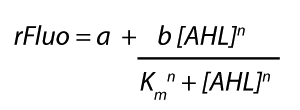Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa I14017:Experience"
(→Results) |
(→Background information) |
||
| (22 intermediate revisions by 3 users not shown) | |||
| Line 30: | Line 30: | ||
== Background information == | == Background information == | ||
| − | + | We used an ''E. coli'' TOP10 strain transformed with two medium copy plasmids (about 15 to 20 copies per plasmid and cell). The first plasmid contained the commonly used p15A origin of replication, a kanamycin resistance gene, and promoter [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0079 pLas (BBa_R0079)] followed by [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0034 RBS (BBa_B0034)] and superfolder green fluorescent protein (sfGFP). In general, for spacer and terminator sequences the parts [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0040 BBa_B0040] and [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0015 BBa_B0015] were used, respectively. The second plasmid contained the pBR322 origin (pMB1), which yields a stable two-plasmid system together with p15A, an ampicillin resistance gene, and a strong promoter [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J23100 (BBa_J23100)] chosen from the [https://parts.igem.org/Promoters/Catalog/Anderson Anderson promoter collection] followed by one of the three different regulators ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0062 LuxR], [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0179 LasR], and [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0171 RhlR]) used in the experiments in order to quantify crosstalk with [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl]. The detailed regulator construct design and full sequences (piG0040, piG0041, piG0042, piG0060) are [http://2014.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/lab/sequences available here]. In the following, we describe the experimental set-up and all the different levels of crosstalk we have assessed. | |
| − | == | + | = Experimental Set-Up = |
| + | |||
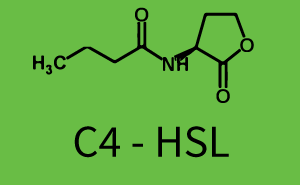
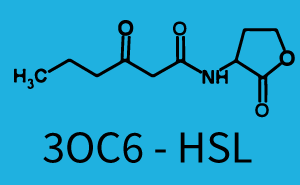
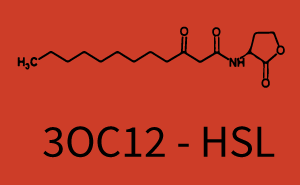
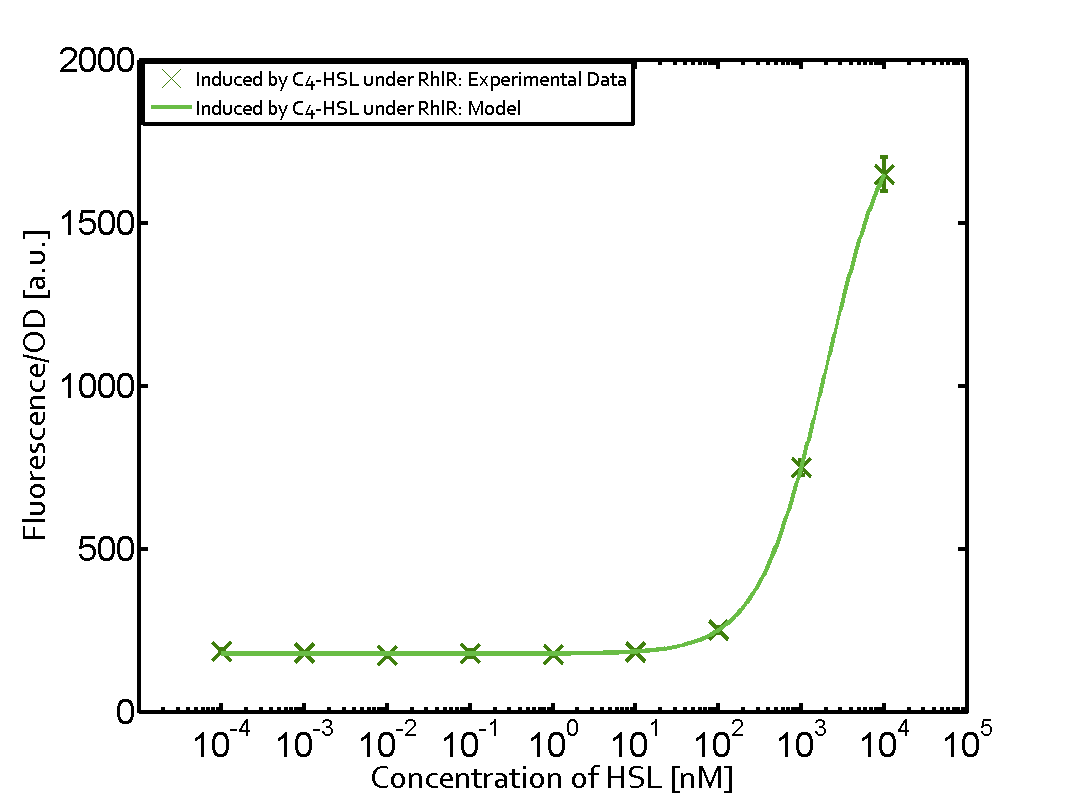
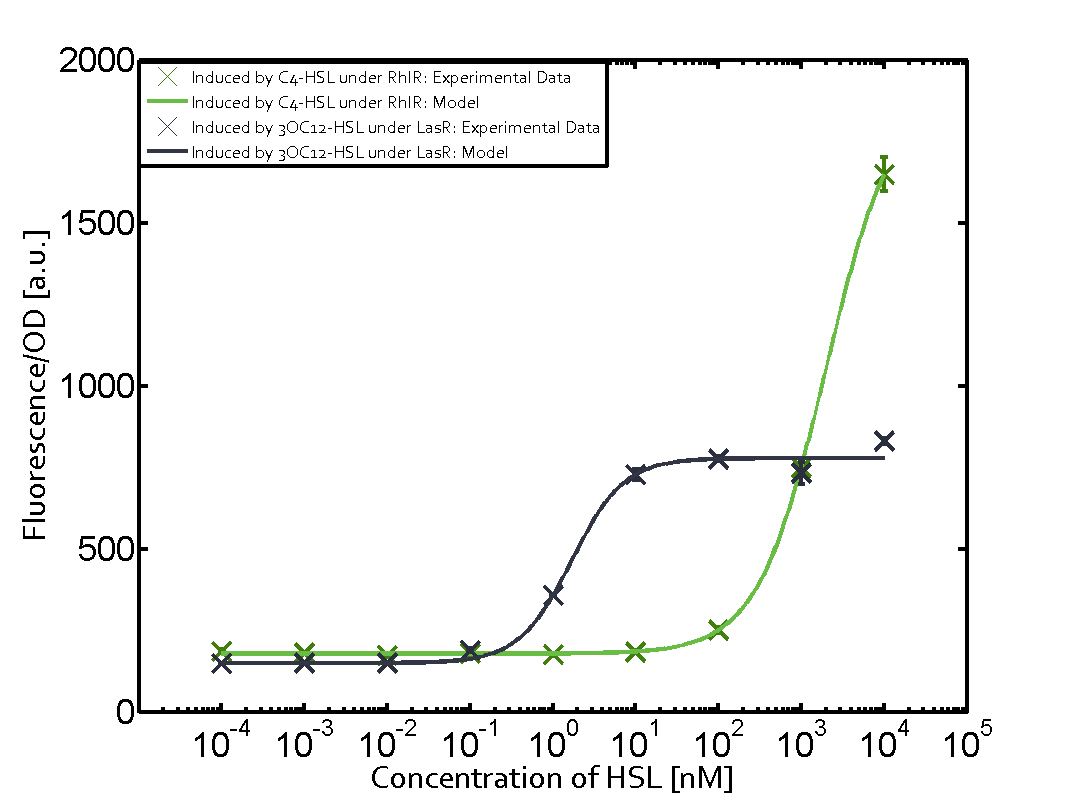
| + | The above described ''E. coli'' TOP10 strains were grown overnight in Lysogeny Broth (LB) containing kanamycin (50 μg/mL) and ampicillin (200 μg/mL) to an OD<sub>600</sub> of about 1.5 (37 °C, 220 rpm). As a reference, a preculture of the same strain lacking the sfGFP gene was included for each assay. The cultures were then diluted 1:40 in fresh LB containing the appropriate antibiotics and measured in triplicates in microtiter plate format on 96-well plates (200 μL culture volume) for 10 h at 37 °C with a Tecan infinite M200 PRO plate reader (optical density measured at 600 nm; fluorescence with an excitation wavelength of 488 nm and an emission wavelength of 530 nm). After 200 min we added the following concentrations of inducers ([[3OC6HSL|3OC6-HSL]], [[AHL|3OC12-HSL]], and [[AHL|C4-HSL]]): 10<sup>-4</sup> nM and 10<sup>4</sup> nM (from 100 mM stocks in DMSO). Attention: All the dilutions of [[AHL|3OC12-HSL]] should be made in DMSO in order to avoid precipitation. In addition, in one triplicate only H<sub>2</sub>O was added as a control. From the the obtained kinetic data, we calculated mean values and plotted the dose-response-curves for 200 min past induction. | ||
== First-order crosstalk == | == First-order crosstalk == | ||
| + | |||
| + | In the first order crosstalk section we describe crosstalk of [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl] due to [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0171 RhlR] binding to inducers different from [[AHL|C4-HSL]] or [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl] itself binding a regulator-inducer pair different from [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0171 RhlR]-[[AHL|C4-HSL]]. | ||
=== First Level crosstalk: RhlR binds to different HSL and activates the promoter === | === First Level crosstalk: RhlR binds to different HSL and activates the promoter === | ||
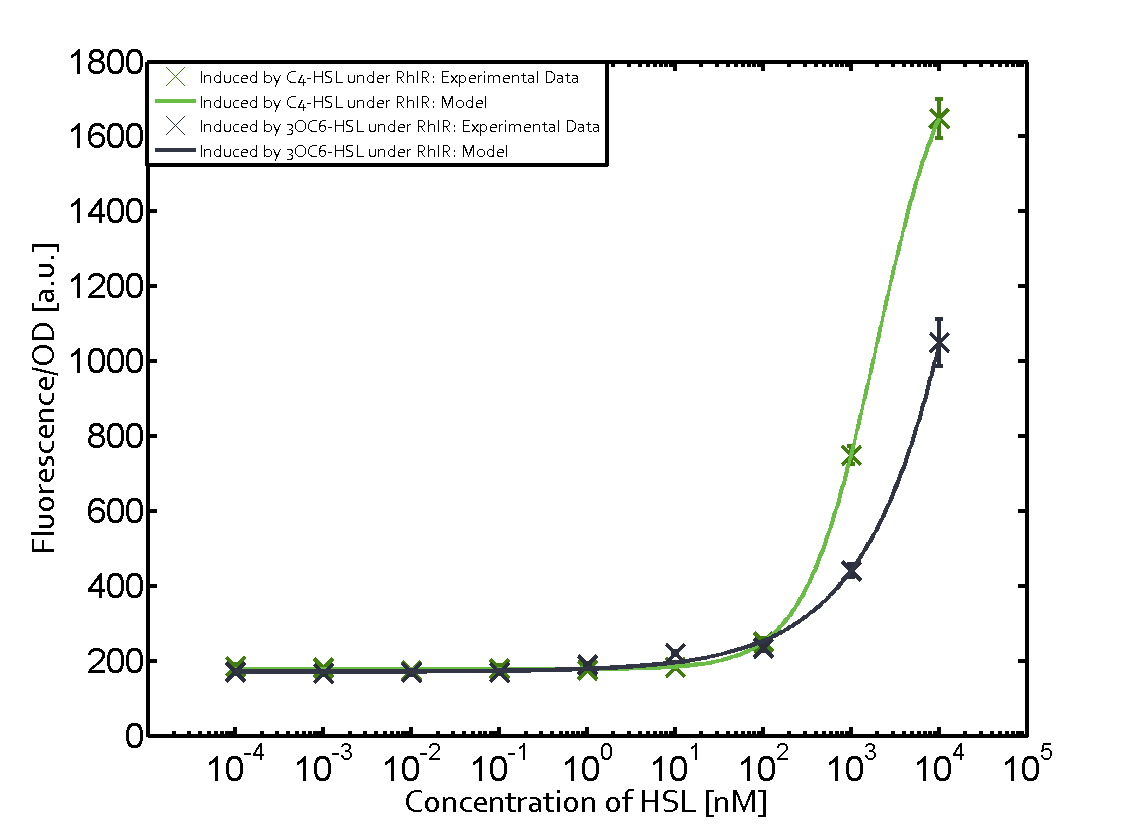
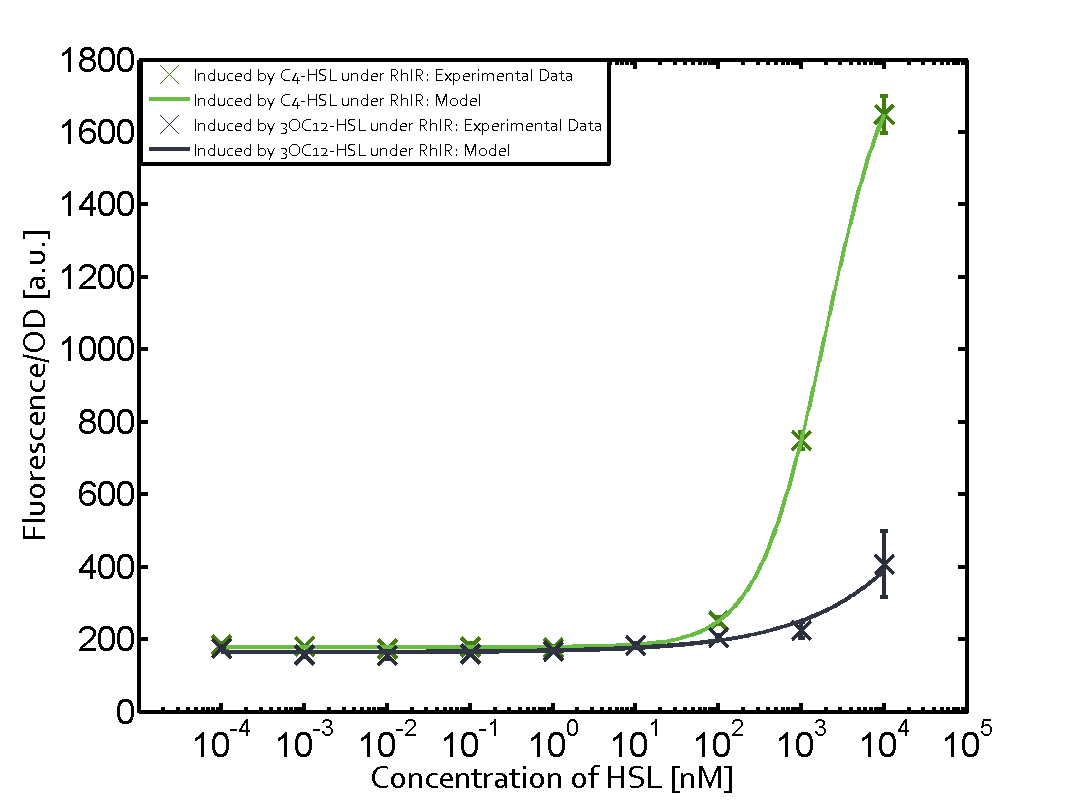
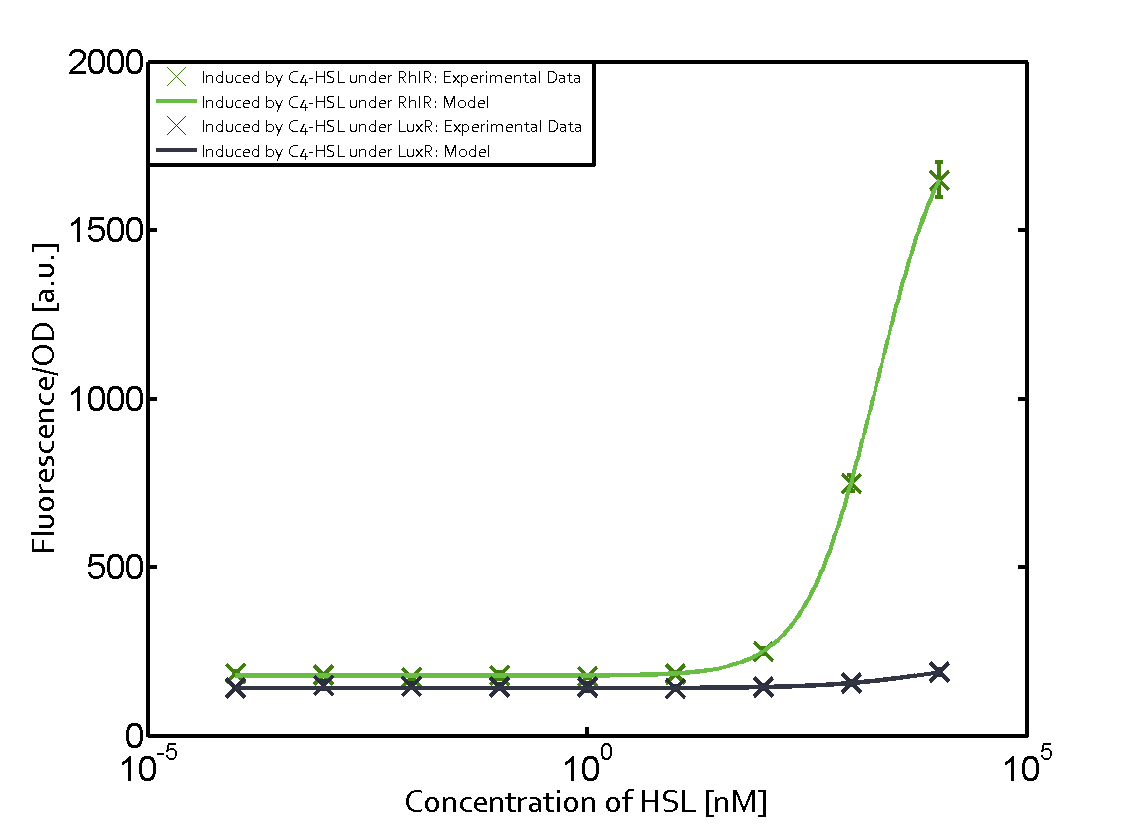
| + | In the conventional system [[AHL|C4-HSL]] binds to its corresponding regulator, [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0171 RhlR], and activates the pRhl promoter (figure 2, green). However, RhlR can potentially also bind other AHLs and then activate pRhl (Figure 2, [[AHL|3OC12-HSL]] in red and [[3OC6HSL|3OC6-HSL]] in light blue). This leads then to unwanted gene expression (crosstalk). | ||
| − | [[File:ETH Zurich 1crosstalkPrhl.png|400px|center]] | + | [[File:ETH Zurich 1crosstalkPrhl.png|400px|thumb|center| '''Figure 1 Overview of possible crosstalk of the [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0171 RhlR]/[https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl] system with three different [[AHL|AHLs]].''' Usually, [[AHL|C4-HSL]] binds to its corresponding regulator, [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0171 RhlR], and activates the [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl] promoter (green). However, [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0171 RhlR] may also bind [[AHL|3OC12-HSL]] (red) or [[3OC6HSL|3OC6-HSL]] (light blue) and then unintentionally activate [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl].]] |
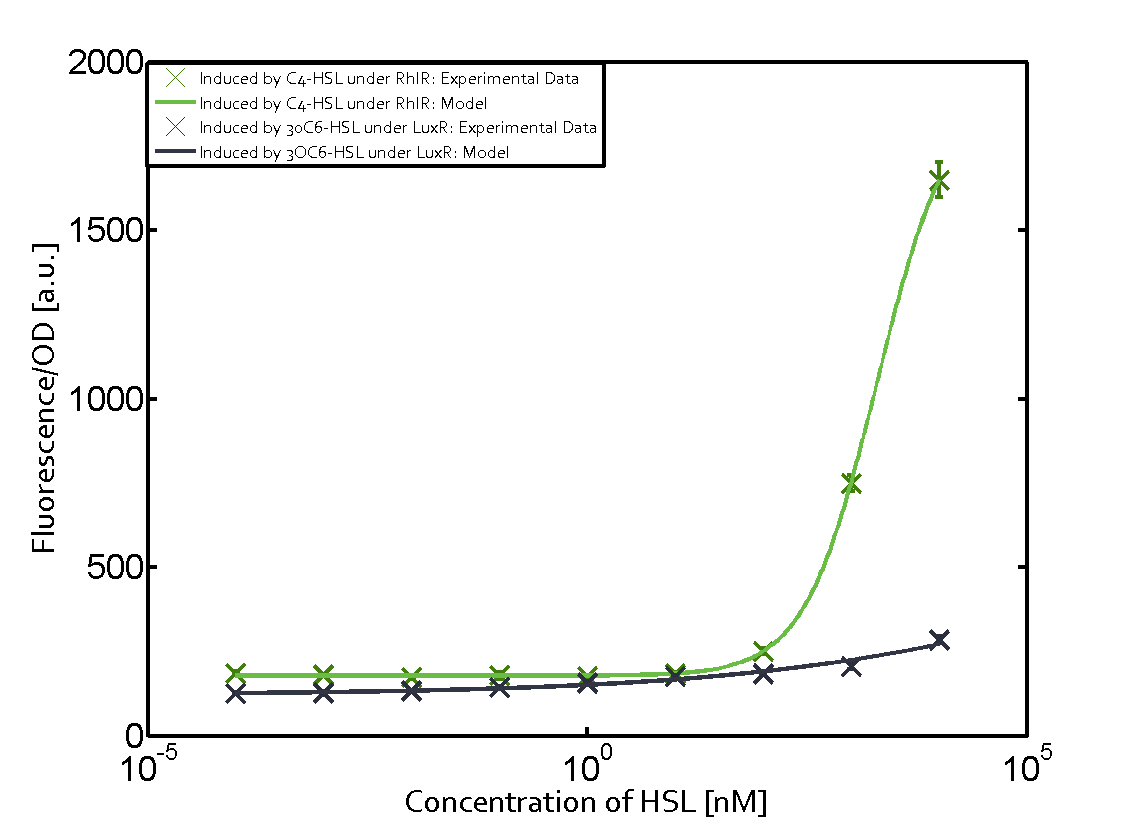
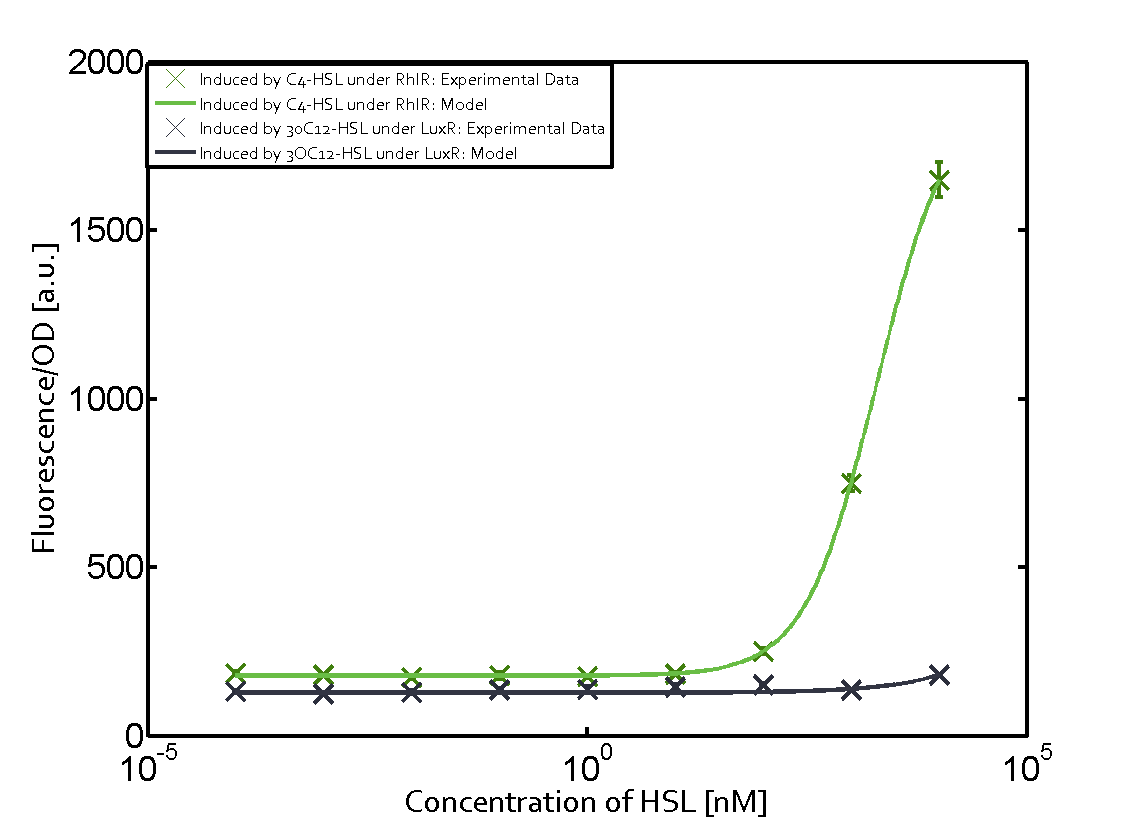
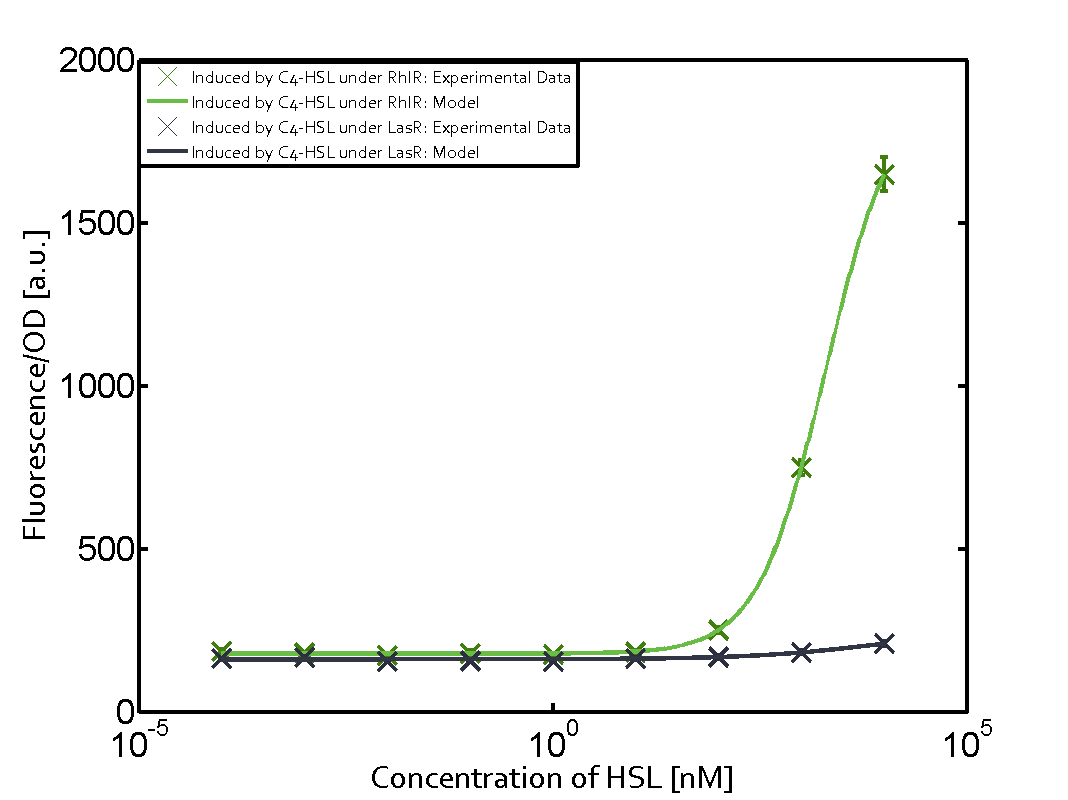
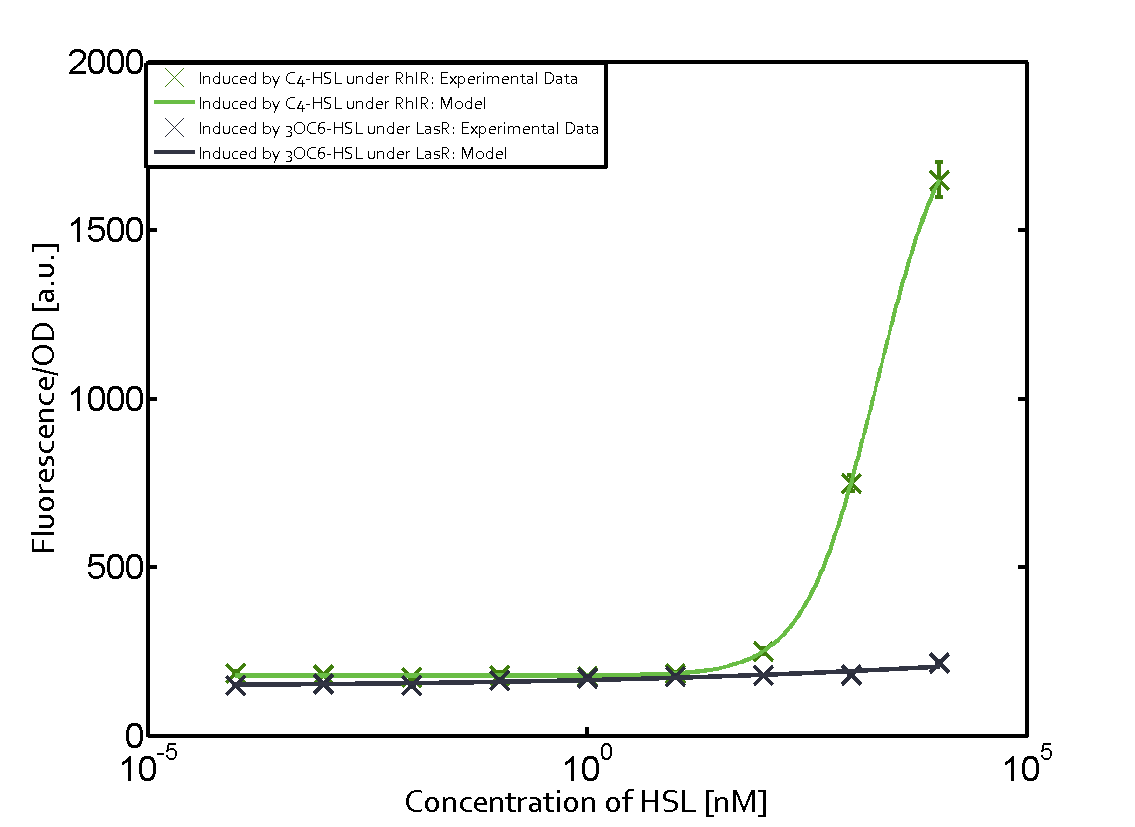
| − | === Second Level crosstalk: other regulatory proteins, like LuxR, bind to their natural | + | ==== Second Level crosstalk: other regulatory proteins, like LuxR and LasR, bind to their natural AHL substrate and activate the pRhl promoter ==== |
| − | [[File:ETH_Zurich_2crosstalkPrhl.png|400px|center]] | + | In the conventional system [[AHL|C4-HSL]] binds to its corresponding regulator, [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0171 RhlR], and activates the [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl] promoter (Figure 2, green). However, [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl] can potentially be activate by other regulators ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 LuxR], [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0179 LasR]), binding their corresponding regulator (figure 2, [[3OC6HSL|3OC6-HSL]] in light blue, [[AHL|3OC12-HSL]] in red). This leads then to unwanted gene expression (crosstalk). |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ETH_Zurich_2crosstalkPrhl.png|thumb|400px|center|'''Figure 2 Overview of possible crosstalk of the [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0171 RhlR]/[https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_i14017 pRhl] system with two additional regulators ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 LuxR] and [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0179 LasR]).''' Usually, [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0171 RhlR] together with inducer [[AHL|C4-HSL]] activate their corresponding promoter [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl] (green). However, [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl] may also be activated by the [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0062 LuxR] regulator together with [[3OC6HSL|3OC6-HSL]] (light blue) or by the [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0179 LasR] regulator together with [[AHL|3OC12-HSL]] (red).]] | ||
== Second order crosstalk: Combination of both cross-talk levels == | == Second order crosstalk: Combination of both cross-talk levels == | ||
| − | + | The second order crosstalk describes unintended activation of [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl] by a mixture of both the levels described above. The regulator and inducer are being different from [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0171 RhlR] and [[AHL|C4-HSL]], respectively, and at the same time they do not belong to the same module. For example, the inducer [[3OC6HSL|3OC6-HSL]] (light blue), usually binding to the regulator [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_R0062 LuxR], could potentially interact with [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0179 LasR] regulator (red) and together activate [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl] (green). This kind of crosstalk is explained in Figure 3. | |
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ETH Zurich 2014 2nd order rhl.png|400px|thumb|center| '''Figure 3 Overview of possible crosstalk of the [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl] promoter with both the regulator and inducer being unrelated to the promoter and each other.''' Usually, [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0171 RhlR] together with inducer [[AHL|C4-HSL]] activate their corresponding promoter [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl] (green). However, [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl] may also be activated by another regulator together with an unrelated inducer. For example, the inducer [[3OC6HSL|3OC6-HSL]] (light blue) may interact with the [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0179 LasR] regulator (red) and together activate [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017 pRhl] (green).]] | ||
== Results == | == Results == | ||
{|class="wikitable" style="background-color: white; text-align:center; width:auto; margin: auto;" | {|class="wikitable" style="background-color: white; text-align:center; width:auto; margin: auto;" | ||
| − | |+'''Table | + | |+'''Table 1''' Crosstalk matrix for the promoter prhl ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017:Experience BBa_I14017]) |
|colspan="4" style='font-size:10pt';text-align:left| | |colspan="4" style='font-size:10pt';text-align:left| | ||
| Line 58: | Line 67: | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | |style="width: | + | |style="width:100px"|[[File:ETH_Zurich_2014_qs-table_CornerRhl.png|100px|link=https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017:Experience]] |
|[[File:ETH_Zurich_2014_qs-table_C4-HSL.png|100px|link=https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017:Experience]] | |[[File:ETH_Zurich_2014_qs-table_C4-HSL.png|100px|link=https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017:Experience]] | ||
|[[File:ETH_Zurich_2014_qs-table_3OC6-HSL.png|100px|link=https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017:Experience]] | |[[File:ETH_Zurich_2014_qs-table_3OC6-HSL.png|100px|link=https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_I14017:Experience]] | ||
| Line 79: | Line 88: | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | === Modeling crosstalk === | ||
| + | |||
| + | Each experimental data set was fitted to an Hill function using the Least Absolute Residual method. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ETHZ_HillEq.png|center|200px]] | ||
| + | <p>The fitting of the graphs was performed using the following equation :<br><br> | ||
| + | rFluo = the relative fluorescence (absolute measured fluorescence value over OD)[a.u.]<br> | ||
| + | a = basal expression rate [a.u.](“leakiness”)<br> | ||
| + | b = maximum expression rate [a.u.]("full induction")<br> | ||
| + | n = Hill coefficient (“cooperativity”)<br> | ||
| + | K<sub>m</sub> = Half-maximal effective concentration (“sensitivity”)<br> | ||
| + | [AHL] = AHL concentration [nM]</p> | ||
| + | <br clear="all"/> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| border="1" class="wikitable" style="margin: 1em auto 1em auto;text-align:center;" | ||
| + | |+ Parameters of HillFunction for crosstalk with Prhl (with 95% confidence bounds) | ||
| + | ! | ||
| + | ! [[AHL|C4-HSL]] | ||
| + | ! [[3OC6HSL|3OC6-HSL]] | ||
| + | ! [[AHL|3OC12-HSL]] | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0171 RhlR] | ||
| + | | a = 178.4 (174.9, 182) [a.u.]<br> n = 1.053 (0.9489, 1.157)<br> Km = 1969 (1625, 2313) [nM]<br>b = 1736 (1629, 1842) [a.u.]<br> | ||
| + | | a = 169.1 (155.2, 182.9) [a.u.]<br> n = 0.507 (0.2303, 0.7837) <br> Km = 1.08e8(0, 2.681e10) [nM]<br> b = 9.708e4 (0, 1.192e7) [a.u.]<br> | ||
| + | | a = 162.8 (150.4, 175.1) [a.u.]<br> n = 0.404 (0, 0.998)<br> Km = 9.627e8 (0, 7.824e11) [nM]<br>b = 2.537e4 (0, 8.109e6) [a.u.]<br> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0062 LuxR] | ||
| + | | No crosstalk | ||
| + | | No crosstalk | ||
| + | | No crosstalk | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | ! [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_C0179 LasR] | ||
| + | | No crosstalk | ||
| + | | No crosstalk | ||
| + | | a = 149.3 (140.6, 158.1) [a.u.]<br>n = 1.366 (0.808, 1.923) <br> Km = 1.674 (1.259, 2.09) [nM]<br> b = 628.9 (599, 658.7) [a.u.]<br> | ||
| + | |} | ||
|} | |} | ||
Latest revision as of 17:03, 26 October 2014
This experience page is provided so that any user may enter their experience using this part.
Please enter
how you used this part and how it worked out.
Applications of BBa_I14017
User Reviews
UNIQe9fb607784d5bf13-partinfo-00000000-QINU
|
••••
ETH Zurich 2014 |
Characterization of two-order crosstalk on the promoterBackground informationWe used an E. coli TOP10 strain transformed with two medium copy plasmids (about 15 to 20 copies per plasmid and cell). The first plasmid contained the commonly used p15A origin of replication, a kanamycin resistance gene, and promoter pLas (BBa_R0079) followed by RBS (BBa_B0034) and superfolder green fluorescent protein (sfGFP). In general, for spacer and terminator sequences the parts BBa_B0040 and BBa_B0015 were used, respectively. The second plasmid contained the pBR322 origin (pMB1), which yields a stable two-plasmid system together with p15A, an ampicillin resistance gene, and a strong promoter (BBa_J23100) chosen from the Anderson promoter collection followed by one of the three different regulators (LuxR, LasR, and RhlR) used in the experiments in order to quantify crosstalk with pRhl. The detailed regulator construct design and full sequences (piG0040, piG0041, piG0042, piG0060) are [http://2014.igem.org/Team:ETH_Zurich/lab/sequences available here]. In the following, we describe the experimental set-up and all the different levels of crosstalk we have assessed. Experimental Set-UpThe above described E. coli TOP10 strains were grown overnight in Lysogeny Broth (LB) containing kanamycin (50 μg/mL) and ampicillin (200 μg/mL) to an OD600 of about 1.5 (37 °C, 220 rpm). As a reference, a preculture of the same strain lacking the sfGFP gene was included for each assay. The cultures were then diluted 1:40 in fresh LB containing the appropriate antibiotics and measured in triplicates in microtiter plate format on 96-well plates (200 μL culture volume) for 10 h at 37 °C with a Tecan infinite M200 PRO plate reader (optical density measured at 600 nm; fluorescence with an excitation wavelength of 488 nm and an emission wavelength of 530 nm). After 200 min we added the following concentrations of inducers (3OC6-HSL, 3OC12-HSL, and C4-HSL): 10-4 nM and 104 nM (from 100 mM stocks in DMSO). Attention: All the dilutions of 3OC12-HSL should be made in DMSO in order to avoid precipitation. In addition, in one triplicate only H2O was added as a control. From the the obtained kinetic data, we calculated mean values and plotted the dose-response-curves for 200 min past induction. First-order crosstalkIn the first order crosstalk section we describe crosstalk of pRhl due to RhlR binding to inducers different from C4-HSL or pRhl itself binding a regulator-inducer pair different from RhlR-C4-HSL. First Level crosstalk: RhlR binds to different HSL and activates the promoterIn the conventional system C4-HSL binds to its corresponding regulator, RhlR, and activates the pRhl promoter (figure 2, green). However, RhlR can potentially also bind other AHLs and then activate pRhl (Figure 2, 3OC12-HSL in red and 3OC6-HSL in light blue). This leads then to unwanted gene expression (crosstalk). 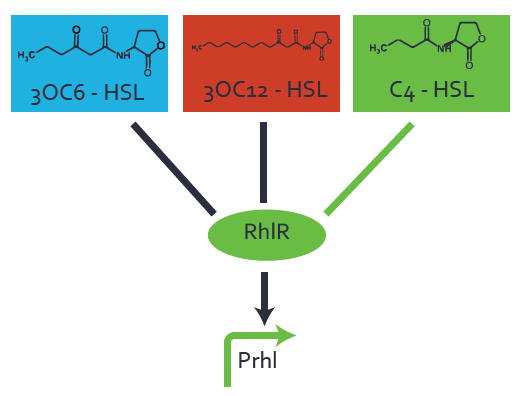 Figure 1 Overview of possible crosstalk of the RhlR/pRhl system with three different AHLs. Usually, C4-HSL binds to its corresponding regulator, RhlR, and activates the pRhl promoter (green). However, RhlR may also bind 3OC12-HSL (red) or 3OC6-HSL (light blue) and then unintentionally activate pRhl. Second Level crosstalk: other regulatory proteins, like LuxR and LasR, bind to their natural AHL substrate and activate the pRhl promoterIn the conventional system C4-HSL binds to its corresponding regulator, RhlR, and activates the pRhl promoter (Figure 2, green). However, pRhl can potentially be activate by other regulators (LuxR, LasR), binding their corresponding regulator (figure 2, 3OC6-HSL in light blue, 3OC12-HSL in red). This leads then to unwanted gene expression (crosstalk). 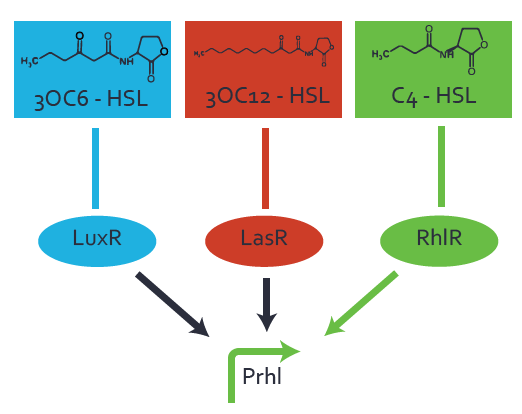 Figure 2 Overview of possible crosstalk of the RhlR/pRhl system with two additional regulators (LuxR and LasR). Usually, RhlR together with inducer C4-HSL activate their corresponding promoter pRhl (green). However, pRhl may also be activated by the LuxR regulator together with 3OC6-HSL (light blue) or by the LasR regulator together with 3OC12-HSL (red). Second order crosstalk: Combination of both cross-talk levelsThe second order crosstalk describes unintended activation of pRhl by a mixture of both the levels described above. The regulator and inducer are being different from RhlR and C4-HSL, respectively, and at the same time they do not belong to the same module. For example, the inducer 3OC6-HSL (light blue), usually binding to the regulator LuxR, could potentially interact with LasR regulator (red) and together activate pRhl (green). This kind of crosstalk is explained in Figure 3. 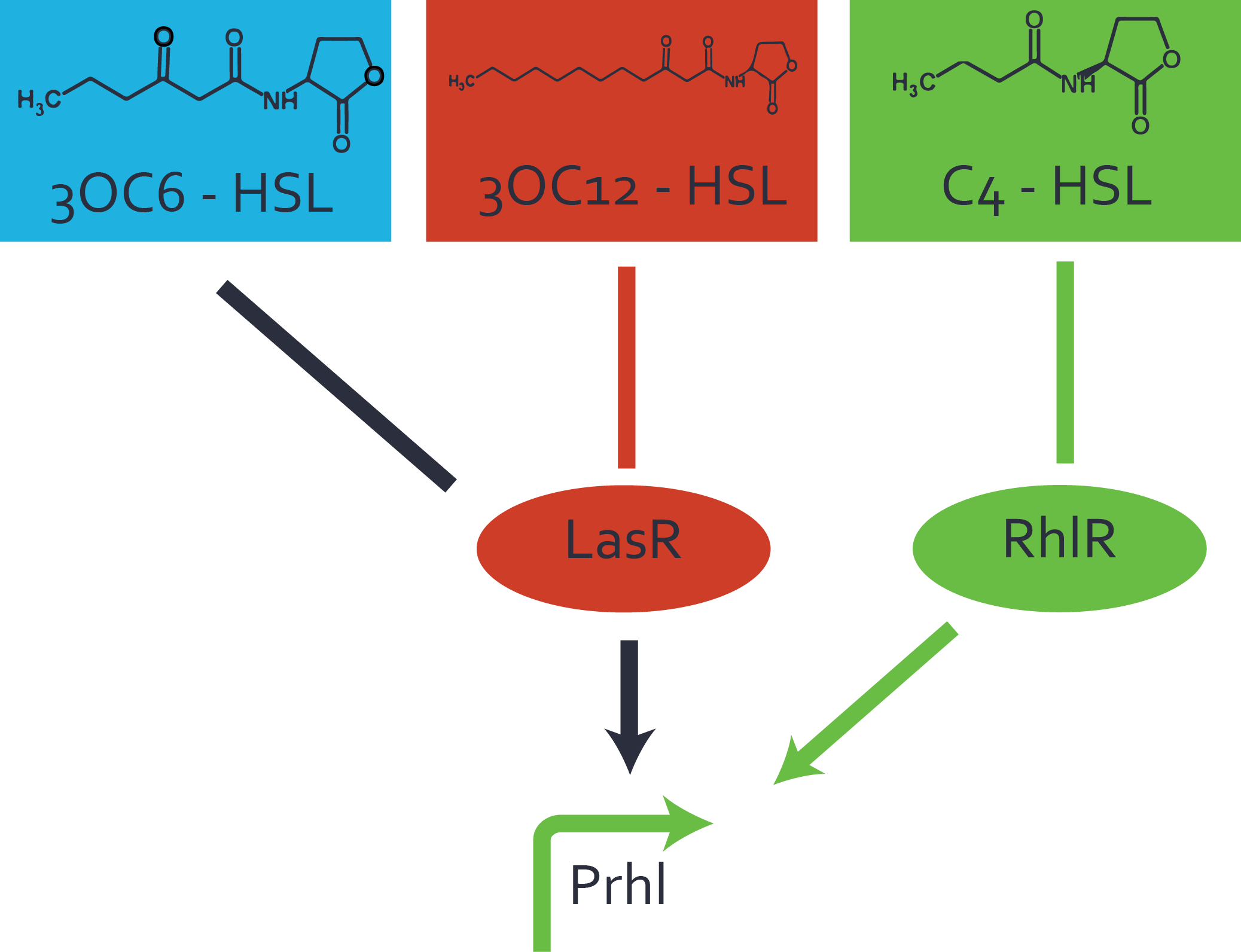 Figure 3 Overview of possible crosstalk of the pRhl promoter with both the regulator and inducer being unrelated to the promoter and each other. Usually, RhlR together with inducer C4-HSL activate their corresponding promoter pRhl (green). However, pRhl may also be activated by another regulator together with an unrelated inducer. For example, the inducer 3OC6-HSL (light blue) may interact with the LasR regulator (red) and together activate pRhl (green). Results
Modeling crosstalkEach experimental data set was fitted to an Hill function using the Least Absolute Residual method. The fitting of the graphs was performed using the following equation :
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Antiquity |
This review comes from the old result system and indicates that this part did not work in some test. |
UNIQe9fb607784d5bf13-partinfo-00000003-QINU