Plasmid backbones/Operation
| Part assembly | System operation | Protein expression | Assembly of protein fusions | Part measurement | Screening of part libraries | Building BioBrick vectors | DNA synthesis | Other standards | Archive |
| Or get some help on plasmid backbones. |
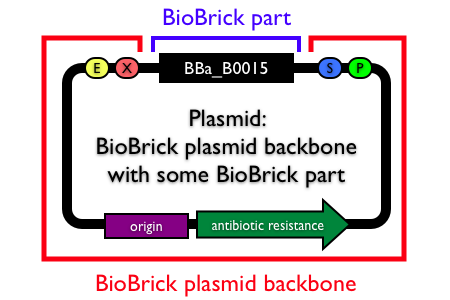
Plasmids are circular, double-stranded DNA molecules typically containing a few thousand base pairs that replicate within the cell independently of the chromosomal DNA. Plasmid DNA is easily purified from cells, manipulated using common lab techniques and incorporated into cells. Most BioBrick parts in the Registry are maintained and propagated on plasmids. Thus, construction of BioBrick parts, devices and systems usually requires working with plasmids.
Note: In the Registry, plasmids are made up of two distinct components:
- the BioBrick part, device or system that is located in the BioBrick cloning site, between (and excluding) the BioBrick prefix and suffix.
- the plasmid backbone which propagates the BioBrick part. The plasmid backbone is defined as the sequence beginning with the BioBrick suffix, including the replication origin and antibiotic resistance marker, and ending with the BioBrick prefix. [Note that the plasmid backbone itself can be composed of BioBrick parts.]
Many BioBrick parts in the Registry are maintained on more than one plasmid backbone!
Once you have assembled your BioBrick device or system, you're then ready to "run" it in your chassis of choice. You might be interested in characterizing its performance, demo'ing your engineered systems to your friends, or documenting its performance for the iGEM jamboree or a publication.
Regardless, it is oftentimes helpful to operate your system on a low or medium copy plasmid backbone. By lowering the DNA copy number of your BioBrick device or system, it will consume less of the cell's resources and thus you can operate more devices in parallel and potentially achieve more reliable system performance.
Note, however, that low or medium copy plasmid backbones tend to have reduced resource consumption because fewer transcripts and proteins are made. Thus, characterization of device or system performance can be more difficult, since you are measuring a smaller number of molecules.
Reshma's low and medium copy operation plasmid backbones
All of these "operation" plasmid backbones have a common set of features.
- A complete BioBrick® cloning site for easy cloning and assembly of BioBrick® parts.
- A low or medium copy replication origin to reduce consumption of cellular resources during device or system operation.
- Forward and reverse terminators both upstream and downstream of the BioBrick® cloning site to insulate the vector from read-through transcription originating in the cloned BioBrick® device or system and to insulate the cloned BioBrick® system from the vector.
- Stop codons in all reading frames to prevent inadvertent translation into or out of the BioBrick cloning site.
- Primer binding sites for the standard BioBrick® verification primers VF2 (BBa_G00100) and VR (BBa_G00101). These primers are located for convenient sequencing and [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Colony_PCR screening by colony PCR] of cloned BioBrick® devices and systems.
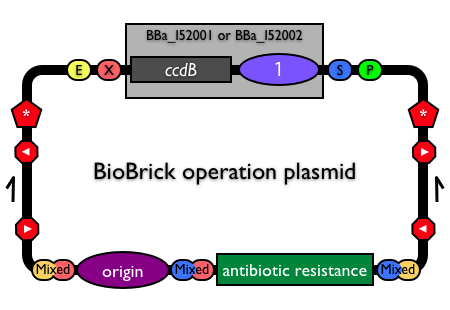
Plasmid backbones are distributed by the Registry with a default insert. There are just a handful of default plasmid inserts used in the Registry. All of the available plasmid backbones include the RFP expression cassette (BBa_J04450) as the default plasmid insert within the BioBrick® cloning site. The RFP cassette enables red/white screening of colonies and ensures that when assembling two BioBrick® parts together, the uncut plasmid (or a plasmid that get the RFP cassette as insert) will be red on the plate whereas the correct colonies will be white.
Plasmid backbones with the plasmid insert of BBa_I52002 also include a high copy replication origin in the default insert. Thus, these plasmid backbones are easily [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Miniprep/Qiagen_kit purified in large quantities]. Cloning or assembly of a BioBrick® part into the BioBrick® cloning site of the plasmid backbone eliminates the default insert returning the plasmid to the control of the replication origin in the plasmid backbone.
| Name | Description | Resistance | Replicon | Copy number | Chassis | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_K1362095 | pSB4A50: Low copy BioBrick cloning/expression backbone carrying Amp resistance | A | pSC101 | ~5 | 3446 | |
| BBa_K1362096 | pSB4C50: Low(?) copy BioBrick cloning/expression backbone carrying Cm resistance | C | pSC101 | unsure | 3408 | |
| BBa_K1362097 | Low copy BioBrick expression backbone carrying Kan resistance | K | pSC101 | ~5 | 3470 | |
| BBa_K864000 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector | A | pSC101 | ~5 | 3639 | |
| BBa_K864001 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector | C | pSC101 | ~5 | 3466 | |
| BBa_K864002 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector | K | pSC101 | ~5 | 3663 | |
| BBa_K864003 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector | S | pSC101 | ~5 | 3793 | |
| BBa_K864004 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector | A | pSC101 | ~5 | 3708 | |
| BBa_K864005 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector | C | pSC101 | ~5 | 3534 | |
| BBa_K864006 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector | K | pSC101 | ~5 | 3732 | |
| BBa_K864007 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector | S | pSC101 | ~5 | 3861 | |
| BBa_K864008 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector with LacI | A | pSC101 | ~5 | 4819 | |
| BBa_K864009 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector with LacI | C | pSC101 | ~5 | 4646 | |
| BBa_K864010 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector with LacI | K | pSC101 | ~5 | 4843 | |
| BBa_K864011 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector with LacI | S | pSC101 | ~5 | 4973 | |
| BBa_K864012 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector with LacI | A | pSC101 | ~5 | 4888 | |
| BBa_K864013 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector with LacI | C | pSC101 | ~5 | 4714 | |
| BBa_K864014 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector with LacI | K | pSC101 | ~5 | 4912 | |
| BBa_K864015 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector with LacI | S | pSC101 | ~5 | 5041 | |
| BBa_K864016 | Low copy BioBrick temperature sensitive standard vector | A | pSC101ts | ~5 | 3639 | |
| BBa_K864017 | Low copy BioBrick temperature sensitive standard vector | C | pSC101ts | ~5 | 3466 | |
| BBa_K864018 | Low copy BioBrick temperature sensitive standard vector | K | pSC101ts | ~5 | 3663 | |
| BBa_K864019 | Low copy BioBrick temperature sensitive standard vector | S | pSC101ts | ~5 | 3793 | |
| BBa_K864020 | Low copy BioBrick temperature sensitive standard vector | A | pSC101ts | ~5 | 3708 | |
| BBa_K864021 | Low copy BioBrick temperature sensitive standard vector | C | pSC101ts | ~5 | 3534 | |
| BBa_K864022 | Low copy BioBrick temperature sensitive standard vector | K | pSC101ts | ~5 | 3732 | |
| BBa_K864023 | Low copy BioBrick temperature sensitive standard vector | S | pSC101ts | ~5 | 3861 | |
| pSB3C5 | Low to medium copy BioBrick standard vector | C | p15A | 10-12 | 2738 | |
| pSB3K5 | Low to medium copy BioBrick standard vector | K | p15A | 10-12 | 2936 | |
| pSB3T5 | Low to medium copy BioBrick standard vector | T | p15A | 10-12 | 3252 | |
| pSB4A5 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector | A | pSC101 | ~5 | 3395 | |
| pSB4C5 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector | C | pSC101 | ~5 | 3221 | |
| pSB4K5 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector | K | pSC101 | ~5 | 3419 | |
| pSB4T5 | Low copy BioBrick standard vector | T | pSC101 | ~5 | 3735 |
| Reshma Shetty, Drew Endy, and Tom Knight constructed this set of plasmid backbones. You can read more about the design and construction of these plasmid backbones in their open-access paper, [http://www.jbioleng.org/content/2/1/5 Engineering BioBrick vectors from BioBrick parts] published in the Journal of Biological Engineering. |
Additional low and medium copy operation plasmid backbones
There are additional low and medium copy BioBrick® plasmid backbones available, all of which have a complete BioBrick cloning site.
| Stefan Luzi constructed the three plasmid backbones (pSB6A1, pSB4C1, and pSB3K1) as a member of the [http://2007.igem.org/ETHZ 2007 ETH Zurich iGEM team]. | |
| Jeff Tabor constructed plasmid backbone BBa_J64100 in Chris Voigt's lab. | |
| Reshma Shetty constructed plasmid backbone pSB3K3 in Tom Knight's lab. |
| Name | Description | Resistance | Replicon | Copy number | Chassis | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_J61031 | Amplifiable BAC plasmid | K | ColE1/R6K/F | 10662 | ||
| BBa_K125000 | Broad host range BioBrick plasmid derived from pRL1383a with low to medium copy number | 9047 | ||||
| BBa_K592200 | Low to medium copy BioBrick standard vector | S | p15A | 10-12 | 3137 | |
| pSB3K1 | pACYC177 converted into BioBrick vector (formerly BBa_I739202) | K | p15A | 10-12 | 3064 | |
| pSB3K3 | Low to medium copy BioBrick standard vector | K | p15A | 10-12 | 2750 | |
| pSB4C1 | pCK01 converted into BioBrick vector (formerly BBa_I739202) | C | pSC101 | 5-12 | 3155 | |
| pSB6A1 | pBR322 converted to BioBrick vector (formally BBa_I739201) | A | pMB1 | 15-20 | 4022 |
Inducible copy number operation plasmid backbones
Sometimes it is nice to have the best of both worlds. For example, you'd usually like a BioBrick® part to propagate at low copy, but you'd also like to switch the part over to high copy when you're interested in purifying plasmid DNA. The solution is an inducible copy number plasmid backbone. Both plasmid backbones listed below have a high copy replication origin under the control of a LacI-repressible promoter. When the plasmid is propagated in an E. coli strain that expresses the repressor lacI in high quantities, such as D1210 (or BBa_V1003), the plasmid is maintained at low copy by the F' origin. To increase the plasmid copy number, simply add the small molecule [http://openwetware.org/wiki/IPTG IPTG] to induce the LacI-repressible promoter controlling the high copy number origin.
- Note: because these inducible copy number vectors rely on LacI for control of the high copy number origin, they are incompatible with any BioBrick® part, device, or system that include lacI or a LacI-regulatable promoter.
The plasmid backbones listed below have a common set of features.
- A complete BioBrick® cloning site for easy cloning and assembly of BioBrick parts.
- Terminators flanking the BioBrick® cloning site to insulate the vector from read-through transcription originating in the cloned BioBrick® part, device or system.
- Primer binding sites for the standard BioBrick® verification primers VF2 (BBa_G00100) and VR (BBa_G00101). These primers are located for convenient sequencing and [http://openwetware.org/wiki/Colony_PCR screening by colony PCR] of cloned BioBrick® parts, devices, and systems.
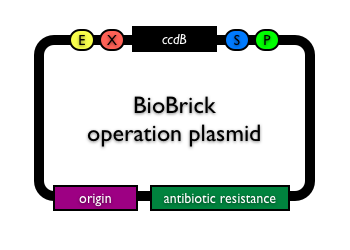
Plasmid backbones are distributed by the Registry with a default insert. There are just a handful of default plasmid inserts used in the Registry. Many the available plasmid backbones have the ccdB positive selection marker (BBa_P1010) as the default plasmid insert within the BioBrick® cloning site. The ccdB gene ensures that when assembling two BioBrick® parts together, the uncut plasmid is not transformed. However, inclusion of the ccdB gene means that these vectors must be propagated in a ccdB tolerant strain, such as E. coli strain DB3.1 (BBa_V1005).
| Name | Description | Resistance | Replicon | Copy number | Chassis | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| pSB2K3 | Inducible copy number BioBrick plasmid | K | F' and P1 lytic | <10 or >100 | lacIq like BBa_V1003 | 4425 |
| pSB2K4 | pSB2K3-derived BioBrick plasmid free of many restriction sites | K | F' and P1 lytic | <10 or >100 | lacIq like BBa_V1003 | 4467 |
| Sri Kosuri and Leon Chan constructed plasmid backbone pSB2K3 in Drew Endy's lab based on the [http://genome.bnl.gov/Vectors/pscans.php pSCANS] vector from Brookhaven National Lab. They, together with Austin Che, constructed pSB2K4. |
Multi-host operation plasmid backbones
| Sarah Hollingshead constructed this multi-host BioBrick plasmid backbone as a member of the [http://2007.igem.org/Edinburgh 2007 University of Edinburgh iGEM team] from the pTG262 vector generously provided by Dr Mike Gasson & Dr. Claire Shearman of the Institute of Food Research in Norwich. The Edinburgh team used the plasmid backbone as a shuttle plasmid backbone between lactic acid bacteria and E. coli. It has a gram positive replication origin. |
There are no parts for this table
Eukaryotic operation plasmid backbones
| Monika Ciglic constructed this E. coli high copy plasmid backbone with a eukaryotic terminator as a member of the [http://2006.igem.org/Ljubljana,_Slovenia_2006 2006 Slovenija iGEM team] from pSB1AK3. |
There are no parts for this table
Notes
- Part:BBa_I742123 - physical location unknown?
References
<biblio>
- Hershfield74 pmid=4610576
- Mandecki90 pmid=2227445
- Viera82 pmid=6295879
- YanishPerron85 pmid=2985470
- Messing91 pmid=2055478
- Chang74 pmid=4598290
- Cohen77 pmid=334752
- Cabello76 pmid=765836
- Sugiura93 pmid=8376344
- Miller95 pmid=7665462
- Bolivar77 pmid=344136
- Bolibar77b pmid=344137
- Chang78 pmid=149110
- Murakami87 pmid=3031019
- Uga89 pmid=10393200
- Kawasaki96 pmid=9003285
- Stueber82 pmid=6327267
- Bernard84 pmid=7926841
</biblio>