Part:BBa_K3728002
pTol2: a Tol2 vector - the Tol2 transposable element
ThisTol2 transposon system is highly used in zebrafish transgenesis. The transposase protein (TPase) is from the Medaka fish (Oryzias latipes) aka Japanese rice fish, which catalyzes the transposition of the Tol2 elements through cut-and-paste mechanism. The minimal transposable Tol2 sequence (mTol2) contains 200-bp left arm and 150-bp right arm[1]. Up to 11kb DNA insert between Tol2 sequence can be integrated into the genome of nearly all vertebrates including zebrafish, frog, chicken, mouse, and human [2].
ThisA further application in synthetic biology was demonstrated by Jun Ni, et. al.[3], in which the recombinant TPase protein is fully functional in HeLa cell line and Zebrafish germline cells. In addition, the TPase can be expressed under T7 promoter in E. coli BL21 and purified with N-terminal 6xHis tag. The transposase is active in vitro and mediated the integration of DNA fragments between plasmids with Tol2 elements.
ThisIn our study, we constructed BioBrick Parts of TPase (Part:BBa_K3728000) and the BioBrick compatible Tol2 vectors (Part:BBa_K3728003) with reporter (KanR:Part:BBa_K3728004; GFP:Part:BBa_K3728005; RFP:Part:BBa_K3728006; amilCP:Part:BBa_K3728007) and Phi29 DNA polymerase genes (Part:BBa_K3728008). We prepared the In vitro transcription-translation (TXTL) system [4][5]and expressed the functional reporter proteins. The recombinant TPase and Phil29 DNA polymerase with His tag were expressed in E. coli BL21. The purified proteins were functional in the plasmid integration assay and rolling circle amplification(RCA) application, respectively.
CONSTRUCTION – BIOBRICK COMPATIBLE VECTOR
ThisMinimal Tol2 transposable element (mTol2) has been characterized that is composed of 200-bp left arm and 150-bp right arm[6]. The 19-bp to 11-kbp DNA inserts between the arms can be excised and transposed efficiently by Tol2 transposase (TPase). Therefore, we’d like to make a BioBrick compatible vector based on Tol2 mobile element (pTol2), which can be further assembled through a BioBrick standard EcoRI-XbaI-SpeI-PstI rule.
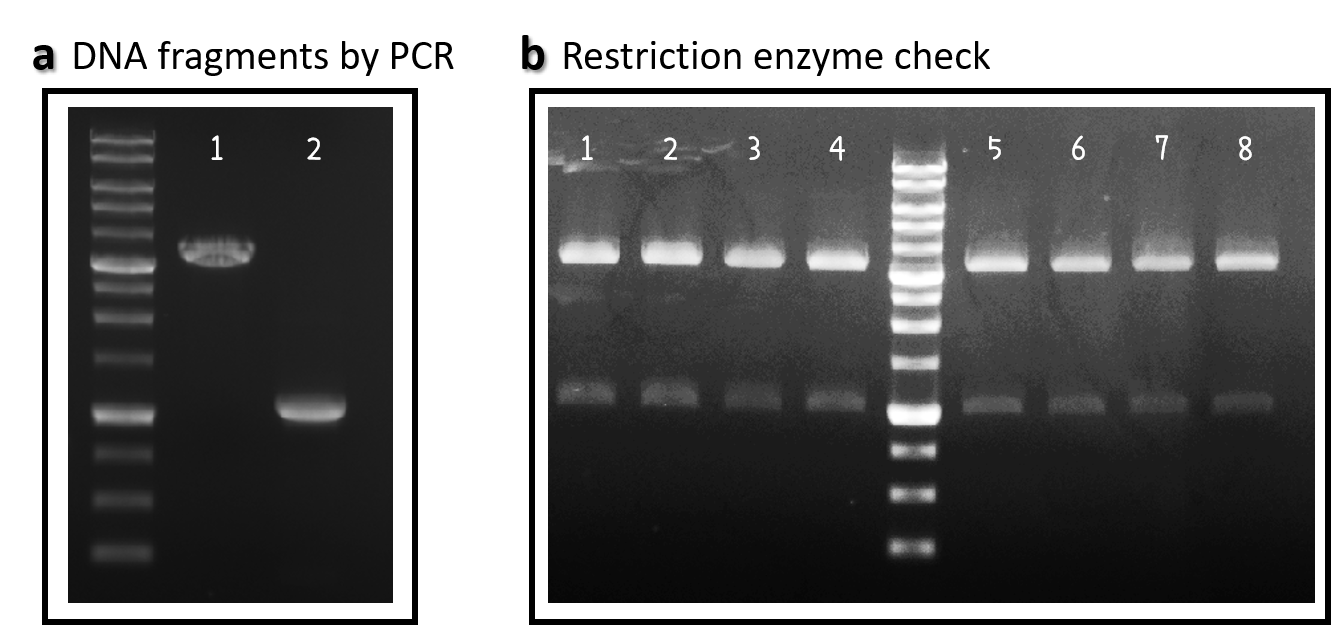
ThisWe obtained the backbone of pBSII-SK-mTol2-MCS from Addgene (Plasmid #51817), which was given by Elly Tanaka[7]. We deleted restriction enzyme sites in MCS and generated novel BioBrick Prefix (EcoRI-NotI-XbaI) and BioBrick Suffix (SpeI-NotI-PstI) elements in the both ends by PCR. The resulting DNA plasmid backbone called pTol2 (Part:BBa_K3376002) was further assembled with the Part BBa_J04450 (i.e., the iGEM official standard insert on pSB1C3). The resulting J04450/pTol2 (Part:BBa_K3376003) was checked by PCR (Fig. 1a) and restriction enzymes (Fig. 1b) and also confirmed by sequencing.
Figure 1 | pTol2 and J04450/pTol2 constructs check. DNAs were run electrophoresis on 1% agarose gel with 1kb marker. (a) PCR producs of pTol2 (lane 1, 3429 bp) and BBa_J04450 (lane 2, 1112 bp). (b) 4 clones of J04450/pTol2 were checked by restriction enzymes (~ 3432 bp and ~1110 bp). Lanes 1-4 by EcoRI and SpeI. Lanes 5-8 by XbaI and PstI.
CHARACTERIZATION - TXTL & REPORTER ASSAY
CHARACTERIZATION – PLASMID INTEGRATION
APPLICATION – PHAGE ENGINEERING
Reference
- ↑ Urasaki A, Morvan G, Kawakami K. Functional dissection of the Tol2 transposable element identified the minimal cis-sequence and a highly repetitive sequence in the subterminal region essential for transposition. Genetics. 2006 Oct;174(2):639-49. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.060244.
- ↑ Kawakami K. Tol2: a versatile gene transfer vector in vertebrates. Genome Biol. 2007;8 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):S7. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-s1-s7
- ↑ Ni J, Wangensteen KJ, Nelsen D, Balciunas D, Skuster KJ, Urban MD, Ekker SC. Active recombinant Tol2 transposase for gene transfer and gene discovery applications. Mob DNA. 2016 Mar 31;7:6. doi: 10.1186/s13100-016-0062-z.
- ↑ Garenne D, Noireaux V. Cell-free transcription-translation: engineering biology from the nanometer to the millimeter scale. Curr Opin Biotechnol. 2019 Aug;58:19-27. doi: 10.1016/j.copbio.2018.10.007.
- ↑ Rustad M, Eastlund A, Marshall R, Jardine P, Noireaux V. Synthesis of Infectious Bacteriophages in an E. coli-based Cell-free Expression System. J Vis Exp. 2017 Aug 17;(126):56144. doi: 10.3791/56144.
- ↑ Urasaki A, Morvan G, Kawakami K. Functional dissection of the Tol2 transposable element identified the minimal cis-sequence and a highly repetitive sequence in the subterminal region essential for transposition. Genetics. 2006 Oct;174(2):639-49. doi: 10.1534/genetics.106.060244.
- ↑ Khattak S, Murawala P, Andreas H, Kappert V, Schuez M, Sandoval-Guzmán T, Crawford K, Tanaka EM. Optimized axolotl (Ambystoma mexicanum) husbandry, breeding, metamorphosis, transgenesis and tamoxifen-mediated recombination. Nat Protoc. 2014 Mar;9(3):529-40. doi: 0.1038/nprot.2014.040.
Note: The map was generated and sponsored by SnapGene.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal EcoRI site found at 3452
Illegal SpeI site found at 2
Illegal PstI site found at 16
Illegal NotI site found at 9
Illegal NotI site found at 29
Illegal NotI site found at 3458 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal EcoRI site found at 3452
Illegal BglII site found at 3340
Illegal XhoI site found at 3419 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal prefix found at 3452
Illegal suffix found at 2 - 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal prefix found at 3452
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal XbaI site found at 3467
Illegal SpeI site found at 2
Illegal PstI site found at 16
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 642 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal BsaI site found at 1818
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 2900
| None |