Part:BBa_K1041000
RFP Coding Device
Team NRP-UEA_Norwich 2013 added an NdeI restriction site at the start of the RFP coding region of BBa_J04450 using mutagenesis. This was to allow either the promoter region or RFP gene to be excised and exchanged for a different promoter or gene and provide restriction sites for further cloning such as part Bba_K1041002.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 781
Illegal AgeI site found at 893 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Composite part of the following BioBricks:
- BBa_R0010: Promoter (lacI regulated)
- BBa_B0034: RBS (Elowitz 1999)
- BBa_E1010: Red Fluorescent Protein from Discosoma striata
- BBa_B0015: Double Terminator
Characterisation
Characterisation of this biobrick involved comparisons with the original Bba_J04450 biobrick by performing transformations, restriction digests and BLAST analysis. We also had our biobrick sequenced.
Transformation
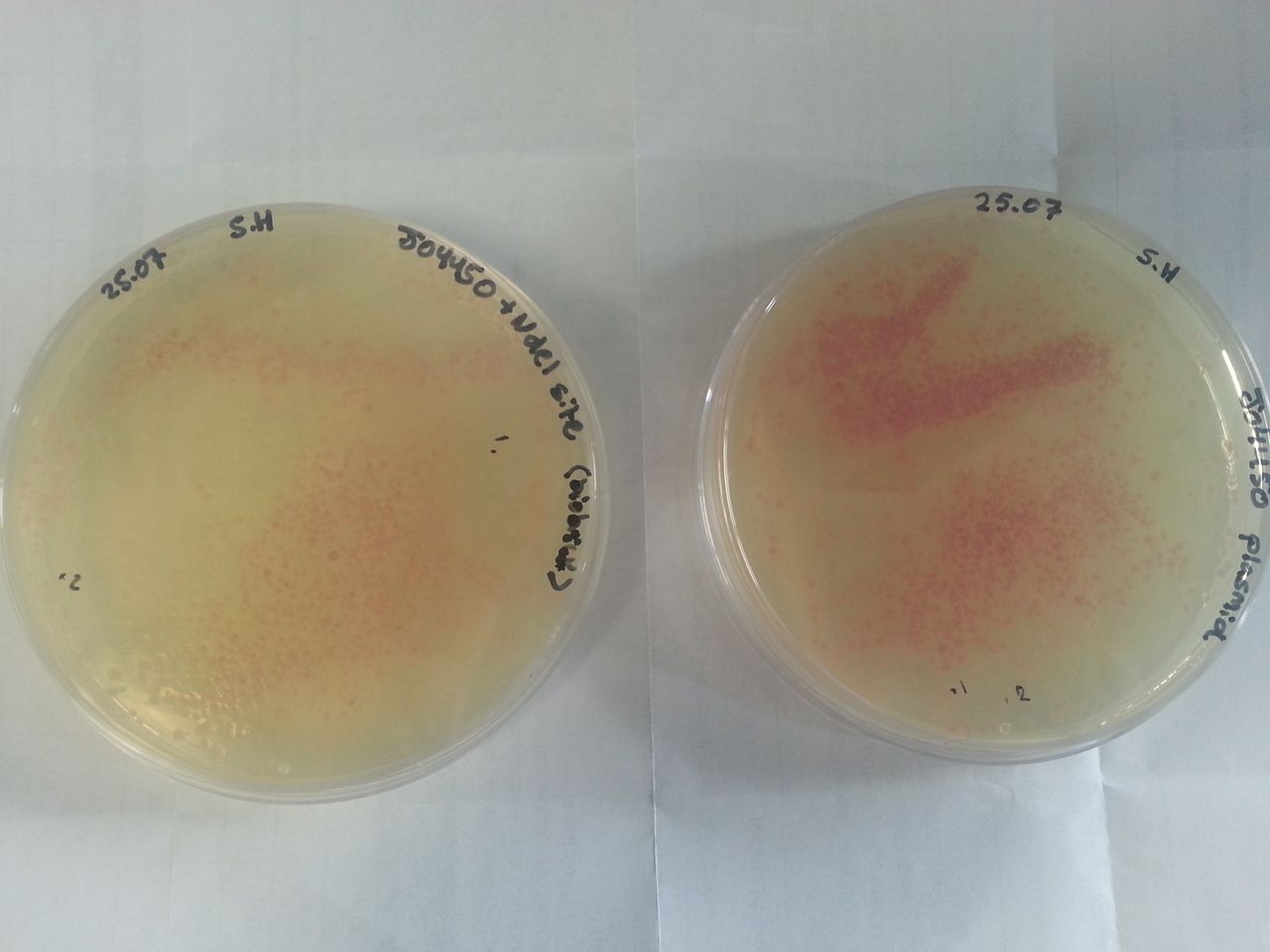
Parts BBa_K1041000 and BBa_J04450 were transformed into Alpha-Select competent E.Coli cells and plated onto LB Agar plates which contained the antibiotic ampicillin. Both plates have colonies that appear red under natural light Fig.1. Therefore the addition of a NdeI site has not effected the ability for the RFP gene to be transcribed.
Restriction Digests
Parts Bba_K1041000 and Bba_J04450 were analysed by restriction digests and run on agarose gels. Both biobricks were cut with no enzyme and NdeI, Fig 2 and PvuII Fig 3.
[[image:K1041000 digest.JPG|thumb|left|Fig 3:Analysis of Restriction enzyme digest with PvuII. Lanes 2 and 3 contain uncut BBa_J04450 and BBa_J04450 digested with PvuII respectively. Lane 5 contains Bba_K1041000 with PvuII.
Sequencing
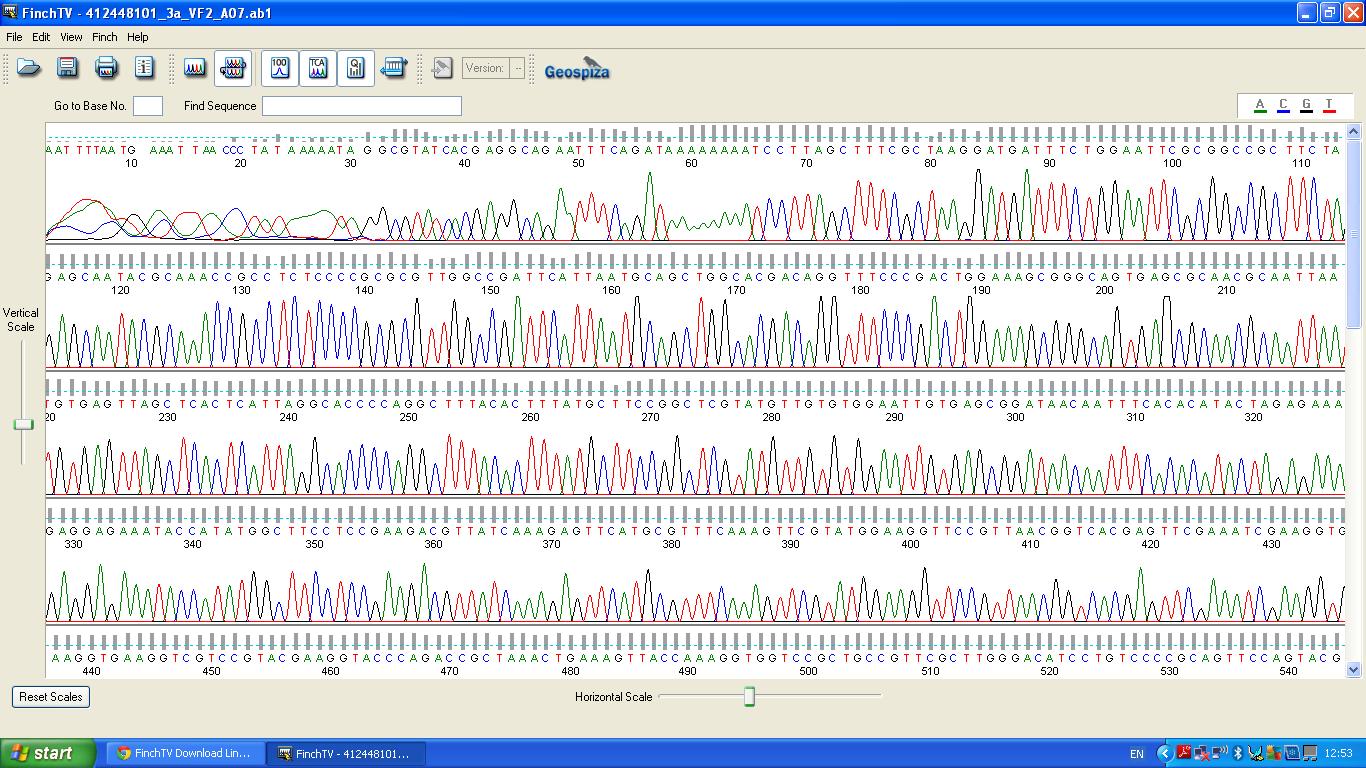
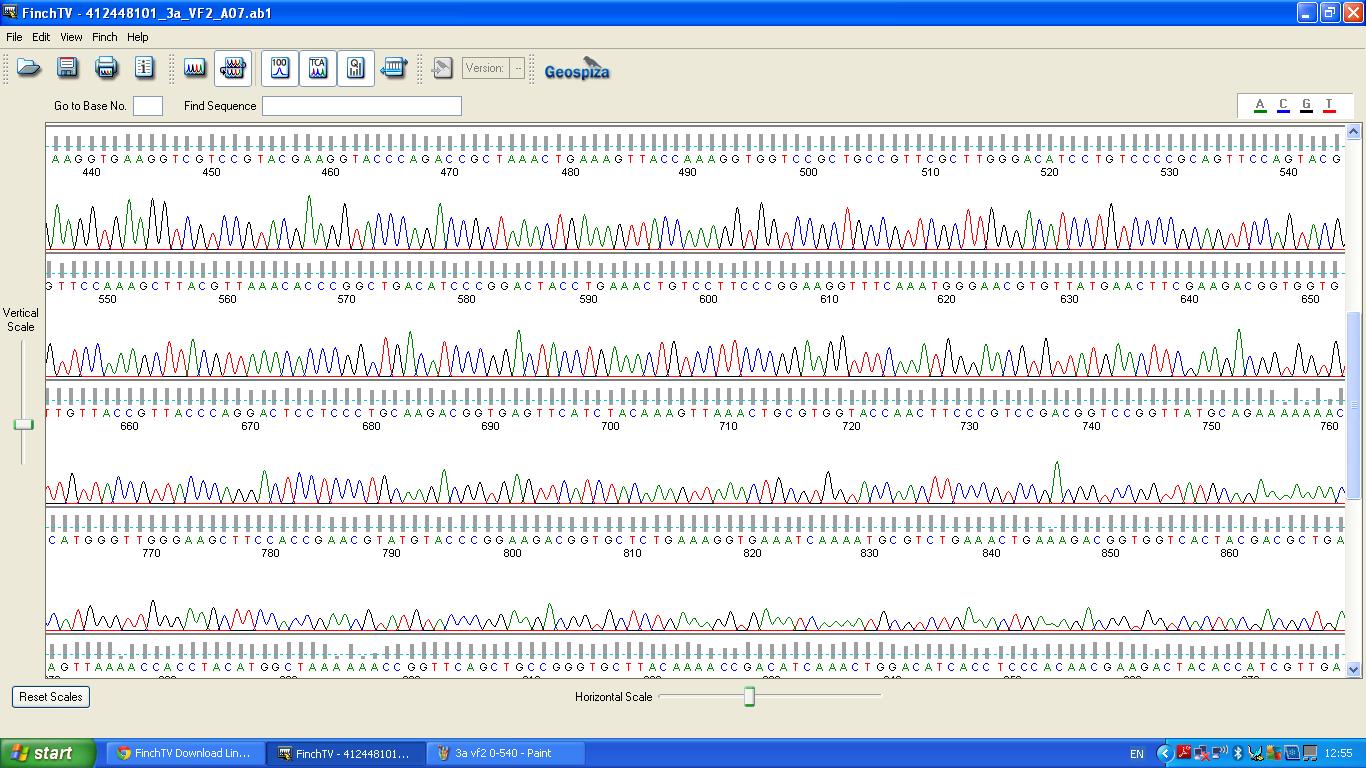
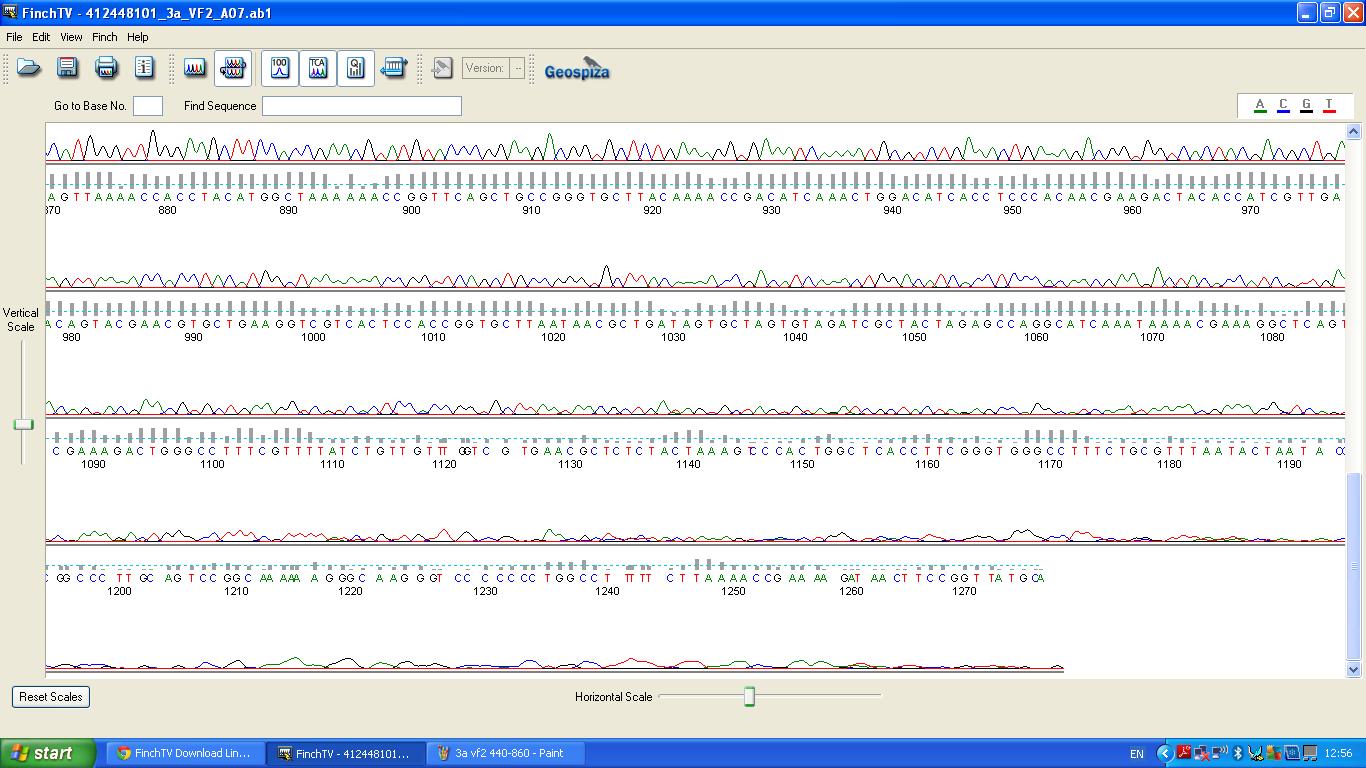
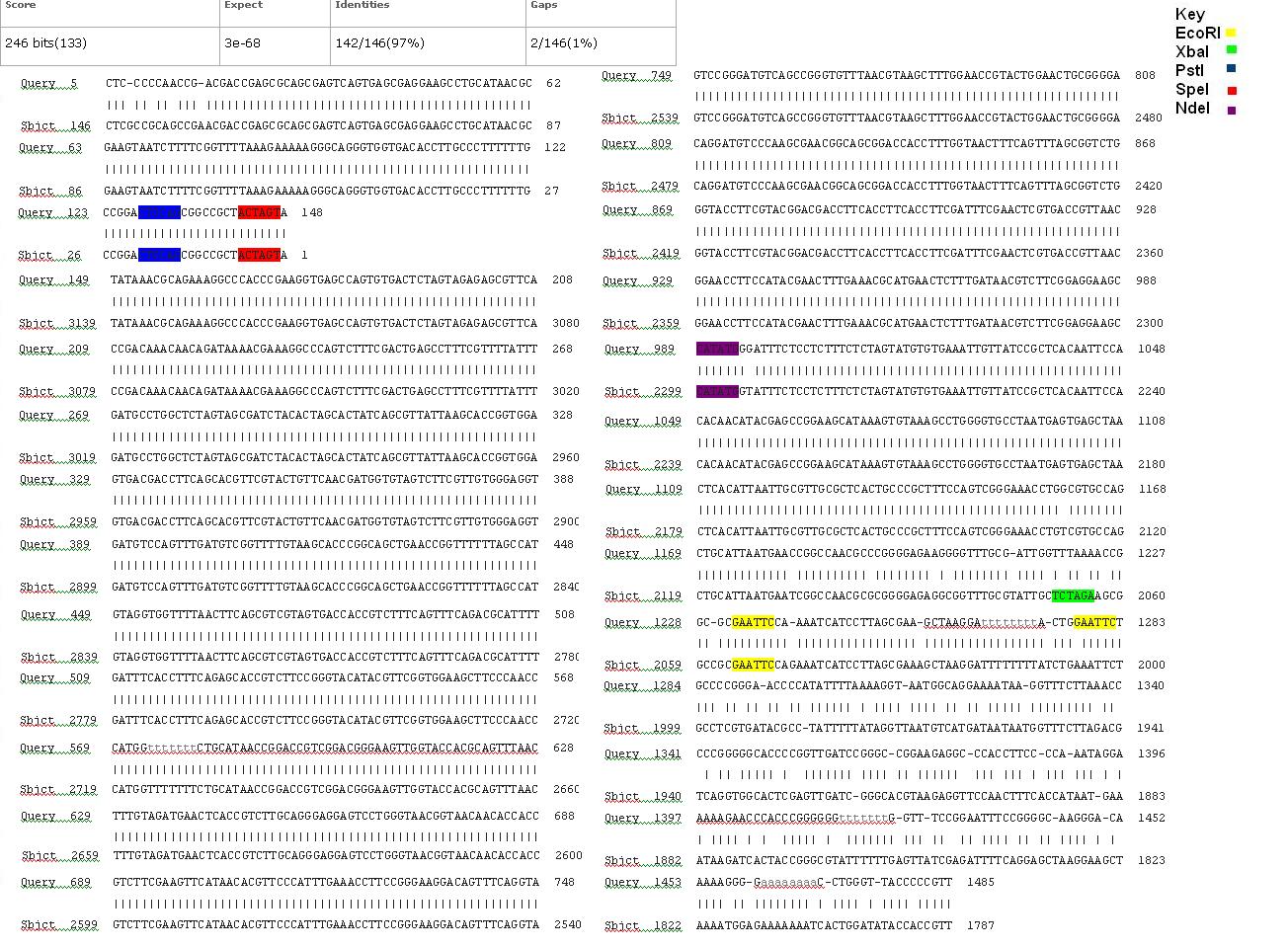
The biobrick was sent off to a company for sequencing, Fig 3,4,5.The data we recieved back showed the DNA is of good quality.
BLAST Analysis
The data we recieved back from the sequencing company was aligned using BLAST with the expected DNA sequence Fig 6,7
| emission | RFP |
| excitation | |
| tag | None |