DNA/Recombination
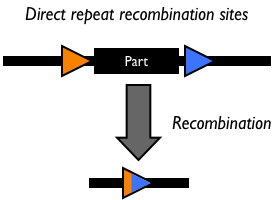
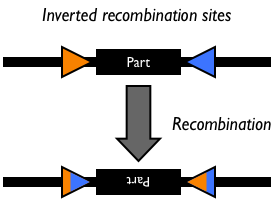
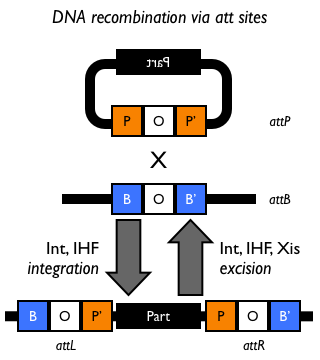
Site-specific DNA recombination requires both a recombinase protein and a pair of repeated DNA sites at which recombination takes place. Depending on the number and orientation of the DNA sites, there can be either an inversion, deletion or insertion of DNA (Figure 1). While some DNA recombination systems, such as Cre/lox only require the recombinase and the two DNA sites for recombination to occur, others either require or are modulated by additional accessory factors.
Figure 1: Schematic of different types of recombination events.
Site-specific recombination systems derived from Salmonella, different bacteriophages, yeast, and E. coli are all available from the Registry. For more details on individual DNA recombination systems including DNA recombination sites, click the links below.
- Salmonella typhimurium-derived Hin/hix DNA recombination system
- Bacteriophage P1-derived Cre/lox DNA recombination system
- Bacteriophage λ-derived att DNA recombination system
- Bacteriophage P22 att DNA recombination system
- Yeast Flp/FRT DNA recombination system
- Escherichia coli XerCD/dif DNA recombination system
- Escherichia coli FimBE/fimS DNA recombination system
Recombination sites are DNA sequences at which recombination events take place.
For details on the different recombination systems available via the Registry, see Recombination.
| Name | Description | Sequence | Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_I11022 | Lambda attB, reverse complement | accactttgtacaagaaagctgggt | 25 |
| BBa_I11023 | Lambda attP | . . . tcactatcagtcaaaataaaatcattattt | 232 |
| BBa_I11032 | P22 ''attB'', reverse complement | acgaccttcgcattacgaatgcgctgc | 27 |
| BBa_I11033 | P22 ''attP'' | . . . gggacatatttgggacagaagtaccaaaaa | 260 |
| BBa_I718016 | lox66 | . . . cttggtatagcatacattatacgaacggta | 34 |
| BBa_I718017 | lox71 | . . . gttcgtatacgatacattatacgaagttat | 34 |
| BBa_I742101 | dif site with forward orientation | . . . tcggtgcgcataatgtatattatgttaaat | 31 |
| BBa_I742102 | dif site with reverse orientation | . . . tcatttaacataatatacattatgcgcacc | 31 |
| BBa_J3101 | Recombinational Enhancer (RE) for Hin/Hix inverting | . . . ctttctagtgcaaattgtgaccgcattttg | 77 |
| BBa_J44000 | hixC binding site for Salmonella typhimurium Hin recombinase | ttatcaaaaaccatggtttttgataa | 26 |
| BBa_J61020 | [FRT] | . . . ttcctatactttttagagaataggaacttc | 34 |
| BBa_J61046 | [Lox] site for recombination | . . . cttcgtataatgtatgctatacgaagttat | 34 |
| BBa_J72001 | {FRT} recombination site for flp recombinase in BBb | . . . ttcctatactttctagagaataggaacttc | 36 |
| BBa_K112141 | attR2 recombination site | . . . gttcagctttcttgtacaaagtggttgatc | 136 |
| BBa_K112142 | attR2 recombination site-reverse orientation | . . . aacacaacatatccagtcactatggtcgac | 136 |
| BBa_K137008 | fimE IRR | . . . gaaacatttggggccaaactgtccatatta | 35 |
| BBa_K137010 | fimE IRL | . . . gagtcaaaatggccccaattgtcttgtatt | 35 |
| BBa_K1680005 | loxP Site | . . . cttcgtatagcatacattatacgaagttat | 34 |
| BBa_K315011 | Variant reverse lox N | . . . cttcgtatagtataccttatacgaagttat | 34 |
| BBa_K3697003 | Homology Arms for KanR integration in B. Subtilis | . . . gcttgcaaacaaaaaaaccaccgctaccag | 1103 |
| BBa_K416002 | 36 Base Pair LoxP | . . . tcgtataatgtatgctatacgaagttatcg | 36 |
| BBa_K5276011 | TP901B-TC | . . . atcaaggtaaatgctttttgctttttttgc | 53 |
| BBa_K5276012 | TP901P-TC | . . . ttaattgaaataaacgaaataaaaactcgc | 50 |
| BBa_K863201 | 3' UTR site of alcohol oxidase 1 gene (aox1) | . . . tcatcaacttgaggggcactatcttgtttt | 676 |
| BBa_K886000 | Fixed lox71 | . . . gttcgtatagcatacattatacgaagttat | 34 |