Part:BBa_K3332072
J23100-RBS-phnO-his-tag-terminator
Aminoalkylphosphonate N-acetyltransferase with a 6*histidine-tag, which can degradate AMPA. We use BBa_K823004-BBa_B0034 to construct a new part that can improve the capability of chassis bacteria to degrade glyphosate.
Biology
Under natural conditions, many microorganisms can use the glyphosate oxidoreductase to oxidize glyphosate to aminomethylphosphoric acid (AMPA).
Phn system is a gene cluster for organophosphorus transportation and degradation in many microorganisms. The phnO gene encodes the acyltransferase which catalyzes the transfation of acyl to AMPA by acetyl-coa. Through this one-step acyl transfer reaction, AMPA can be converted into glyphosate analogue, which can be degraded by C-P lyase later.
Usage
In order to purify PhnO easily, we added a his-tag (6*His) at the C-terminal. we ligased the strong promoter、RBS、Terminator(BBa_J23100、BBa_B0034、BBa_B0015) and the parts (phnO) on the expression vector pSB1C3 by standard assembly. Then the ligation mixture was transformed into E. coli DH5α & E. coli BL21 (DE3), and the correct recombinant one was confirmed by chloramphenicol, enzyme-cut identification and sequencing.
Characterization
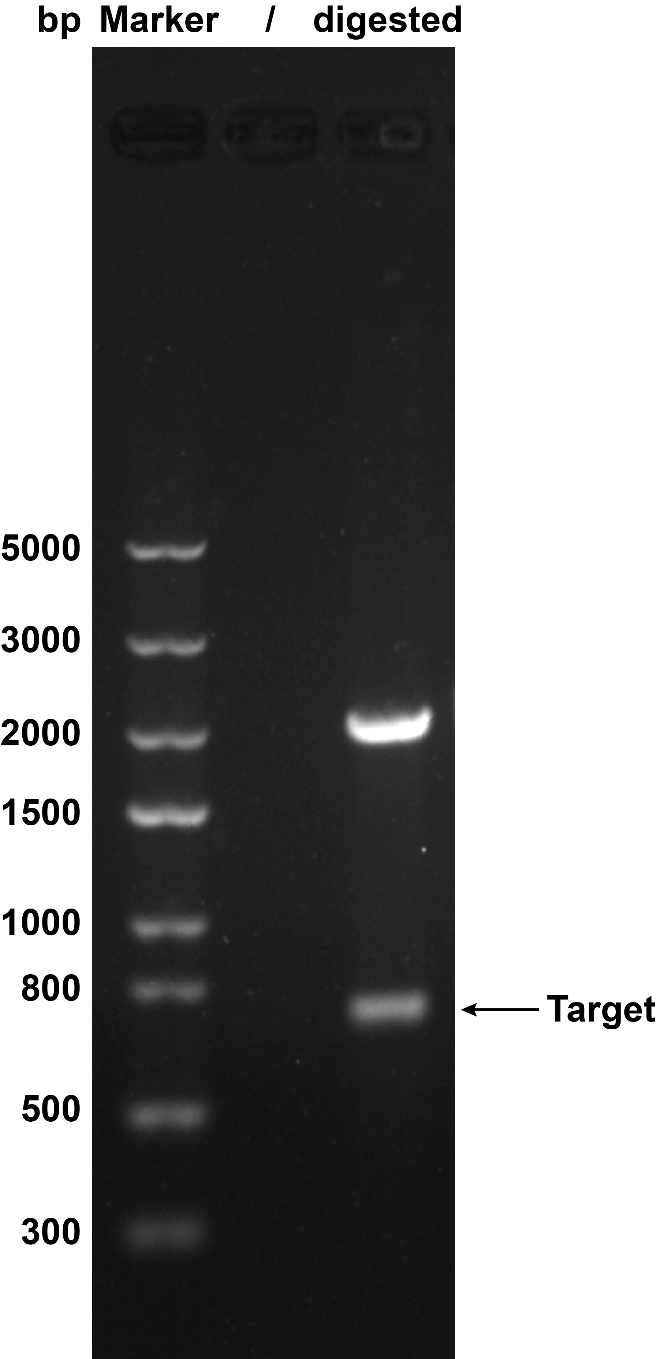
1. Agarose Gel Electrophoresis
We use restriction enzyme to digest this circuit with EcoR I and Pst I to cut the plasmid to certify that the plasmid was correct. Then we got the target separate fragment-686bp.
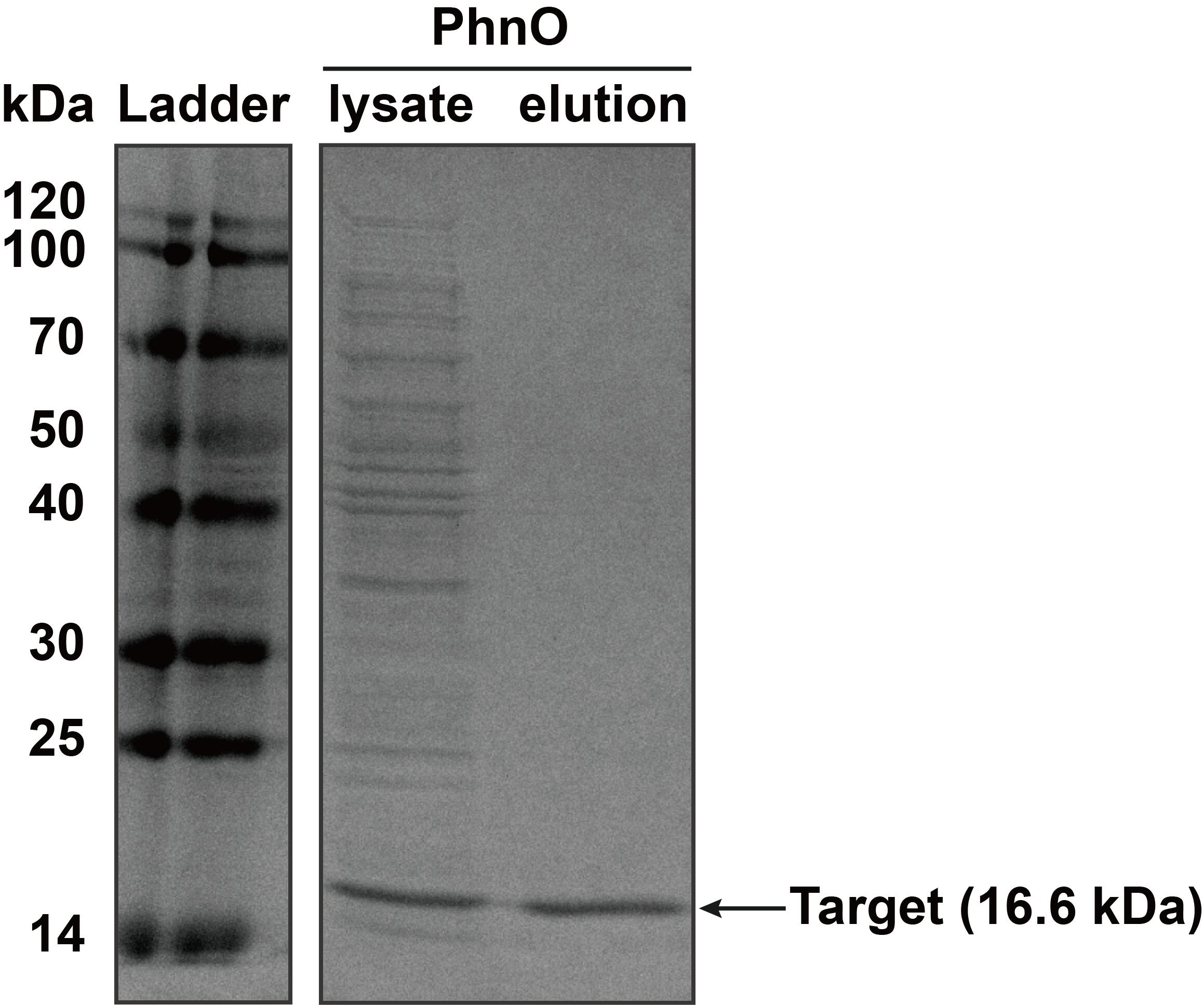
2. SDS-PAGE
The constructed plasmid was transformed into E. coli BL21 (DE3). Owing to the his-tag, the PhnO could be easily purified through AKTA with Ni-NTA. Compared with the lysate, the PhnO in the eluant can be found at around 16 kDa. Both of them were electrophoresed on a sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS)-12% (wt/vol) polyacrylamide gel, followed by Coomassie blue staining.
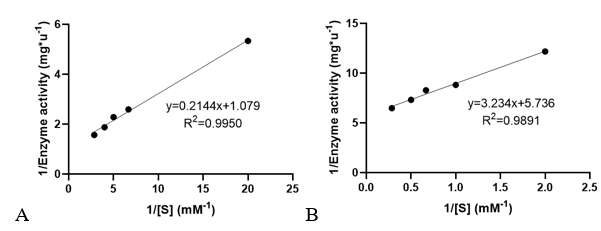
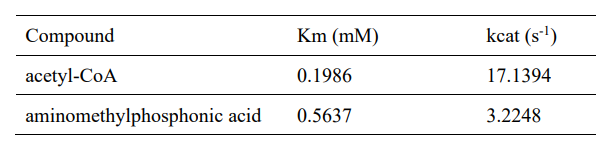
3. Determination of enzyme kinetic constants
Velocities for the reaction of PhnO were determined using 4,4′-dithiodipyridine (DTDP) to continuously detect the formation of the product CoA at 324 nm (thiopyridone: ε= 19800 M-1·cm-1) at 25 °C. (1) Enzyme activity was determined through enzyme-labeled instrument.
Km and kcat of different substrates were determined with a concentration gradient.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 220
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
- ↑ 1. J. C. Errey, J. S. Blanchard, Functional Annotation and Kinetic Characterization of PhnO from Salmonella enterica. Biochemistry 45, 3033-3039 (2006).
| None |