Part:BBa_K3453111
Rosewood DmMatK Toehold Switch 1.1 with sfGFP-LVAtag
This part is an sfGFP-LVAtag (BBa_K2675006) expression cassette under the control of the Rosewood DmMatK Toehold Switch 1.1 (BBa K3453011) for sequence-based detection of the rosewood species Dalbergia maritima var. pubescens.
Usage and Biology
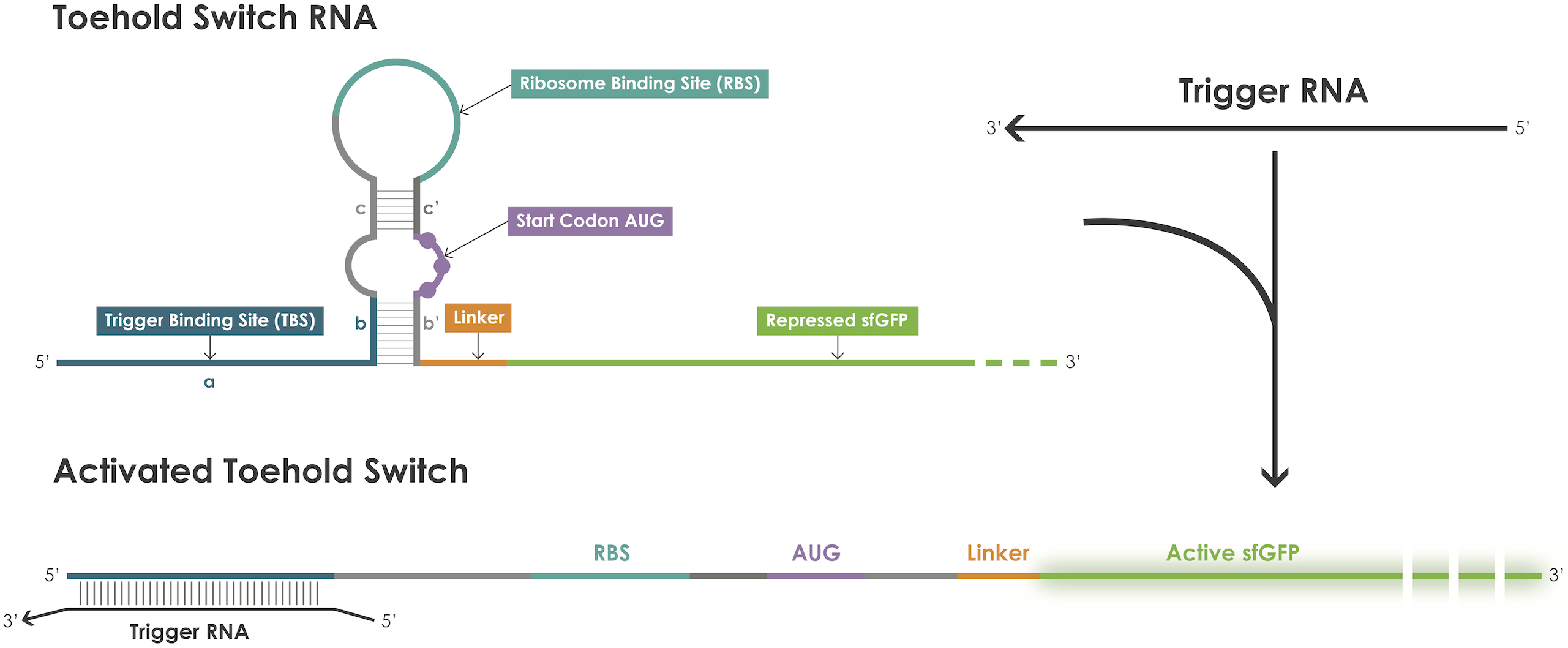
A toehold switch is an RNA–based device containing a ribosome binding site (RBS) and an ATG start codon embedded in the middle of a hairpin structure that blocks translation initiation [1]. The hairpin can be unfolded upon binding of a trigger RNA thereby exposing the RBS and the ATG start codon and thus permitting translation of the reporter protein (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Toehold switches principle.
In this composite part sfGFP-LVAtag (BBa_K2675006) was equipped by the synthetic Rosewood DmMatK Toehold Switch 1.1 (BBa K3453011) and placed under the control of the T7 promoter (BBa_K2150031) and of the strong SBa_000587 synthetic terminator (BBa_K3453000).
The corresponding trigger sequence of this toehold switch is the rosewood DmMatK Trigger 1.1 (Table 1).
| Table 1. Rosewood DmMatK triggers. | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Label | Part number | Transcriptional units’ part numbers | Specificity |
| Rosewood DmMatK Trigger (Full) | BBa_K3453020 | BBa_K3453120 | all Rosewood DmMatK switches |
| Rosewood DmMatK Trigger 1.1 | BBa_K3453021 | BBa_K3453121 | Rosewood DmMatK switch 1.1, but also 2.3 |
| Rosewood DmMatK Trigger 1.3 | BBa_K3453022 | BBa_K3453122 | Rosewood DmMatK switch 1.3, but also 1.1 & 1.4 |
| Rosewood DmMatK Trigger 1.4 | BBa_K3453023 | BBa_K3453123 | Rosewood DmMatK switch 1.4, but also 1.1 & 2.3 |
| Rosewood DmMatK Trigger 2.1 | BBa_K3453024 | BBa_K3453124 | Rosewood DmMatK switch 2.1 |
| Rosewood DmMatK Trigger 2.2 | BBa_K3453025 | BBa_K3453125 | Rosewood DmMatK switch 2.2 |
| Rosewood DmMatK Trigger 2.3 | BBa_K3453026 | BBa_K3453126 | Rosewood DmMatK switch 2.3 |
BBa_K3453111 was assembled by Golden Gate in the low copy plasmid pSB3T5. For this, a fragments containing the BBa_K3453011 was synthesized flanked by BbsI type IIS restriction sites, and then inserted into BBa_K3453103, a platform in which a Golden Gate adapter with BbsI sites is present upstream of the sfGFP-LVAtag.
The trigger sequences (Table 1) were placed under the control of the T7 promoter and followed by the strong SBa_000587 synthetic terminator for the T7 RNA polymerase and the resulting transcriptional units were synthesized and assembled in the high copy plasmid pSB1C3.
For toehold switch characterisation we decided to use E. coli BL21 Star™(DE3) cells (Thermo Fisher Scientific), genotype F- ompT hsdSB (rB-mB-) gal dcm rne131 (DE3). As all BL21(DE3) E. coli strains, these cells contain the T7 RNA polymerase under control of the lacUV5 promoter and thus require IPTG to induce expression. The particularity of BL21 Star™(DE3) cells is that they contain a truncated version of the RNaseE gene (rne131) that leads to reduced level of mRNA degradation and thus increased RNA stability. For fluorescence measurements, E. coli cells containing switch and trigger plasmids were first grown overnight in 96-deep-well plates containing 1 mL of LB medium supplemented with 5 µg/mL tetracycline and 17.5 µg/mL chloramphenicol, then diluted by 40x into similar media. Upon reaching early log-phase, cells were further diluted 20x in 100 µL of LB medium supplemented with 5 µg/mL tetracycline, 17.5 µg/mL chloramphenicol and 10 µM IPTG in an opaque wall 96-well polystyrene microplate, the COSTAR 96 (Corning). The plate was incubated at 37°C at 200 rpm and the sfGFP fluorescence (λexcitation 483 nm and λemission 530 nm) and OD600nm were measured every 10 min for 24 hours in a CLARIOstar (BMGLabtech) plate reader. Fluorescence values were normalised by OD600nm and, using the calibration curves presented on the ‘Measurement’ page of our wiki, we converted the arbitrary units into Molecules of Equivalent FLuorescein (MEFL) / particle.
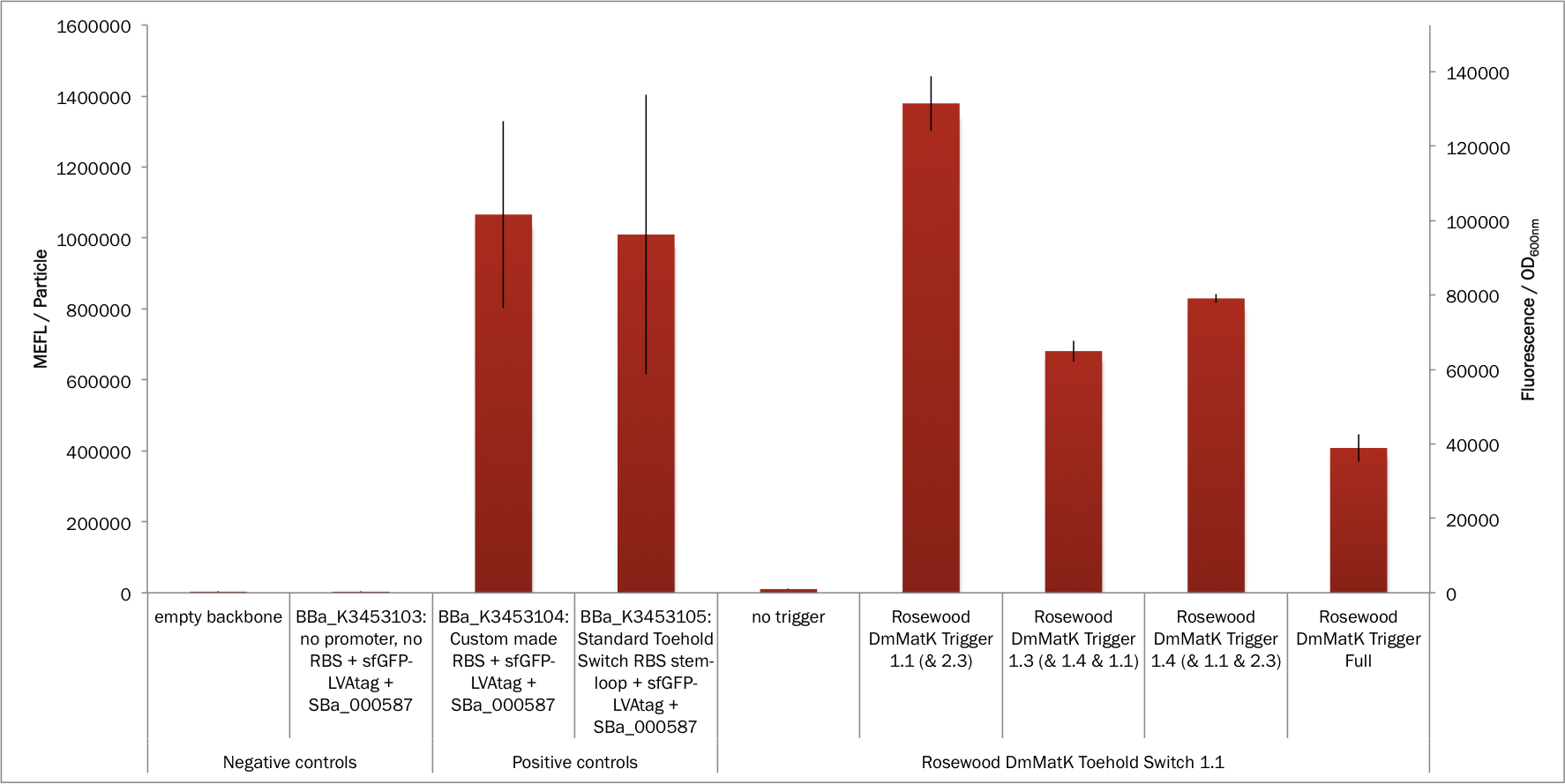
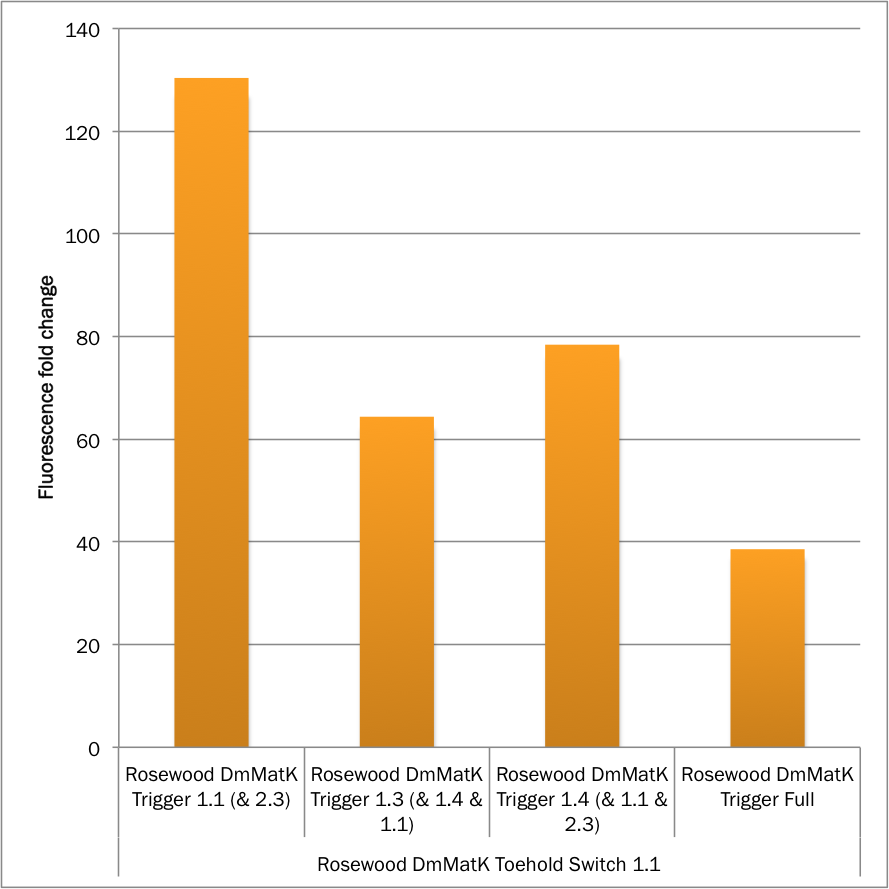
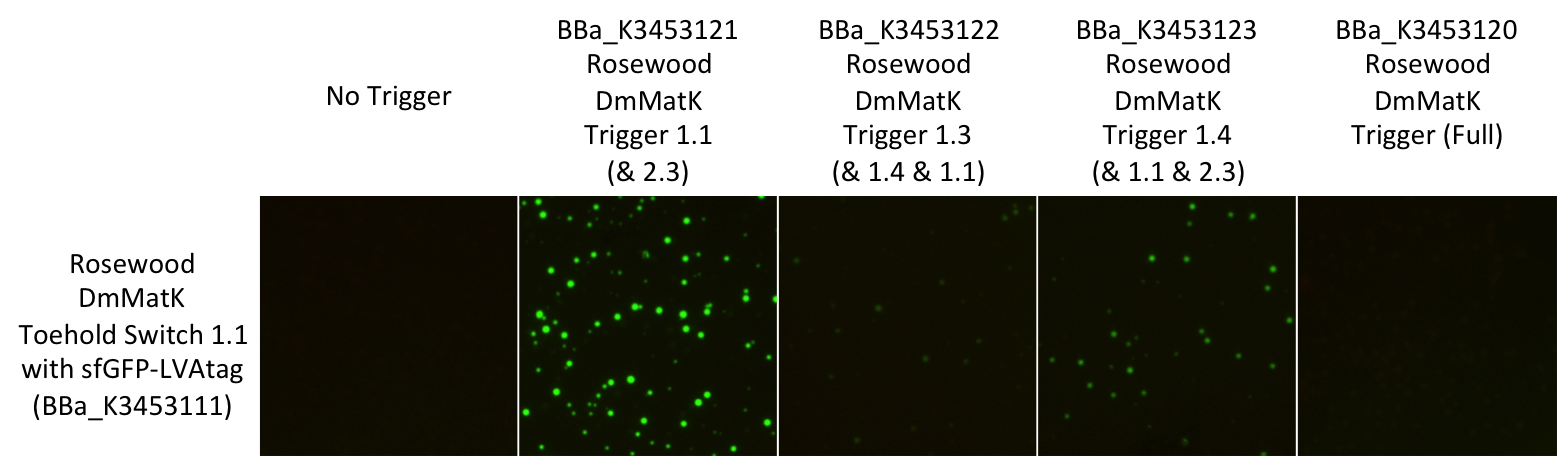
The results presented in figures 2, 3 and 4 show that the rosewood DmMatK toehold switch 1.1 is functional and behave as expected.
The results presented in Figure 2 show also that the sfGFP expression was readily detected in the positive controls and that the two RBS (BBa_K2675017 and BBa_K3453005) have comparable strength. As expected, no fluorescence was detected in the negative controls as either the sfGFP gene was not present or the promoter and the RBS were absent.
Figure 2. In vivo characterization of sfGFP expression by E. coli BL21 Star™(DE3) cells harbouring the rosewood DmMatK toehold switch 1.1 and the rosewood DmMatK triggers (Table 1). The negative controls have been performed with an empty pSB3T5, pSB1C3 (no trigger) and BBa_K3453103 (no promoter, no RBS) and the positive controls with BBa_K3453104 and BBa_K3453105. The data and error bars are the mean and standard deviation of at least three measurements on independent biological replicates.
Figure 3. MEFL / Particle fold changes of the rosewood DmMatK toehold switch 1.1 in the presence of the rosewood DmMatK triggers (Table 1) compared to the MEFL / Particle value in the absence of the trigger.
Figure 4: Pictures of E. coli BL21 Star™(DE3) cells harbouring this part in the presence of the rosewood DmMatK triggers (Table 1). The negative control was performed with an empty pSB1C3 (no trigger).
References
[1] Green AA, Silver PA, Collins JJ, Yin P. Toehold switches: de-novo-designed regulators of gene expression. Cell (2014) 159, 925-939.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 149
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
| None |