Plasmid backbones/Expression
| Part assembly | System operation | Protein expression | Assembly of protein fusions | Part measurement | Screening of part libraries | Building BioBrick vectors | DNA synthesis | Other standards | Archive |
| Or get some help on plasmid backbones. |
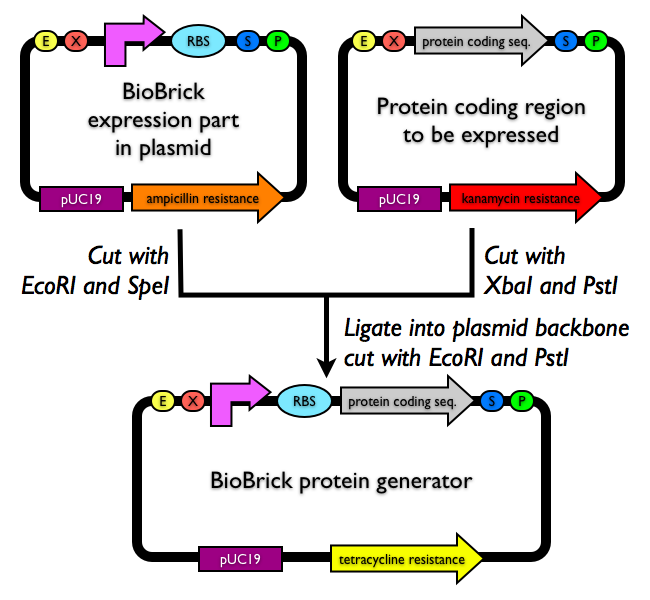
| In molecular biology, researchers are often interested in expressing proteins for purification or characterization. Hence, several groups and companies have designed expression plasmids to make it easy to express recombinant proteins. Expression plasmids generally include a promoter and ribosome binding site for ready protein expression.
To express a protein coding sequence that adheres to the BioBrick assembly standard, simply assemble one of the parts below with your coding region of interest into any BioBrick plasmid backbone. Each of the parts below includes a promoter and a ribosome binding site for expression of a downstream protein coding region. There are many plasmid backbones from which to choose. You might consider one of the high copy plasmid backbones for a plasmid backbone similar to pUC19. Or alternatively, you might consider a low or medium copy plasmid backbone, since lower copy number plasmids can in some cases give better protein expression. |
Constitutive
If you're interested in constitutively expressing your protein of interest, use one of these plasmids.
There are no parts for this table
| Jeff Tabor constructed the composite expression part BBa_J13002 in Andy Ellington's lab. Note that if BBa_J13002 is combined with another part that expressed TetR repressor, then BBa_J13002 is inducible via anhydrous tetracycline or aTC. | Samantha Liang, as a member of the 2006 UC Berkeley iGEM team, constructed the composite expression part BBa_J23038. |
Inducible
If you're interested in controlled or inducible expression of your protein, use one of these plasmids. Generally, inducible expression plasmids only express your protein of interest upon addition of an exogenous inducer, such as IPTG, AHL, or arabinose.
| Name | Description | Resistance | Replicon | Copy number | Chassis | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_J04500 | IPTG inducible promoter with RBS | 220 | ||||
| BBa_J13023 | 3OC6HSL+LuxR dependent POPS/RIPS generator | 117 | ||||
| BBa_K081006 | Plambda promoter and RBS | 72 | ||||
| BBa_K1065203 | Efe+Bba_B0015 in pSpac (BBa_K823026) | A(E. coli) + K(B. subtilis) | pDG148 | B. subtilis + E. coli | 9512 | |
| BBa_K1065204 | Efe+Bba_B0015 in BBa_K823024 (pXyl) | A(E. coli) S(B. subtilis) | B. subtilis + E. coli | 6017 | ||
| BBa_K1362091 | pSB1A30: High copy BioBrick cloning/expression backbone carrying Amp resitance | A | pMB1 | 100-300 | 2206 | |
| BBa_K1362095 | pSB4A50: Low copy BioBrick cloning/expression backbone carrying Amp resistance | A | pSC101 | ~5 | 3446 | |
| BBa_K1362096 | pSB4C50: Low(?) copy BioBrick cloning/expression backbone carrying Cm resistance | C | pSC101 | unsure | 3408 | |
| BBa_K1362097 | Low copy BioBrick expression backbone carrying Kan resistance | K | pSC101 | ~5 | 3470 | |
| BBa_K1680026 | pETUE | 3324 | ||||
| BBa_K215000 | R0011+B0034, strong IPTG-inducible promoter with strong RBS. | 75 | ||||
| BBa_K2387032 | CpxR-eYFPn[1-154] and CpxR-eYPFc[155-238] + araC/pBAD promoter | Chloramphenicol | Escherichia coli | 3424 | ||
| BBa_K2637009 | Gal2 promoter | 535 | ||||
| BBa_K2637017 | CYC1 terminator | 261 | ||||
| BBa_K2637059 | mutant Gal1 promoter | 457 | ||||
| BBa_K2812002 | pBAD-ara promoter - Arabinose inducible regulatory promoter | 71 | ||||
| BBa_K2812003 | Coding sequence for trunctated Lysostaphin regulated by T7-promoter | 776 | ||||
| BBa_K2812004 | Coding sequence for trunctated Lysostaphin fused to His-tagged HlyA | 1458 | ||||
| BBa_K2812005 | Coding sequence for trunctated Lysostaphin with HlyA and His6-tag regulated by T7-promoter | 1496 | ||||
| BBa_K2812007 | Coding sequence for Pyocin S5 with HlyA and His6-tag regulated by pBAD-ara promoter | 2288 | ||||
| BBa_K345667 | Lac regulated insertable promoter | 220 | ||||
| BBa_K4999000 | pBAD driven T4 lysis cassette | 15-20 | 2995 | |||
| BBa_K653003 | IPTG inducible Expression Platform | 1083 | ||||
| BBa_K801004 | pTUM104 yeast shuttle vector with GAL1 promoter | 5837 | ||||
| BBa_K823024 | pSBBs4S-Pxyl: Integrative expression vector for Bacillus subtilis | A(E. coli) S(B. subtilis) | B. subtilis + E. coli | 4794 | ||
| BBa_K823026 | pSBBs0K-Pspac (replicative Bacillus subtilis expression vector; IPTG inducible | A(E. coli) + K(B. subtilis) | pDG148 | B. subtilis + E. coli | 8289 | |
| BBa_S03511 | pLac : RBS | 223 |
| Kristen DeCelle, as a member of the 2005 Davidson College iGEM team, constructed the IPTG-inducible composite expression part BBa_J04500. Note that without LacI-expression by the host chassis, BBa_J04500 is constitutive. | Jeff Tabor constructed the AHL-inducible composite expression part BBa_J13023 in Andy Ellington's lab. Note that BBa_J13023 will only express your protein of interest if the activator LuxR is present and the repressor λ CI is absent. | ||
| . | The 2006 Davidson-Missouri Western joint iGEM team designed and constructed the composite expression part BBa_S03511. Note that without LacI-expression by the host chassis, BBa_S03511 is constitutive. |
References
<biblio>
- Bernard01 pmid=18429183
</biblio>