Part:BBa_K1033926
asPink, pink chromoprotein (incl RBS, J23110)
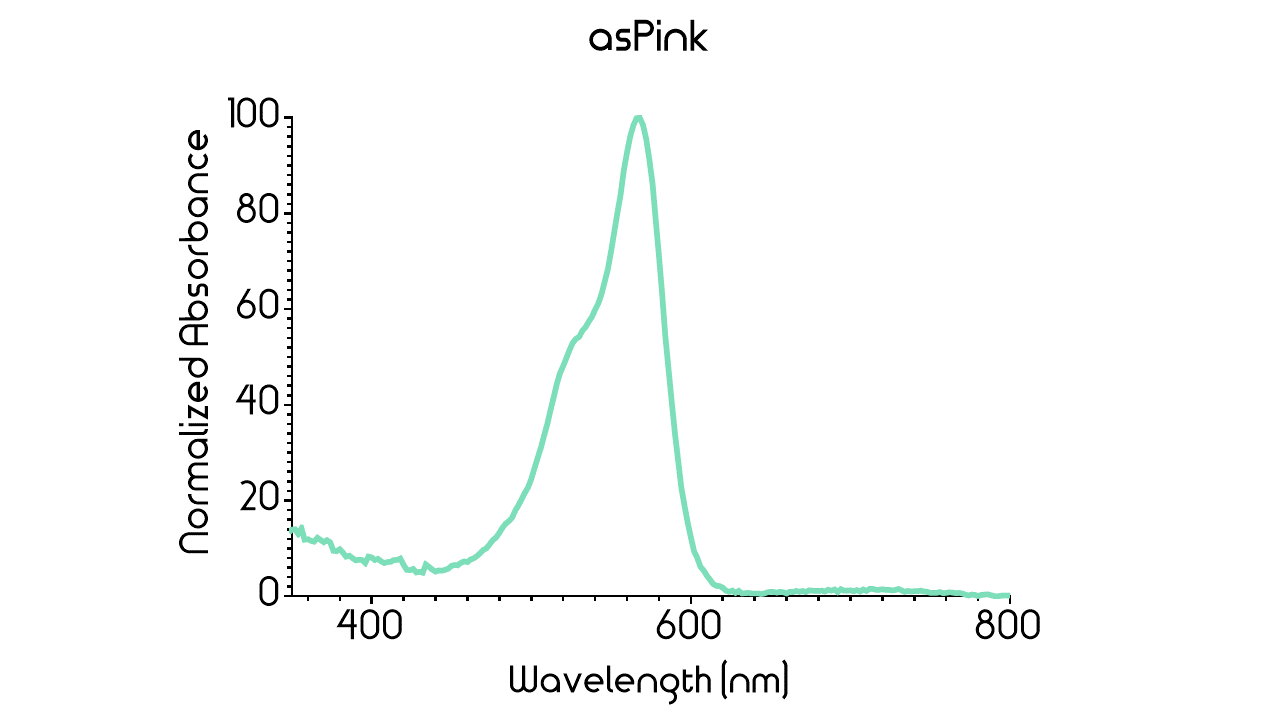
This chromoprotein from the coral Anemonia sulcata, asPink (also known as asCP or asFP595), naturally exhibits strong color when expressed. The protein has an absorption maximum at 572 nm giving it a pink/purple color visible to the naked eye. The strong color is readily observed in both LB or on agar plates after less than 24 hours of incubation. The protein asPink has significant sequence homologies with proteins in the GFP family.
Characterisation
The iGEM team of Rotterdam 2019 characterized this part more as part of the bronze criteria. [1]An addition to the characterization tests is to see whether there will be a change in the absorbance spectrum when the proteins are suspended in acidic or basic environments.
First, full-spectrum analysis with a Synergy™ LX Multi-Mode Microplate Reader (300-1000 nm) was performed to what iGEM Upsala 2013 has done, which is 300-800 nm (Figure 1-3).
The second characterization experiment (figure 4 and 5) was to test the effect of pH: 0.3, 4.3, 7.3, 10.3 and 14. The tests have been performed twice in different wells of a 96-wells plate with a Synergy™ LX Multi-Mode Microplate Reader, 100 uL of each chromoprotein sample was mixed with 100 uL of different pH-samples. Data of the Microplate Reader: https://2019.igem.org/wiki/images/1/18/T--Rotterdam_HR--excelfilepH.xlsx
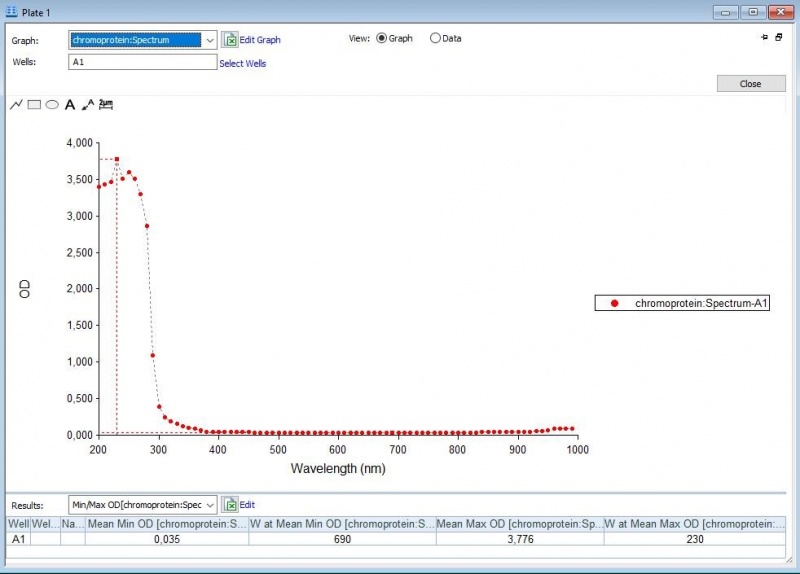
Figure 1: Absorbance spectrum of saline.
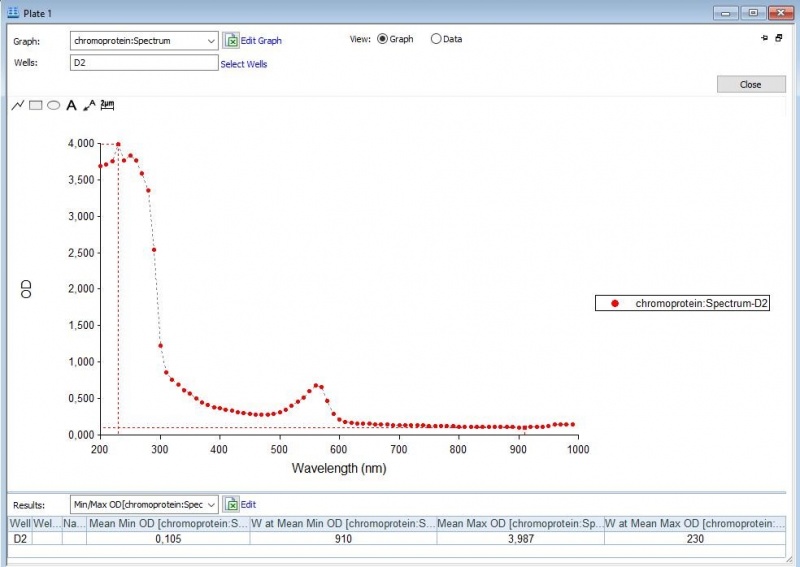
Figure 2: Full spectrum analysis of asPink.
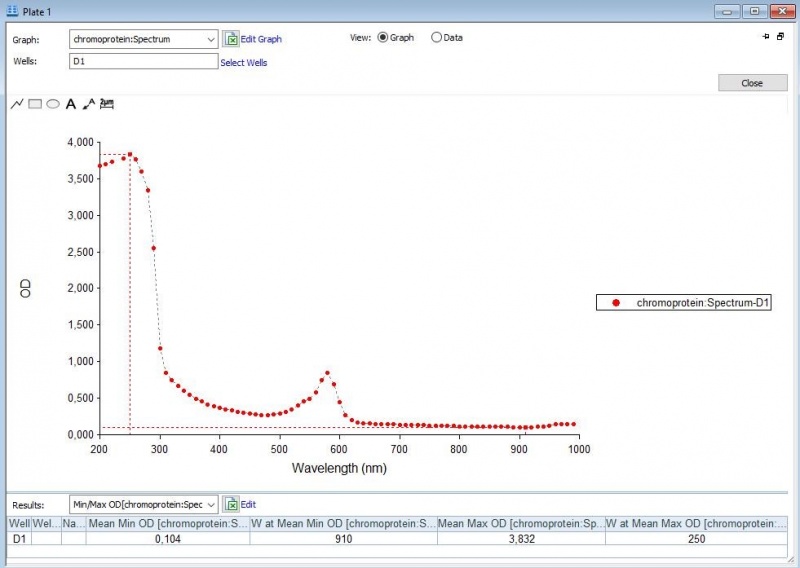
Figure 3: Duplicate of the full spectrum analysis of asPink.
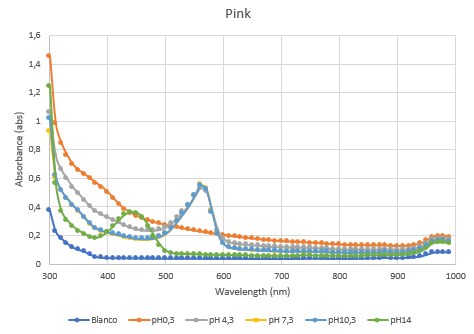
Figure 4: Full spectrum pH-analysis of asPink.
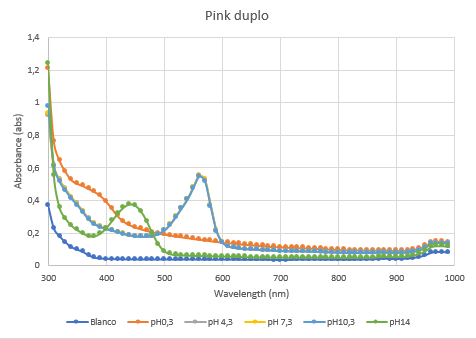
Figure 5: Duplicate of the full spectrum pH-analysis of asPink.
Usage and Biology
This part is useful as a reporter.
iGEM2013 Uppsala: Expression of asPink in E. coli DH5alpha by promoter J23110 from medium copy plasmid pSB3K3 (left) or high copy plasmid pSB1K3 (right).
Contribution
Group: Linkoping_Sweden iGEM 2021
Author: Ewelina Bladh
Summary:
In this contribution, we recorded color development in colonies of E.coli cells of strain XL1. In addition to studying the color development, we confirmed asPink's absorbance maximum wavelength. This also show the reproducibility of previous results.
Color Development
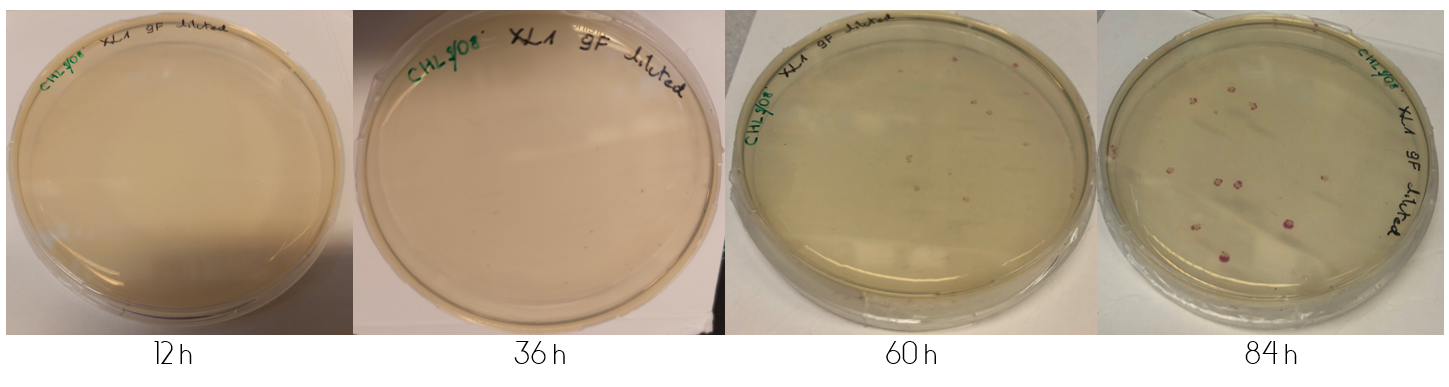
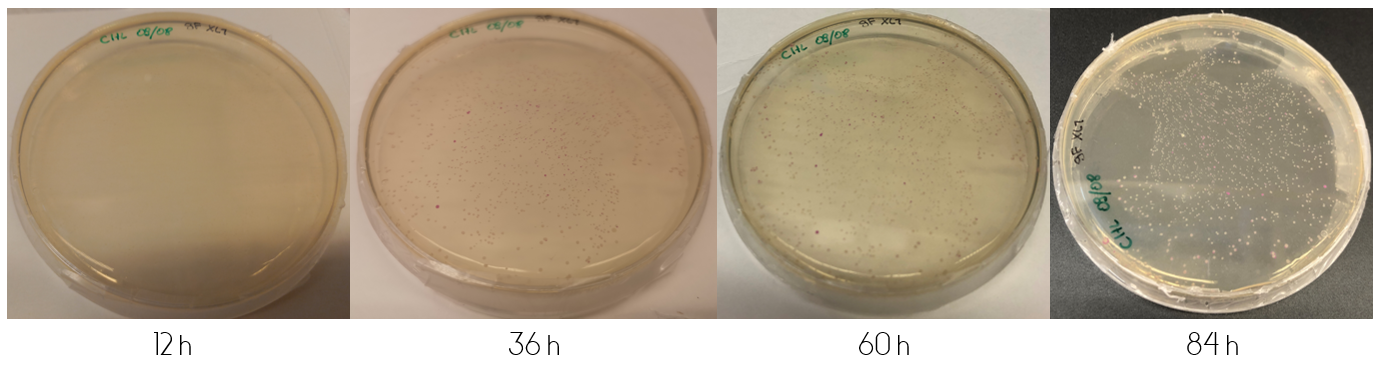
In order to determine the progression of color development in colonies, E.coli cells (XL1) were plated onto LB-Miller agar plates containing a concentration of 25 ug/mL chloramphenicol. The cells were plated in two ways after transformation. The first by plating 100 µL immediately from the liquid culture. The second by first centrifuging the culture, discarding 90% of the supernatant and resuspending the cell pellet in the remaining 10%, followed by plating 100 µL of the resuspension. This results in what is from now on referred to as the diluted and concentrated plate, respectively.
These plates were incubated in 37°C for the following four days, where they were checked upon each day. Figure 1, displayed below, shows the diluted and concentrated plates during this four day study. The illustration of the diluted plate shows that after 12 hours, no color can be seen to the naked eye. This changes over the course of the next 24 hours, where at 36 hours the colonies are clearly visible for the concentrated plate. The colonies on the diluted plate do not clearly display any color until 60 hours have passed. The color intensity continually increases after the first appearance of colored colonies.
Absorbance and Fluorescence
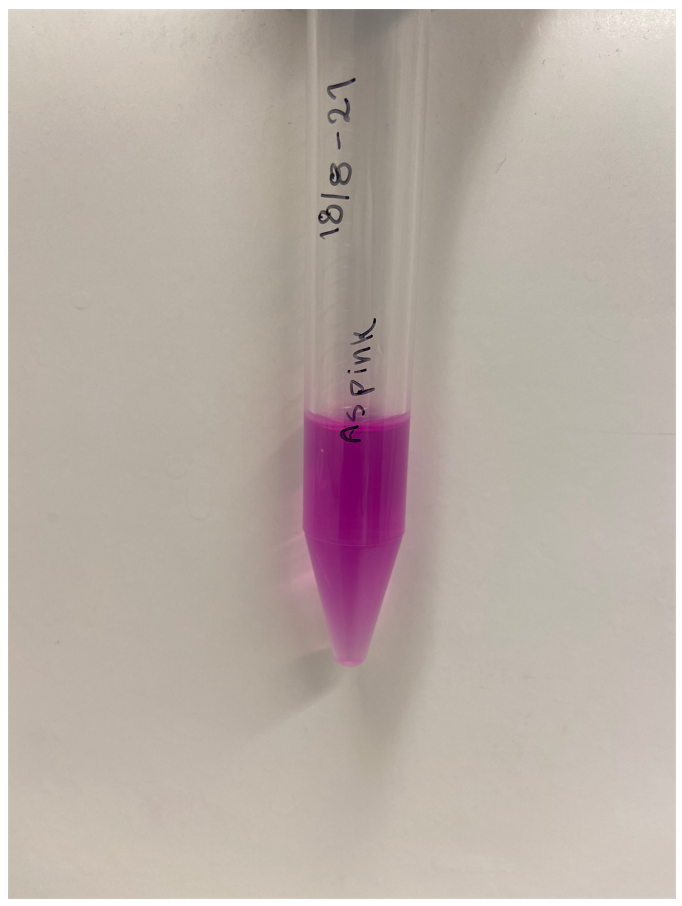
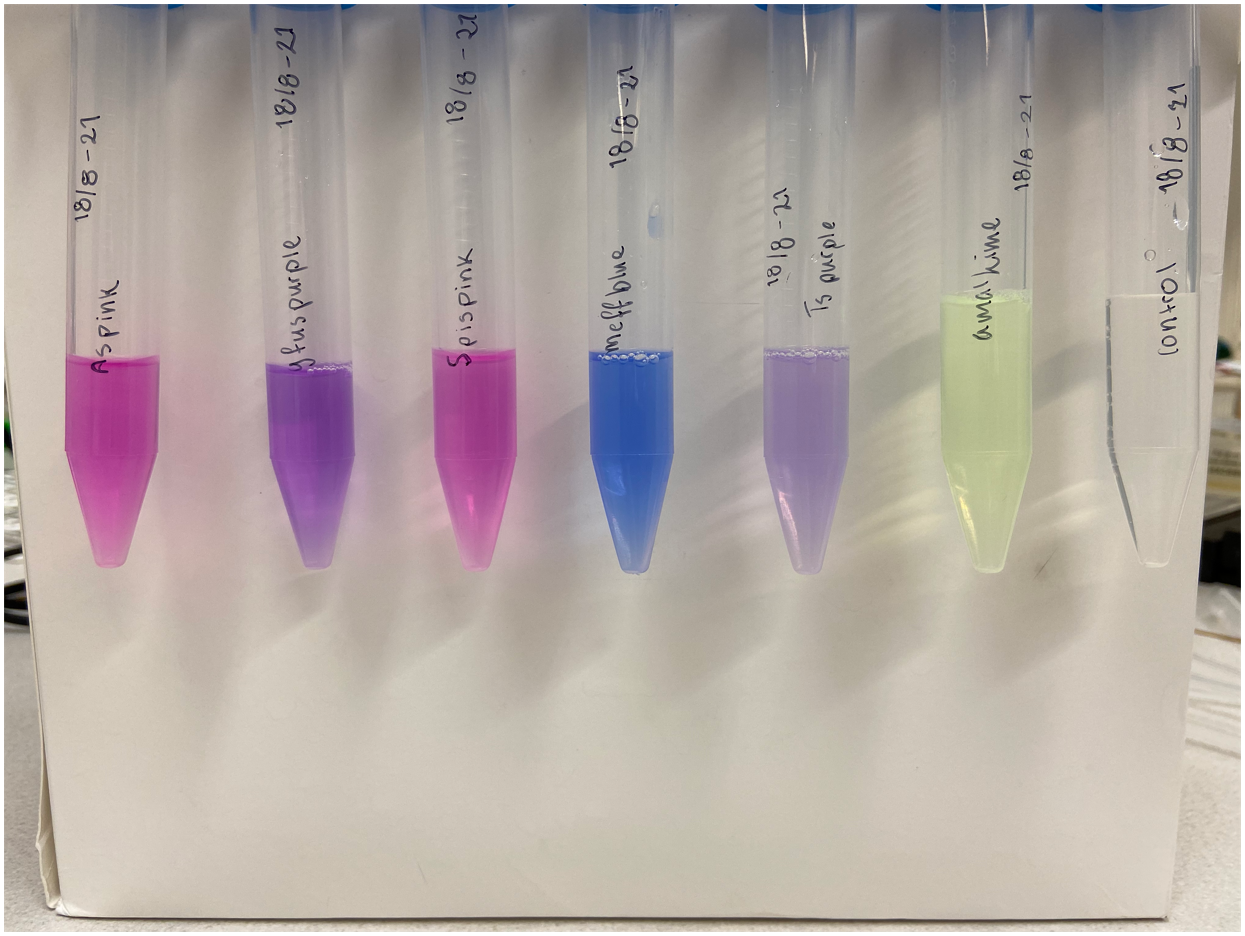
Single colonies displaying a pink color were picked from the diluted plates to create liquid cultures. The liquid cultures consist of 5 mL LB-Miller media and a concentration of 25 µg/mL chloramphenicol. The liquid cultures were incubated at 37°C and 200 rpm for the next two days to ensure protein expression. After incubation, the liquid cultures were centrifuged until a pellet formed. The supernatant was discarded, and the remaining pellet was placed in a -20°C freezer. Cell lysis was done using both water and sonication. The frozen pellet was thawed and 5 mL autoclaved dH2O was added, followed by vortex treatment to resuspend the pellet. Sonication on ice was the next step taken to lyse any cells that did not lyse upon the addition of water. The amplitude of the sonicator was set to 30%, 30 seconds pulsing followed by 30 seconds rest for a total of 2 minutes. Following sonication, the cultures were centrifuged until a pellet formed whereupon the supernatant was transferred to a clean 15 mL Falcon tube and the pellet was discarded. The supernatant of asPink can be see to the left in Figure 2. Simultaneous experiments with other chromoproteins was also made, their supernatant can be seen with asPink to the right in Figure 2. The following chromoproteins were also assessed in the same way as asPink: tsPurple (BBa_K1033903), amajLime (BBa_K1033914), spisPink (BBa_K1033923), gfasPurple (BBa_K1033917), and meffBlue (BBa_K1033900).
As a control, plates were also made with untransformed XL1-cells. A colony was picked from the diluted plate to start a liquid culture, followed by lysis like the cells transformed with asPink. Treatment of control and experimental cells was identical apart from the control culture not being exposed to antibiotics. The supernatant of the control can be seen to the right in Figure 2 along with other chromoproteins.
In order to measure the absorbance, 100 µL supernatant of asPink and 100 µL supernatant of the control were pipetted into a 96-well plate and measurements were made with BMG Clariostar plate reader. Measurements of absorbance were taken every 2 nm in the range 300 nm to 850 nm. This interval was chosen to include the entire visual spectra including margins. The data yielded from the measurements were subsequently baselined by subtracting the control's absorbance values from asPink's absorbance values followed by normalization. The resulting graph for asPink's absorbance can be seen in Figure 3 below. The absorbance maximum of asPink proved to occur at approximately 568 nm. This result appears to be consistent with the results reported by the team of Rotterdam 2019 (see above).
When examining the supernatant extracted from asPink-expressing cells on a UV-table, no fluorescence was detected. The chromoprotein amajLime (BBa_K1033914) was studied at the same time, functioning as a positive control, and the lysate from the control functioned as a negative control.
Source
The protein was first extracted and characterized by Lukyanov et. al. 2000 under the name asFP595 (GenBank: AAG02385.1). This version is codon optimized for E coli by Genscript.
References
[http://www.jbc.org/content/275/34/25879.short]Lukyanov, Konstantin A., et al. "Natural animal coloration can be determined by a nonfluorescent green fluorescent protein homolog." Journal of Biological Chemistry 275.34 (2000): 25879-25882.
[http://www.jbc.org/content/280/4/2401.short]Wilmann, Pascal G., et al. "Variations on the GFP Chromophore - A Polypeptide Fragmentation Within The Chromophore Revealed In The 2.1-Å Crystal Structure Of A Nonfluorescent Chromoprotein From Anemonia Sulcata." Journal of Biological Chemistry 280.4 (2005): 2401-2404.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
| None |