Part:BBa_K2560251
accBC subunit from C. glutamicum, codonoptimized for V. natriegens
accBC encodes the biotin carboxylase domain of the acetyl-CoA-carboxylase (Acc) in C. glutamicum. The enzyme is involved in fatty acid biosynthesis by converting acetyl-CoA into malonyl-CoA. In C. glutamicum the enzyme consists of two subunits, a biotin-carboxylase and a carboxytransferase. To get activ the enzyme has to be biotinylated what is made by an biotin-ligase (BirA).
For this part, accBC was codonoptimized for V. natriegens and then synthetisized and integrated into the vector BBa_K2560002 via BsmBI. It is part of the Marburg Toolbox, a golden gate based system für modular cloning.
If accBC shall be used with an 5' tag use BBa_K2560254, if there is no need for tagging, use this part.
Further down, an overview of the Marburg Toolbox is shown.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 1142
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 423
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Marburg Toolbox
We proudly present the Marburg Collection, a novel golden-gate-based toolbox containing various parts that are compatible with the PhytoBrick system and MoClo. Compared to other bacterial toolboxes, the Marburg Collection shines with superior flexibility. We overcame the rigid paradigm of plasmid construction - thinking in fixed backbone and insert categories - by achieving complete de novo assembly of plasmids.
36 connectors facilitate flexible cloning of multigene constructs and even allow for the inversion of individual transcription units. Additionally, our connectors function as insulators to avoid undesired crosstalk.
The Marburg Collection contains 123 parts in total, including:
inducible promoters, reporters, fluorescence and epitope tags, oris, resistance cassettes and genome engineering tools. To increase the value of the Marburg Collection, we additionally provide detailed experimental characterization for V. natriegens and a supportive software. We aspire availability of our toolbox for future iGEM teams to empower accelerated progression in their ambitious projects.
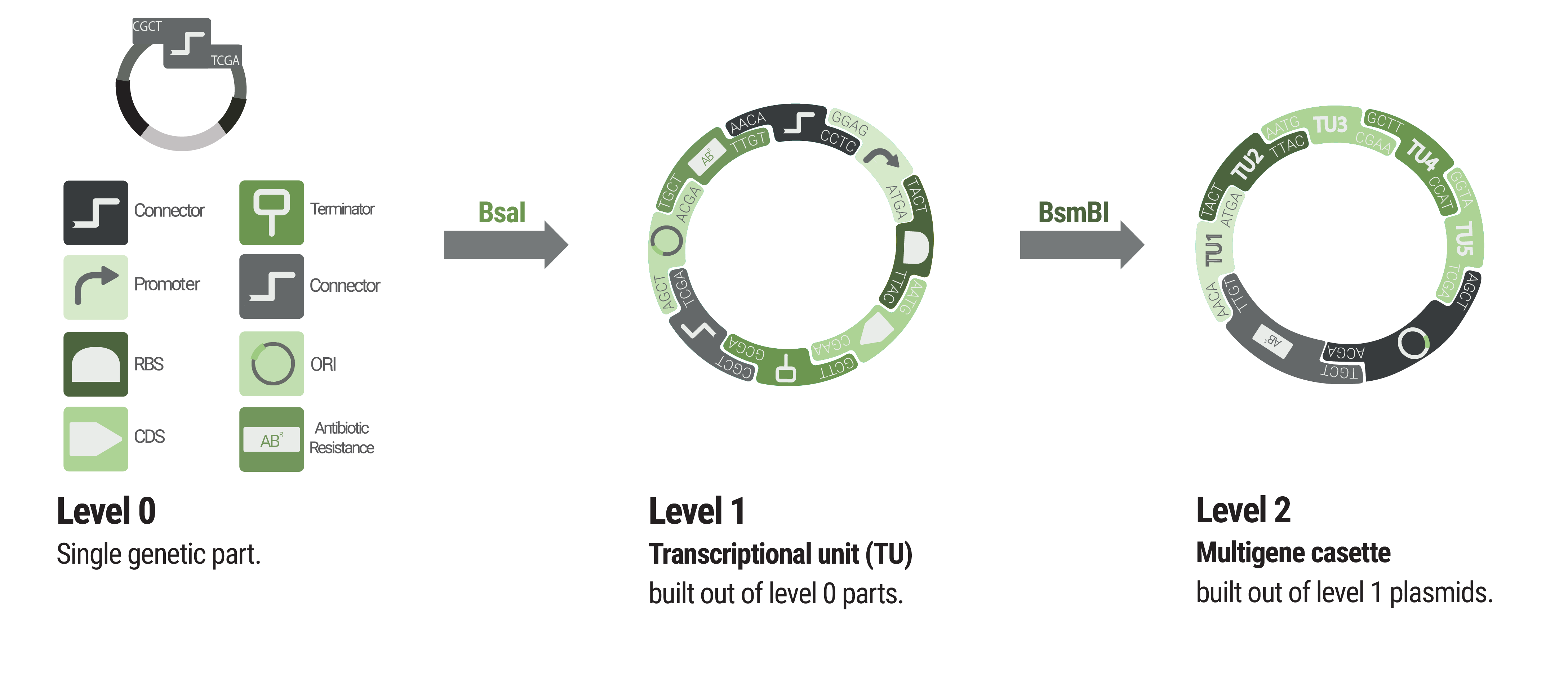
Basic building blocks like promoters or terminators are stored in level 0 plasmids. Parts from each category of our collection can be chosen to built level 1 plasmids harboring a single transcription unit. Up to five transcription units can be assembled into a level 2 plasmid.
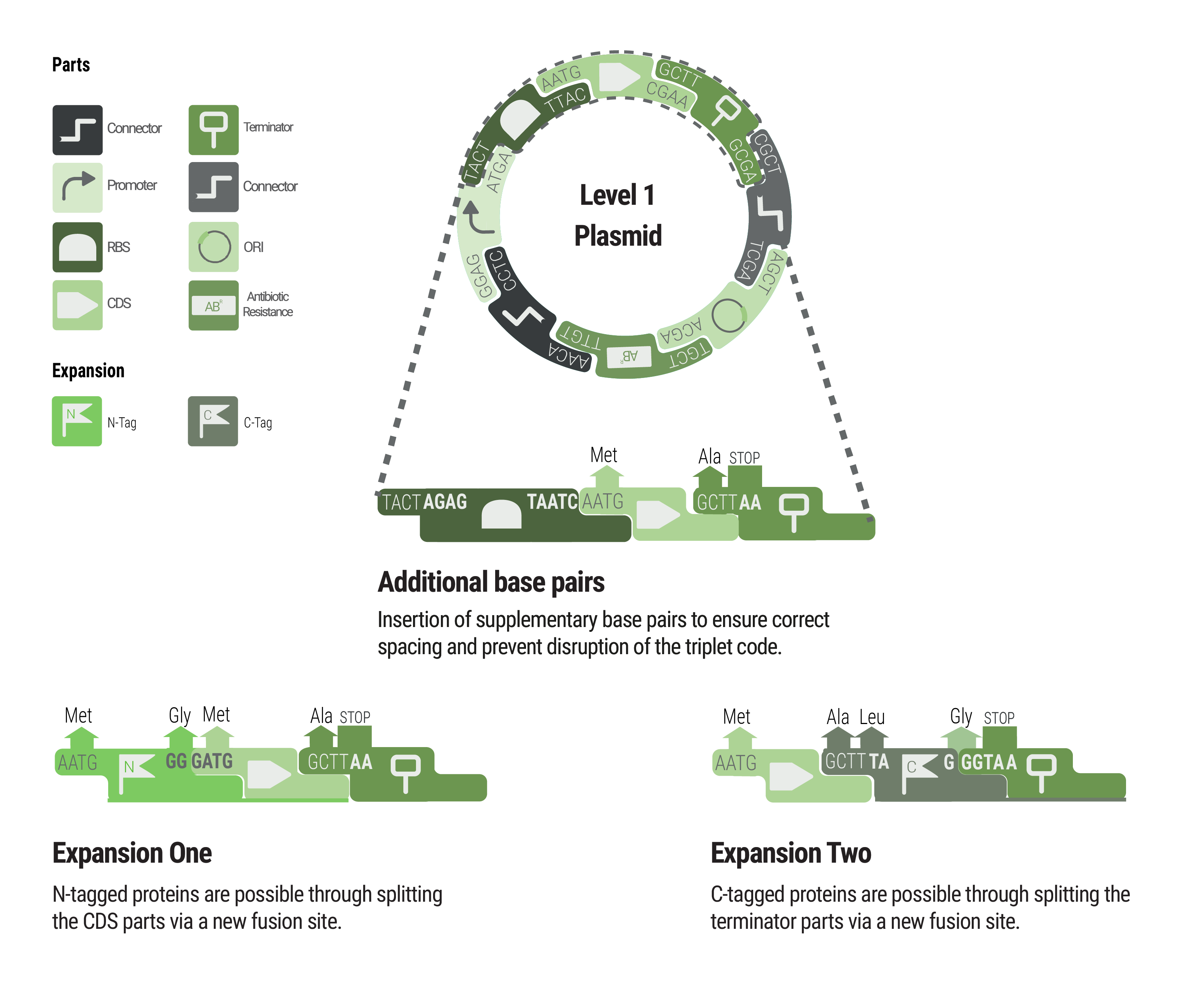
Between some parts, additional base pairs were integrated to ensure correct spacing and to maintain the triplet code. We expanded our toolbox by providing N- and C- terminal tags by creating novel fusions and splitting the CDS and terminator part, respectively.
Parts of the Marburg Toolbox

- K2560011 (5'Connector Dummy)
- K2560055
(1-6
Connector) - K2560065 (5'Con1)
- K2560066 (5'Con2)
- K2560067 (5'Con3)
- K2560068 (5'Con4)
- K2560069 (5'Con5)
- K2560075 (5'Con1
Short Res) - K2560076 (5'Con2
Short) - K2560077 (5'Con3
Short) - K2560078 (5'Con4
Short) - K2560079 (5'Con5
Short) - K2560095 (5'Con1 inv)
- K2560096 (5'Con2 inv)
- K2560097 (5'Con3 inv)
- K2560098 (5'Con4 inv)
- K2560099 (5'Con5 inv)
- K2560105 (5'Con5 inv
Ori) - K2560107 (5'Con1
Res)

- K2560007 (J23100)
- K2560009 (J23104)
- K2560014 (J23106)
- K2560015 (J23115)
- K2560017 (J23101)
- K2560018 (J23102)
- K2560019 (J23103)
- K2560020 (J23105)
- K2560021 (J23107)
- K2560022 (J23108)
- K2560023 (J23109)
- K2560024 (J23110)
- K2560025 (J23111)
- K2560026 (J23113)
- K2560027 (J23114)
- K2560028 (J23116)
- K2560029 (J23117)
- K2560030 (J23118)
- K2560031 (J23119)
- K2560123
(pTet) - K2560124 (pTrc)
- K2560131 (Promoter Dummy)

- K2560012 (3'Connector Dummy)
- K2560070 (3'Con1)
- K2560071 (3'Con2)
- K2560072 (3'Con3)
- K2560073 (3'Con4)
- K2560080 (3'Con5 Ori)
- K2560100 (3'Con1 inv
Short) - K2560101 (3'Con2 inv
Short) - K2560102 (3'Con3 inv
Short) - K2560103 (3'Con4 inv
Short) - K2560104 (3'Con5 inv
Short) - K2560106 (3'Con1 inv
Short Res) - K2560108 (3'Con1 inv)
- K2560109 (3'Con1 inv
Res) - K2560110 (3'Con2 inv)
- K2560111 (3'Con3 inv)
- K2560112 (3'Con4 inv)
- K2560113 (3'Con5 inv)

- K2560048 (Cam. Res. RFP)
- K2560056
(Kan. Res. (pSB3K3) RFP) - K2560057
(Kan. Res. (pSB3K3) GFP) - K2560058
(Tet. Res. (pSB3T5) RFP) - K2560059
(Tet. Res. (pSB3T5) GFP) - K2560125 (Carb. Res. RFP)
- K2560126 (Carb. Res. GFP)
- K2560127 (Carb. Res. into BBa_K2560002)
- K2560132 (Cam. Res. into BBa_K2560002)
- K2560133
(Kan. Res. into BBa_K2560002) - K2560134
(Tet. Res. into BBa_K2560002)
Tags and Entry Vectors
| None |








