Part:BBa_K2934004
AmyE - Glucose Oxidase-Histag for Bacillus subtilis
This part comprises of the glucose oxidase (GOx) gene (BBa_K2934000) connected to the secretory signal peptide AmyE (from the alpha-amylase gene) (BBa_K2273023), using a short nine amino-acids linker (BBa_K2934005). This part was constructed in our lab with the commercial plasmid pBE-S (TaKaRa) as a backbone.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 156
Illegal BsaI site found at 487
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 433
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 1258
Glucose Oxidase Activity Assay
Glucose oxidase (GOx) catalyzes the oxidation of glucose to D-gluconic-lactone and hydrogen peroxide. Therefore, a precise method to determine the amount of hydrogen peroxide found in the solution could indicate the activity of the glucose oxidase. In this experiment, we used the assistance of another commercial enzyme- horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and 2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) (ABTS). Using hydrogen peroxide, the HRP catalyzes the oxidation of reduced ABTS, which is colorless, to oxidized ABTS, which is turquoise. While using excess ABTS and HRP, the absorbance of 416 nm light could indicate to us the amount of hydrogen peroxide created by the glucose oxidase, and therefore - the glucose oxidase activity.
β-D-Glucose + O2 + H2O → D-Glucono-1,5–Lactone + H2O2 (GOx)
H2O2 + 2ABTS (reduced) → 2ABTS(oxidized)+ 1⁄2O2 + H2 (HRP)
To verify that the absorbance-activity relation remains linear under the experiment's conditions, we performed the experiment using commercial GOx with increasing activity, measured the 416 nm light absorbance and plotted a graph to demonstrate that relation. Fortunately, we have proved the absorbance-activity relation linearity under the experiment's conditions (Figure 1).
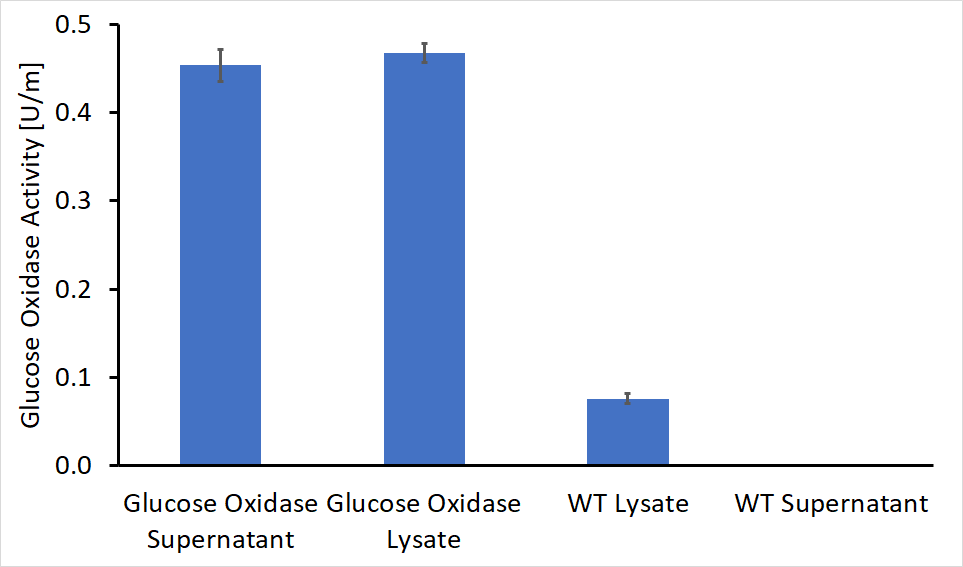
After the cloning process had been completed, we performed the activity test on both the supernatant and the lysate of genetically engineered bacteria as well as WT bacteria as control. The first colony tested contained a gene for glucose oxidase and the AmyE signal peptide. The absorbance detected in the recombinant Bacteria was significantly higher, in both supernatant and lysate (Figure 2). The evaluated activity of glucose oxidase is 0.46U/ml in the bacterial supernatant and 0.45U/ml in the lysate solution.
Secretion Assay By SDS-PAGE
To ensure enzyme expression and secretion from our engineered bacteria, we performed SDS-PAGE. To determine whether the enzyme was secreted or expressed within the bacteria, we compared both lysate and supernatant samples of the engineered bacteria, as well as wild type bacteria samples. Methods are listed at the bottom of the page.
As seen in figure 3 above, there is a faint band in the area of the standard GOx, but we couldn’t get any concrete conclusion since we had a problem with our WT sample preventing us from running them in the gel. In addition, there is a strong band in the range of 40-48 kDa.
To conclude, the SDS-PAGE gave us a vague picture about the success of the protein expression and secretion since we couldn’t compare them to our WT samples.
Methods
This vector was constructed by Gibson assembly, with the pBE-S commercial plasmid (TaKaRa) that served as a backbone, and eventually transformed into Bacillus subtilis (RIK1285).
The bacteria were cultured over-night at 37°C in a shaking incubator (250 rpm), followed by 1:100 dilution. The diluted culture was incubated for another few hours while monitoring the culture turbidity by measuring the O.D600.
When the culture has reached the logarithmic growth phase, the bacterial extracellular and intracellular proteins were separated, after collecting the supernatant and the pellet (followed by lysis, using sonicator).
For further reading of our full protocols (cloning, enzymatic assays and enzymatic assay under different pH levels) look at our wiki protocols page.
| None |