Part:BBa_K3419003
Contents
Tricosanthin with Strong Promoter and TorA T
Usage and Biology
Note: All work on this part was done virtually through literature research due to COVID-19 restrictions.
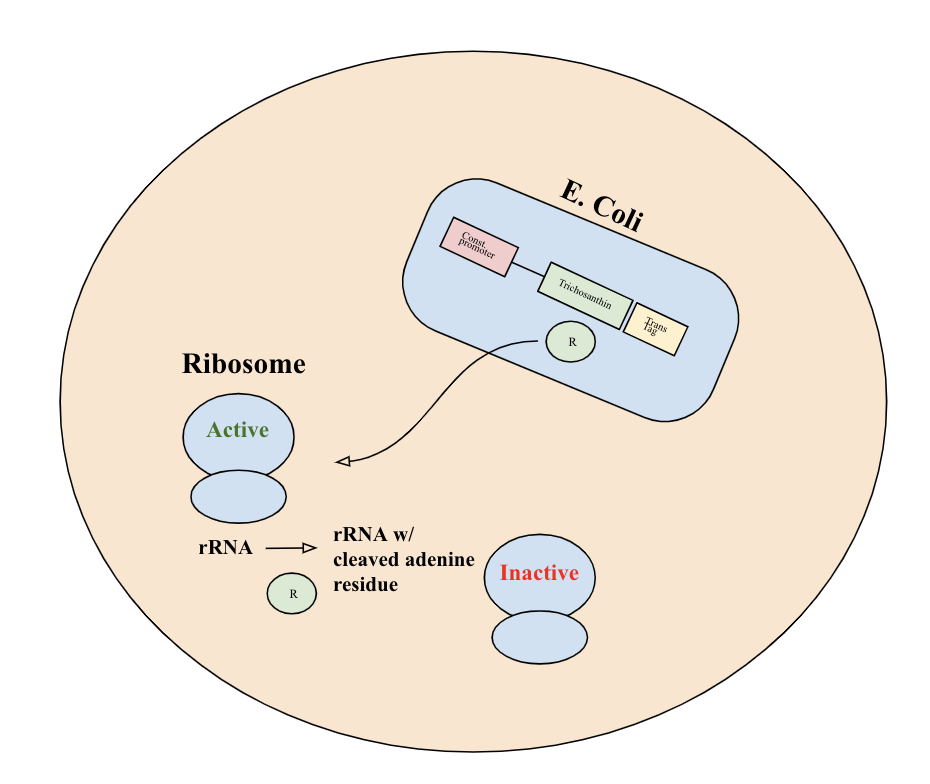
Trichosanthin is a protein derived from Trichosanthes kirilowii, also known as the Chinese cucumber. It has been used in Eastern traditional medicine as an abortifacient and also functions as an antitumor agent due to its inactivation effect on eukaryotic ribosomes [1]. Trichosanthin is used in our project as an anti-cancer therapeutic protein that selectively kills tumor cells while leaving our engineered prokaryotic E. coli unaffected. We were able to confirm that E. coli would be able to produce this therapeutic based on a literature search (SOURCE #: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/j.1399-3011.1992.tb01558.x). Thus, our bacteria would perform their intended function in our genetic circuit
Mechanism
Upon release into the cell, trichosanthin exhibits RNA N-glycosidase activity and depurinates the 28S rRNA of the 60S eukaryotic ribosomal subunit. This will achieve irreversible inactivation of eukaryotic ribosome activity and inhibit tumor cell function.
art Details
This BioBrick part consists of the trichosanthin coding gene (https://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P09989) with stop codon TGA. It is driven by a constitutive promoter (BBa_J23100), has a ribosome binding site (BBa_J61100), and a terminator (BBa_B0015). It also includes a translocase tag (BBa_K2960001), which facilitates the export of the protein from E. coli into the tumor cell.
Modeling
In MATLAB, we modeled the output of the Tricosanthin protein using the following differential equation, and we solved it using MATLAB’s ode45 function. The equation represents the production of Tricosanthin protein. The first term represents the basal expression under the constitutive promoter (BBa_J23100), while the second represents protein degradation.
The MATLAB scripts corresponding to the Tricosanthin modeling can be downloaded here:
File:ModelingCodeCornelliGEM2020.zip
| Variable | Parameter | Value | Source |
|---|---|---|---|
| [Trich] | Concentration of Tricosanthin | -- | -- |
| basT | Basal transcription rate | 0.387 μM/sec | [3] |
| dC | degradation rate of Tricosanthin | 0.000385 sec-1 | [4] |
References:
[1] Li, M. X., Yeung, H. W., Pan, L. P., & Chan, S. I. (1991). Trichosanthin, a potent HIV-1 inhibitor, can cleave supercoiled DNA in vitro. Nucleic acids research, 19(22), 6309–6312. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/19.22.6309
[2] Li, J., Li, H., Zhang, Z., Wang, N., & Zhang, Y. (2016). The anti-cancerous activity of recombinant trichosanthin on prostate cancer cell PC3. Biological research, 49(1), 21. https://www.childrenshospital.org/research/labs/zetter-research-laboratory/tumor-metastasis-research
[3] Yildirim, Necmettin, and Michael C Mackey. “Feedback regulation in the lactose operon: a mathematical modeling study and comparison with experimental data.” Biophysical journal vol. 84,5 (2003): 2841-51. doi:10.1016/S0006-3495(03)70013-7
[4] Rust, Aleksander et al. “The Use of Plant-Derived Ribosome Inactivating Proteins in Immunotoxin Development: Past, Present and Future Generations.” Toxins vol. 9,11 344. 27 Oct. 2017, doi:10.3390/toxins9110344
| None |

