mCherry, Aar1 AB part | Red | 708 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K106005 | mCherry, Aar1 BD part | Red | 708 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K106028 | GFP, AarI AB part | Green | 714 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K125810 | slr2016 signal sequence + GFP fusion for secretion of GFP | Forward | Green | 779 | It's complicated | |||||
| BBa_K106671 | GFP, Aar1 AD part | Green | 714 | It's complicated | 7 | |||||
| BBa_K180008 | mCherry | mCherry (rights owned by Clontech) | forward | Red | 708 | It's complicated | 6 | |||
| BBa_K1740001 | Dronpa145K ORF (E. coli optimized) | Green | 672 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K1742003 | Dronpa 145K | Green | 741 | It's complicated | 3 | |||||
| BBa_K1819000 | GFPmut3b | GFP coding sequence with an N-terminal linker | Forward | Green | 511 | 501 | 750 | It's complicated | 1 | |
| BBa_K1602021 | Green fluorescent protein (GFP) with N-terminal His-Tag | Green | 738 | It's complicated | 2 | |||||
| BBa_K1602024 | HisTag-GFP_Si4-Tag fusion protein | Green | 807 | It's complicated | 2 | |||||
| BBa_K1857000 | mVenus | Yellow | 1236 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K1680017 | Cre-Dronpa Fusion | Green | 1728 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K1680018 | Cre-Dronpa fusion | Green | 1746 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K1680019 | Cre-dronpa fusion | Green | 1764 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K1680020 | Cre-dronpa fusion | Green | 1782 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K1680021 | Dronpa caged Cre with NLS | Green | 2433 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K1680022 | Dronpa caged Cre with NLS | Green | 2451 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K1680023 | Dronpa caged Cre with NLS | Green | 2469 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K1680024 | Dronpa caged Cre with NLS | Green | 2487 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K1673104 | Oxidation-Resistant RFP | Red | 678 | It's complicated | 2 | |||||
| BBa_K1673410 | GFP (Mutation Optimized) | Green | 717 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K2003010 | Inducible Green Fluorescent Protein UnaG+6xHis-tag | 462 | It's complicated | |||||||
| BBa_K2455002 | SYFP2 | CPP-SYFP2 | C-terminal hexa-histidine | Forward | Yellow | 527 | 515 | 804 | It's complicated | |
| BBa_K2455005 | mTag BFP | CPP-mTag BFP | C-terminal hexa-histidine | Forward | Blue | 456 | 399 | 786 | It's complicated | |
| BBa_K2656013 | sfGFP Coding Sequence | 721 | It's complicated | 5 | ||||||
| BBa_K2656023 | GFPmut3b_LVA Coding Sequence | 754 | It's complicated | 1 | ||||||
| BBa_K2656014 | mRFP1 Coding Sequence | 679 | It's complicated | 3 | ||||||
| BBa_K2656024 | mRFP1_LVA Coding Sequence | 715 | It's complicated | 1 | ||||||
| BBa_K2656020 | YFP | YFP_LVA Coding Sequence | LVA | Forward | Yellow | 529 | 516 | 754 | It's complicated | 1 |
| BBa_K2656021 | YFP | YFP Coding Sequence | None | Forward | Yellow | 529 | 516 | 721 | It's complicated | 1 |
| BBa_K2558005 | sfGFP | superfold GFP (+LVA_ | Green | 758 | It's complicated | 6 | ||||
| BBa_K3781002 | mCerulean, MocloMania B3_B4 | 714 | -1 | |||||||
| BBa_K3781003 | mVenus, MoCloMania B3_B4 | 714 | -1 | |||||||
| BBa_K3781015 | mVenus, MocloMania B5 | 717 | -1 | |||||||
| BBa_K3781016 | mCerulean, MocloMania B5 | 717 | -1 | |||||||
| BBa_K3781012 | mCerulean, MocloMania B4 | 714 | -1 | |||||||
| BBa_K3831029 | Green fluorescent protein | 714 | -1 | |||||||
| BBa_K3831016 | sfGFP | 714 | -1 | |||||||
| BBa_K3831021 | mScarlet-I | 696 | -1 | |||||||
| BBa_K3831042 | GFP | 714 | -1 | |||||||
| BBa_K3765010 | sfGFP (Superfolder GFP) | 714 | -1 | |||||||
| BBa_K4139013 | PbEL04 | CAPE-GFP | His-Tag | Forward | 912 | -1 | ||||
| BBa_K4139015 | PbEL04 | COAPE - GFP | OmpA & His-Tag | Forward | 984 | -1 | ||||
| BBa_K4139017 | CAP-FP | CAP-FP | His-Tag | Forward | 1101 | -1 | ||||
| BBa_K4706008 | Green fluorescent GFP-like protein | eechGFP1 codon optimised S.cerevisae | none | forward | 497nm | 687 | -1 | |||
| BBa_K4759012 | sfGFP | 702 | -1 | |||||||
| BBa_K192001 | CFP +tgt +lva | 858 | Not in stock | |||||||
| BBa_K180001 | GFPmut3b | Green fluorescent protein (+LVA) | LVA | forward | Green | 754 | Not in stock | 1 | ||
| BBa_K180009 | mBanana | mBanana (rights owned by Clontech) | forward | Yellow | 708 | Not in stock | 3 | |||
| BBa_K863121 | GFPmut3b | green fluorescent protein derived from jellyfish Aequeora victoria wild-type GFP (His-tag) | His6 | Green | 750 | Not in stock | ||||
| BBa_K863120 | GFPmut3b | green fluorescent protein derived from jellyfish Aequeora victoria wild-type GFP (Freiburg-Standard) | None | Green | 729 | Not in stock | ||||
| BBa_K1491001 | mTagBFP-His | Blue | 723 | Not in stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_K1491004 | SuperYFP2-His | Yellow | 741 | Not in stock | 3 | |||||
| BBa_K1486006 | IFP[1] | Forward | Infrared | 405 | Not in stock | 6 | ||||
| BBa_K1486007 | IFP[2] | Forward | Infrared | 585 | Not in stock | 6 | ||||
| BBa_K1362461 | mRFP1 | **highly** engineered mutant of red fluorescent protein from Discosoma striata (coral) with barcode | None | Forward | Red | 607 | 584 | 706 | Not in stock | 3 |
| BBa_K1583017 | Blue Fluorescent Protein (mTagBFP) without stopcodon | Blue | 699 | Not in stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_K1641224 | mCherry-ssrA | Red | 747 | Not in stock | 2 | |||||
| BBa_K1688019 | dTomato, red fluorescent protein | Red | 708 | Not in stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_K1732020 | GFP-HIS | Green | 732 | Not in stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_K1732021 | BFPCO-His | Blue | 717 | Not in stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_K1732022 | EGFPCO-His | Green | 735 | Not in stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_K1732024 | YFPCO-His | Yellow | 735 | Not in stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_K1732025 | RFPCO-His | Red | 690 | Not in stock | 2 | |||||
| BBa_K1616016 | YC155 - C terminal YFP split | Yellow | 255 | Not in stock | 2 | |||||
| BBa_K1616017 | YN155 - N terminal YFP split | Yellow | 468 | Not in stock | 2 | |||||
| BBa_K1650038 | GFP-His | Green | 1159 | Not in stock | 1 | |||||
| BBa_K1799026 | Discosoma RFP with stp | Red | 675 | Not in stock | 2 | |||||
| BBa_K2040122 | KillerRed + NLS | Red | 744 | Not in stock | ||||||
| BBa_K3128008 | mRFP1 | Engineered mutant of red fluorescent protein with RFC21 restriction sites | None | Forward | Red | 607 | 584 | 690 | Not in stock | 1 |
| BBa_K2929004 | mOrange | mOrange + SpyTag | None | Orange | 562 | 548 | 829 | Not in stock | ||
| BBa_K3013003 | mamC-FbFP BS2 fusion | 819 | Not in stock | |||||||
| BBa_K2984019 | L1c-Psad-YFP-RbcS2, Expression of YFP through light-inducible promoter | 1805 | Not in stock | |||||||
| BBa_K3427000 | Heat-stable fluorescent protein YFP_LOV | 342 | Not in stock | -1 |
Luciferases
Luminescence can be readily quantified using a plate reader or luminescence counter. Luciferases are especially well-suited for measuring low levels of gene expression because cells tend to have little to no background luminescence in the absence of a luciferase.
| Name | Protein | Description | Direction | Uniprot | KEGG | E.C. | Substrate | Product | Length | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_J52011 | dnMyD88-linker-Rluc | 1371 | In stock | |||||||
| BBa_I712019 | Firefly luciferase - luciferase from Photinus pyralis | 1653 | In stock | |||||||
| BBa_K322237 | Firefly luciferase from Photinus pyralis | 1653 | In stock | |||||||
| BBa_K1159001 | NanoLuc Luciferase in RFC[25] | 510 | In stock | |||||||
| BBa_K1761002 | Outer Membrane Protein X (OmpX) with BsoBI-linker and NanoLuc | 1241 | In stock | |||||||
| BBa_K1689001 | Coding sequence of STV-N-luc | 1727 | In stock | |||||||
| BBa_K1689006 | Coding sequence of FKBP-Cluc394 | 875 | In stock | |||||||
| BBa_K1680009 | NanoLuc Luciferase | 516 | In stock | |||||||
| BBa_K1680010 | Firefly Luciferase | 1653 | In stock | |||||||
| BBa_K1734004 | Nanoluc (Codon optimized for Sf9 cells) | 525 | In stock | |||||||
| BBa_K1616025 | NanoLuc | 510 | In stock | |||||||
| BBa_J52013 | dnMyD88-linker-Rluc-linker-PEST191 | 1872 | It's complicated | |||||||
| BBa_K525311 | Fusion Protein of S-Layer SgsE and Firefly-Luciferase | 4062 | It's complicated | |||||||
| BBa_K785003 | Lux(CDABEG) coding gene PoPS->Light | 6427 | It's complicated | |||||||
| BBa_K1486054 | CheY/CheZ + split rLuc | Forward | 3293 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K1486055 | CheY/CheZ + split fLuc | Forward | 4079 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K1732003 | GLUCCO-His | 522 | It's complicated | |||||||
| BBa_K1689004 | Coding sequence of Nluc398-FRB | 1553 | It's complicated | |||||||
| BBa_K1732027 | GLuc-His | 522 | It's complicated | |||||||
| BBa_K2023009 | Gaussia Luciferase | Gaussia luciferase coding sequence optimized for use in E.coli DH5-Alpha | 561 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K2637010 | Nanoluc+PEST | Forward | 642 | It's complicated | ||||||
| BBa_K284999 | Deletar este tamb�m | 1431 | Not in stock | |||||||
| BBa_K525411 | Fusion Protein of S-Layer SbpA and Firefly-Luciferase | 4854 | Not in stock | |||||||
| BBa_K1761005 | LargeBit Split Luciferase | 477 | Not in stock | |||||||
| BBa_K1761006 | SmallBit Split Luciferase | 36 | Not in stock | |||||||
| BBa_K1732029 | FireflyCO-His | 1668 | Not in stock |
Enzymes that produce colored substrates
Enzymes that produce colored substrates can be quantified using spectrophotometers or other instruments that can take absorbance measurements including plate readers. Like luciferases, enzymes like β-galactosidase are good for measuring low levels of gene expression because they tend to amplify low signals.
| Name | Protein | Description | Direction | UniProt | KEGG | E.C. | Substrate | Product | Color | Length | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_I732006 | lacZ alpha fragment | 234 | In stock | ||||||||
| BBa_I732005 | lacZ (encoding beta-galactosidase, full-length) | 3075 | It's complicated | ||||||||
| BBa_K147002 | xylE | 924 | It's complicated |
Miscellaneous
| Name | Protein | Description | Tag | Direction | UniProt | KEGG | Length | Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_K592009 | amilCP, blue chromoprotein | 669 | In stock | |||||
| BBa_K592010 | amilGFP, yellow chromoprotein | 699 | In stock | |||||
| BBa_K592011 | cjBlue, green chromoprotein | 702 | In stock | |||||
| BBa_K592012 | eforRed, red chromoprotein | 681 | In stock | |||||
| BBa_K864401 | aeBlue blue chromoprotein | 699 | In stock | |||||
| BBa_K1122007 | AmilCP (BBa_K592009) compatible with Genabler assembly | 685 | In stock | |||||
| BBa_K1033906 | tsPurple, purple chromoprotein | 690 | In stock | |||||
| BBa_K1033919 | gfasPurple, purple chromoprotein | 669 | In stock | |||||
| BBa_K1023005 | eforRed | 687 | In stock | |||||
| BBa_K1033932 | spisPink, pink chromoprotein | 678 | In stock | |||||
| BBa_K1824017 | AeBlue blue chromoprotein | 699 | In stock | |||||
| BBa_K678035 | yA (green pigment) from Aspergillus nidulans | 2156 | It's complicated | |||||
| BBa_K732001 | Synthetic Chorionic Gonadotropin, beta (synCG-β) | 498 | It's complicated | |||||
| BBa_K1824019 | AeBlue blue chromoprotein with aav tag | 738 | It's complicated | |||||
| BBa_K2656018 | amilCP Coding Sequence | 670 | It's complicated | |||||
| BBa_K4139011 | Truncated PbEL04 | Truncated PbEL04 | Thioredoxin & His-Tag | Forward | 963 | |||
| BBa_K4139012 | PbEL04 | Full Length PbEL04 | His-Tag | Forward | 570 | |||
| BBa_K4139018 | CAPE-AFP | CAPE-AFP | His-Tag | Forward | 537 | |||
| BBa_K4139019 | CP-MAF | Rec. CP-MAF | His-Tag | Forward | 495 | |||
| BBa_K4139020 | Pro1 | Pro1 | His-Tag | Forward | 1302 | |||
| BBa_K5466031 | AntiAFB1-scFv1 EpoR Split-N-mCerulean | 1809 | ||||||
| BBa_K5466032 | AntiAFB1-scFv2 EpoR Split-C-mCerulean | 1542 | ||||||
| BBa_K5527001 | amilCP purple, Purple chromoprotein | 669 | ||||||
| BBa_K5527002 | amilCP yellow, Yellow chromoprotein | 669 | ||||||
| BBa_K5527003 | amilCP light purple, Light purple chromoprotein | 669 | ||||||
| BBa_K1685005 | aeBlue | 699 | Not in stock | |||||
| BBa_K1685007 | aeBlue with LAA tag | 732 | Not in stock | |||||
| BBa_K1685008 | aeBlue with AAV tag | 732 | Not in stock | |||||
| BBa_K3697002 | manP expression cassette | 2142 | Not in stock |
References
<biblio>
- Pardy pmid=7866866
</biblio>
Fluorescent proteins
<biblio>
- Chalfie pmid=8303295
- Prasher pmid=1347277
- Cormack pmid=8707053
- Tsien pmid=9759496
- Andersen pmid=9603842
- Leveau pmid=11698362
- Iafolla pmid=18350571
- Dong pmid=18352052
- Bagh pmid=18352063
- Baird pmid=11050229
- Patterson pmid=15583657
</biblio>
Luciferase
<biblio>
- Bronstein pmid=8080073
</biblio>
β-galactosidase
<biblio>
- Griffith pmid=11779182
- Villarejo pmid=4552692
- Zamenhof pmid=4552986
- Ullman pmid=1345751
</biblio> [http://openwetware.org/index.php?title=Beta-Galactosidase_Assay_%28A_better_Miller%29 Miller Assay on OpenWetWare] by Sean Moore