Part:BBa_K2446037
ZF_GAl4_KRAB
This part is one of our mammalian synthetic transcription factors (SynTFs) based on Gal4 DNA binding domain [1]. Gal4-KRAB (or TF-KRAB-1 in our project) containing three core domains from N-terminal to C-terminal: GAL4 DNA binding domain, nuclear location sequence and KRAB transcription regulating domain [2].And a (G4S) linker was added between DBD and NLS for providing region flexibility [3]. GAL4DBD enable binding to specific DNA sequences, so that we can use Gal4-KRAB as a specific transcription factors to repress the expression of our mammalian synthetic promoter Sv40-UAS (BBa_K2446036).
The information of other SynTF-SynPros is showed in the table below.
| SynTFs | SynPros |
|---|---|
| Gal4-KRAB(TF-KRAB-1) BBa_K2446037 | Sv40-UAS(Sv40-UAS) BBa_K2446036 |
| ZF_PIP_KRAB(TF-KRAB-2) BBa_K2446045 | SV40_2/4/8_PIP BBa_K2446033/BBa_K2446034/BBa_K2446035 |
| ZF_21-16KRAB(TF-KRAB-3) BBa_K2446039 | SV40_8_ZF_21-16 BBa_K2446030 |
| ZF_42-10_KRAB(TF-KRAB-4) BBa_K2446040 | SV40_8_ZF_42-10 BBa_K2446025 |
| ZF_43-8_KRAB(TF-KRAB-5) BBa_K2446041 | SV40_2/4/8_ZF_43-8 BBa_K2446026/BBa_K2446027/BBa_K2446028 |
| ZF_54-8_KRAB(TF-KRAB-6) BBa_K2446042 | SV40_8_ZF_54-8 BBa_K2446029 |
| ZFHD1_KRAB(TF-KRAB-7) BBa_K2446043 | SV40_4_ZFHD1 BBa_K2446032 |
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal PstI site found at 256
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal PstI site found at 256
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal PstI site found at 256
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal PstI site found at 256
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 41
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 176 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Experiments
SynTF-SynPro Pairs
Figure 1: the testing circuits of GAL4-KRAB& Sv40 UAS pair
To make sure the SynTF-SynPro pairs work in mammalian cells, we use the circuits above to test if the Gal4-KRAB can repress the expression of Sv40-UAS indeed. Gal4-KRAB is linked to the C terminal of EGFP by the link of P2A. And mCherry expressions is controlled by corresponding SynPro (Sv40 UAS). These circuits are both inserted in to the mammalian expression vactor pML2. We transfect pML2-Sv40-UAS into Hela cells and measure the fluorescence intensity of mCherry by flow cytometer to get the basic expression intensity of Sv40-UAS. We also co-transfect the pML2-GAL4-KRAB with pML2-Sv40-UAS into Hela cells at the same time. Then measure the fluorescence intensity of mCherry again to get the expression intensity of Sv40-UAS influenced by GAL4-KRAB. The results of the experiment is showed below. The SynTF GAL4 can silence the expression of the SynPro Sv40-UAS in 25 folds.
Figure 2:The results of GAL4-KRAB&SV40 testing: (A) The red points is the cells before co-transfecting GAL4-KRAB and the blue points is the cells after co-transfecting GAL4-KRAB. It’s easy to see that the red points depart from the diagonal and higher than the blue pints. So the expression of mCherry silenced after the expression of GAL4-KRAB;(B) The red area is the fluorescence intensity of mCherry before co-transfecting GAL4-KRAB and the blue area is the intensity after co-transfecting GAL4-KRAB.(C) The statistical result of all of the SynTFs-SynPros pairs: GAL4-KRAB can silence the expression intensity of Sv40-UAS in 25 folds
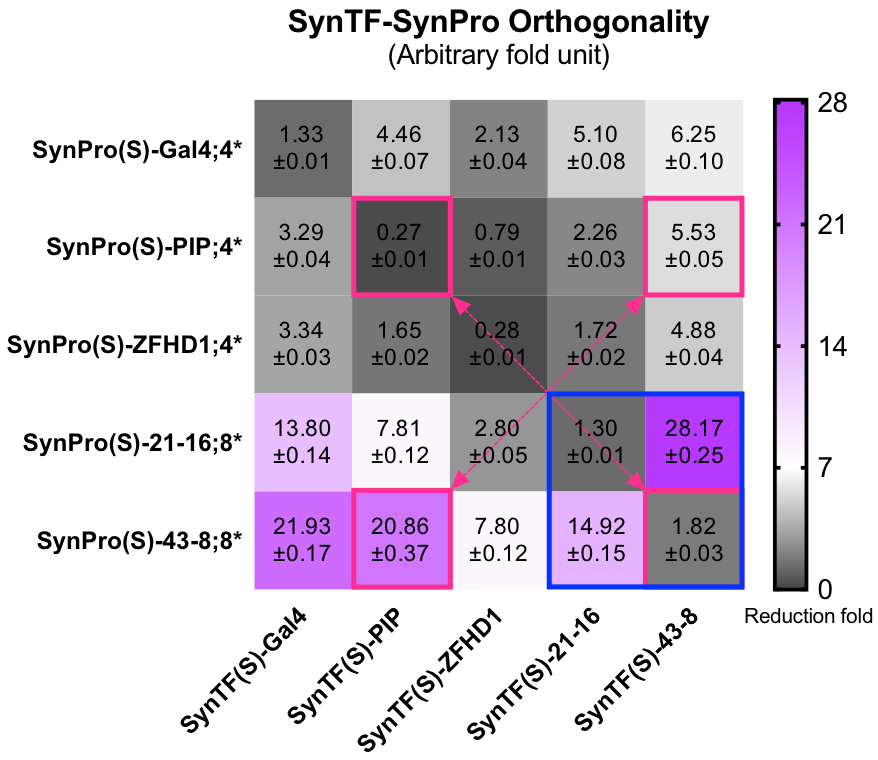
SynTF-SynPro Orthogonality
To construct our [http://2017.igem.org/Team:Fudan/Model/GTN| Strip module], more than one SynTF-SynPro pairs would be applied. Thus, the interaction between the pairs would influence or ruin our construction. We did massive orthogonality experiments to avoid that. We observed all of the 5 pairs were actually orthogonal, as you could see the grids on the diagonal were always the darkest. The three DBDs commonly used in previous works were didn’t let us down. However, the expression level of these RE loaded SynPros were relative low compared to SynPro(S)-ZF serials. As the blue rectangle in the lower right corner of the orthogonality may showed the SynPro(S)-ZF has high basic expression with unpaired SynTFs, but could be silenced to the similar fold of commonly used DBDs corresponding SynPros. The SynPro(S)-ZF was likely won’t be target by other unpaired DBD, hence the purple appeared on the bottom rows.
Figure 3: the SynTF-SynPro pairs’ Orthogonality. Grids in blue rectangle showed that SynTF-SynPro pairs constructed by using SynZF as DBD with well orthogonality. Grids in pink rectangles replaced our favorite SynTF-SynPro pairs. At least 20,000 cells were analyzed for each condition in both histogram and each grid in heat map. Data are recorded by FACS at 24h after cotransfecting.
References
[1] Morsut, L. et al. Engineering Customized Cell Sensing and Response Behaviors Using Synthetic Notch Receptors. Cell 164, 780--791 (2016).
[2] Witzgall, R., O'Leary, E., Leaf, A., Onaldi, D. & Bonventre, J. V. The Krüppel-associated box-A (KRAB-A) domain of zinc finger proteins mediates transcriptional repression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 91, 4514-4518 (1994).
[3] Chen, X., Zaro, J. L. & Shen, W.-C. Fusion protein linkers: property, design and functionality. Advanced drug delivery reviews 65, 1357-1369 (2013).
Contribution
Team: CSU-CHINA 2023
pGL4.35-3XHA-9XGAL4UAS-KRAB-NLS
The pGL4.35-3×HA-9×GAL4UAS-KRAB-NLS plasmid, which could express GAL4-KRAB, was used for Luciferase detection experiment. GAL4 is a protein that can find and bind UAS (upstream activation sequence). KRAB is a transcription factor that represses downstream gene expression when combined with GAL4.
pGL4.35-3×HA-9×GAL4UAS-KRAB-NLS
The pGL4.35-3×HA-9×GAL4UAS-KRAB-NLS plasmid was obtained through homologous recombination of the KRAB homologous recombination insert (BBa_K4585003) with pGL4.35-3×HA-9×GAL4UAS-KRAB-NLS linearized vector (BBa_K4585008). The homologous recombination plasmid product was identified as the target product by sequencing and enzyme cutting and agarose gel electrophoresis.
1 Pattern Diagram

Fig.1 The model diagram of pGL4.35-3×HA-9×GAL4UAS-KRAB-NLS
2 Experiment
2.1 Method
The pGL4.35-3×HA-9×GAL4UAS-KRAB-NLS plasmid could express GAL4-KRAB, and GAL4-KRAB could bind 9×UAS and inhibit downstream gene expression, therefore GAL4-KRAB could inhibit GnRH expression. Considering that the plasmid itself contains a 9×UAS sequence, GAL4-KRAB can also suppress its own expression.
2.2 Results
HEK 293T cells were transiently transfected with GAL-VP64 and GAL-KRAB plasmids, and an appropriate amount of Luciferase plasmids were transfected to simulate GnRH. The experiment showed that the GAL-VP64 plasmid could initiate the expression of GAL4-KRAB and Luciferase.

Fig 2. Bioluminescence intensity when GAL4-VP64=GAL4-KRAB=400 ng
3 Caution
After sequencing and ensuring the sequence was correct, we applied it to the experiments. Store at 4℃.
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal EcoRI site found at 177
Illegal XbaI site found at 138
Illegal XbaI site found at 216
Illegal SpeI site found at 4980
Illegal PstI site found at 182
Illegal PstI site found at 1611 - 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal EcoRI site found at 177
Illegal SpeI site found at 4980
Illegal PstI site found at 182
Illegal PstI site found at 1611
Illegal NotI site found at 203 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal EcoRI site found at 177
Illegal BglII site found at 4743
Illegal XhoI site found at 210 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal EcoRI site found at 177
Illegal XbaI site found at 138
Illegal XbaI site found at 216
Illegal SpeI site found at 4980
Illegal PstI site found at 182
Illegal PstI site found at 1611 - 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal EcoRI site found at 177
Illegal XbaI site found at 138
Illegal XbaI site found at 216
Illegal SpeI site found at 4980
Illegal PstI site found at 182
Illegal PstI site found at 1611
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 721
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 2062
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 2347
Illegal AgeI site found at 274 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 3875
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 5613
Illegal SapI site found at 2792
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 1911
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 2121
| None |