Part:BBa_K639003
rrnB P1-LacI-pLac-mCherry plausible stress sensor
The stringent response in bacteria is caused by amino-acid starvation, fatty acid limitation, iron limitation, heat shock and other stress conditions. As a response under these conditions, in vitro studies have suggested that the alarmone guanosine tetraphosphate (ppGpp) increase to modulate transcription to promote survival. The increase in ppGpp levels causes a redirection of transcription so that genes important for survival are favoured at the expense of those required for growth and proliferation [1].
So, could we use ppGpp as signal molecule to find out when cells are stressed?
The solution
Our system will be based on a promoter that is important for regulating growth and proliferation. At the moment we are trying to use the rrnB-p1 promoter, which has been shown in earlier studies to be highly regulated by the ppGpp molecule. Hopefully the promoter will be down regulated enough by increased levels of ppGpp to turn the repressor lacI it controls completely off. The lacI represses a second promoter pLac that induces the production of red fluorescent protein (mCherry) and turns the cells red.
An overview of the construct is seen in the picture below.
The stress sensor is made from these biobricks.
| Biobrick | Part number |
|---|---|
| rrnB P1 | BBa_K639002 |
| LacI with RBS | BBa_J24679 |
| Terminator | BBa_B0015 |
| pLac | BBa_R0011 |
| mCherry with RBS and terminator | BBa_J06702 |
The promotor is a variant of BBa_K112118, that we have made ourselves using PCR, and the PCR product was directly used as insert and connected with the rest of the construct. The final construct was cut with BstBI to verify that the rrnB P1 had been insertet.
The stress sensor has a total length of 2653 bp. It was originally constructed and tested in the pSB1A2 plasmid but transfered to the pSB1C3 plasmid prior to shipping to the registry.
We have put the stress sensor through several tests.
Sequencing
Sequencing confirmed the sequence of the BioBrick.
Stress sensor characterization
To test our [http://2011.igem.org/Team:NTNU_Trondheim/rrnB+LacI+pLac+mCherry stress sensor], pre-cultures of the construct with, and without the rrnB P1 promoter were grown ON, pelleted and resuspended in M9 medium. The cultures were inoculated 1% in LB, LB+IPTG, M9 and M9+IPTG. IPTG will induce pLac, by inhibiting lacI's inhibition. M9 is a minimal medium, lacking amino-acids. M9 was used because ppGpp is mainly produced in the stringent response during amino-acid starvation.
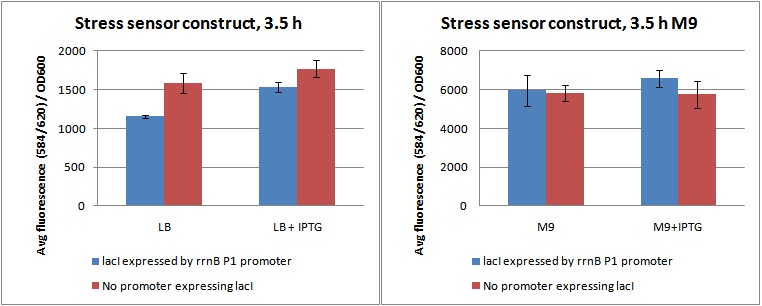
Cultures were grown in flasks in a shaking incubator at 37C for 3,5 hours, and 3 parallels of 100 µL from each flask were sampled to a 96 well fluorometer plate. Fluorescence was measured at ex: 584 em: 620, as well as OD600. Data from the experiment is shown in figures below, as fluorescence divided by OD600.
The figures shows fluorescence at ex: 584 em: 620 diveded by OD600 for cultures grown 3,5 hour in LB and M9 with and without IPTG.
As shown in the figures above, the cells do produce a substantial amount of mCherry even when they are not stressed (LB, and LB+IPTG). This is possibly due to the rrnB P1 promoter not being strong enough to produce sufficient amounts of lacI to inhibit pLac's expression of mCherry.
Looking at the difference between samples with (+P) and without promoter (-P) in LB and LB+IPTG, it is clear that the rrnB P1 promoter does produce lacI. The fluorescence/OD value of +P in LB is lower than -P in LB, indicating production of lacI. When it is induced by IPTG, inhibiting lacI, the level rises to approximately the same as -P, indicating a nullifying effect of the lacI produced.
The fluorescence / OD of the M9 samples is much higher than the LB. This was due to the slow growth rate in M9. The OD600 was unchanged from the inital OD in all M9 parallels after 3,5 hours (data not shown). What is interesting here, is that the difference between +P and -P seems to be gone. This indicates that the rrnB P1 promoter does indeed produce less lacI when the cells are grown in M9, possibly due to amino-acid starvation and ppGpp shutting it down. As the data was quite variable, this is hard to say for sure.
In future work with this construct, one could try to increase rrnB P1's strength by maybe tweaking the UTR, or try to lower pLac's strength, to give less leakage. A combination of both strategies would probably give the best result.
Flow Cytometry
Several measurements were performed using a Flow Cytometer, this allowed us to measure the flouresence from single cells. The resulting plots shows the distributions of the flouresence for the red end of the spectrum (i.e around the wavelength corresponding to mCherry).
First of all there is a remarkable difference between the distributions for M9 and LB. The distribution for LB is relatively sharp compared to M9 which means there is little difference in the level of light emitted from the individual cells. The distribution for M9 is much broader showing a greater variance and it is also shifted to the right. A distribution shifted to the right means stronger emission of red light.
Reference:
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0966842X05000788 1 Magnusson, L. U., A. Farewell, et al. (2005). "ppGpp: a global regulator in Escherichia coli." Trends Microbiol 13(5): 236-242
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 1666
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Functional Parameters
Functional Parameters: Austin_UTexas
Burden Imposed by this Part:

Burden is the percent reduction in the growth rate of E. coli cells transformed with a plasmid containing this BioBrick (± values are 95% confidence limits). This part exhibited a significant burden. Users should be aware that BioBricks with a burden of >20-30% may be susceptible to mutating to become less functional or nonfunctional as an evolutionary consequence of this fitness cost. This risk increases as they used for more bacterial cell divisions or in larger cultures. Users should be especially careful when combining multiple burdensome parts, as plasmids with a total burden of >40% are expected to mutate so quickly that they become unclonable. Refer to any one of the BBa_K3174002 - BBa_K3174007 pages for more information on the methods and other conclusions from a large-scale measurement project conducted by the 2019 Austin_UTexas team.
This functional parameter was added by the 2020 Austin_UTexas team.
| None |