Part:BBa_K1499004
Cellulose binding domains with streptavidin domain generator
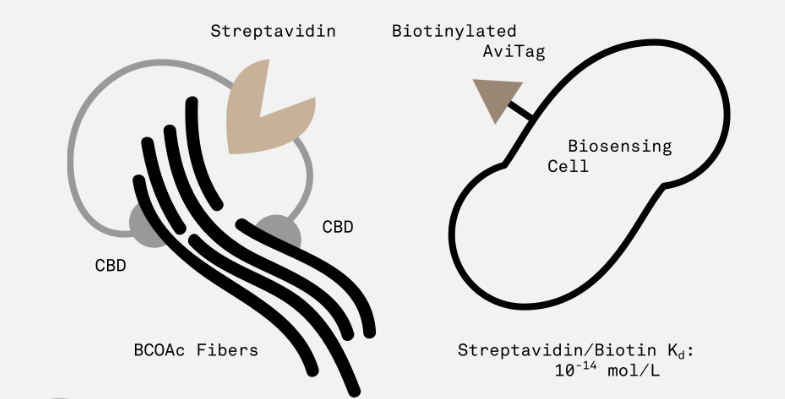
This part encodes a protein with two cellulose-binding domains on either end joined by a streptavidin domain.
Usage and Biology
The idea behind this part is that each domain binds to a single cellulose fiber, thus providing a way to cross-link and strengthen cellulose polymers. In addition, the streptavidin domain allows for the modular addition of sensor cells with a biotinylated AviTag peptide (expressed on the surface of the cell by appending it to outer membrane protein OmpA).
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 703
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 304
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI.rc site found at 651
Characterization
Verification of Part
The part was sequence verified before submission to the registry with two reads using VF2 and VR.
Results
We plan to assay the functionality of this part using a GFP construct inside a cell with the AviTag/OmpA surface complex. We will purify and apply our CBD/Streptavidin fusion protein to a cellulosic surface, followed by the above transformed cells, and attempt to wash off the cells using an isotonic solution. If the level of fluorescence does not change, we can assume our system has been successful.
The 2016 Stanford-Brown iGEM Team purified this linker protein and used it to create a BioDevice. Used in tandem with a biotinylated fluorophore, this CBD/Streptavidin fusion protein served as a linker between cellulose paper and the fluorophore-quencher biosensor described here: http://2016.igem.org/Team:Stanford-Brown/SB16_BioSensor_FQsensor.
INSA Lyon 2016 Experiments on this partCharacterization
1. Purification Using Cellulose AffinityThe BBa_K1934020 part conceived by the 2016 INSA-Lyon team and synthesized by IDT was cloned into pSB1C3 and transformed into the E. coli NM522 strain. One recombinant clone was grown overnight in LB at 24°C, with IPTG 1 mmol.L-1 and glucose 5 mmol.L-1. Cells were harvested and resuspended in 1 mL lysis buffer (50 mmol.L-1 Tris, 300 mmol.L-1 NaCl, 10% glycerol). Then the mix was sonicated 5 times 30 seconds on ice at moderate power. The lysate was centrifuged at 14,000 g for 10 min. The supernatant was treated as follow:
2. BBa_K1934020 encodes a protein able to bind both biotin and cellulose
|
|
••••
mbecich |
The part worked as specified for our needs! We cloned it in pSB1C3, with a pTac promotor, strong RBS and a double terminator. It is important to note that this protein tends to dimerize when it is over-expressed driving to a loss of function. |
Improvements by SHSBNU_China 2021
BBa_K3798033 https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3798033 is modified from this part. From BBa_K1499004, we optimized the Condon usage of this protein for Bacillus subtilis. CBD-SA is the linker module which connects cellulose and aptamer. It is a fusion protein composed of two cellulose-binding-domain and one Streptavidin domain that is produced by engineered Bacillus subtilis. The actual structure of this linker module refers to CBD-SA-CBD. We wanted to use system with B. subtilis to optimize our production of CBD-SA. But, the plasmids of CBD-SA were not transformed successfully into competent cells of B. subtilis.
| None |