Part:BBa_K2549036
VP64-ZF21.16N-CfaN
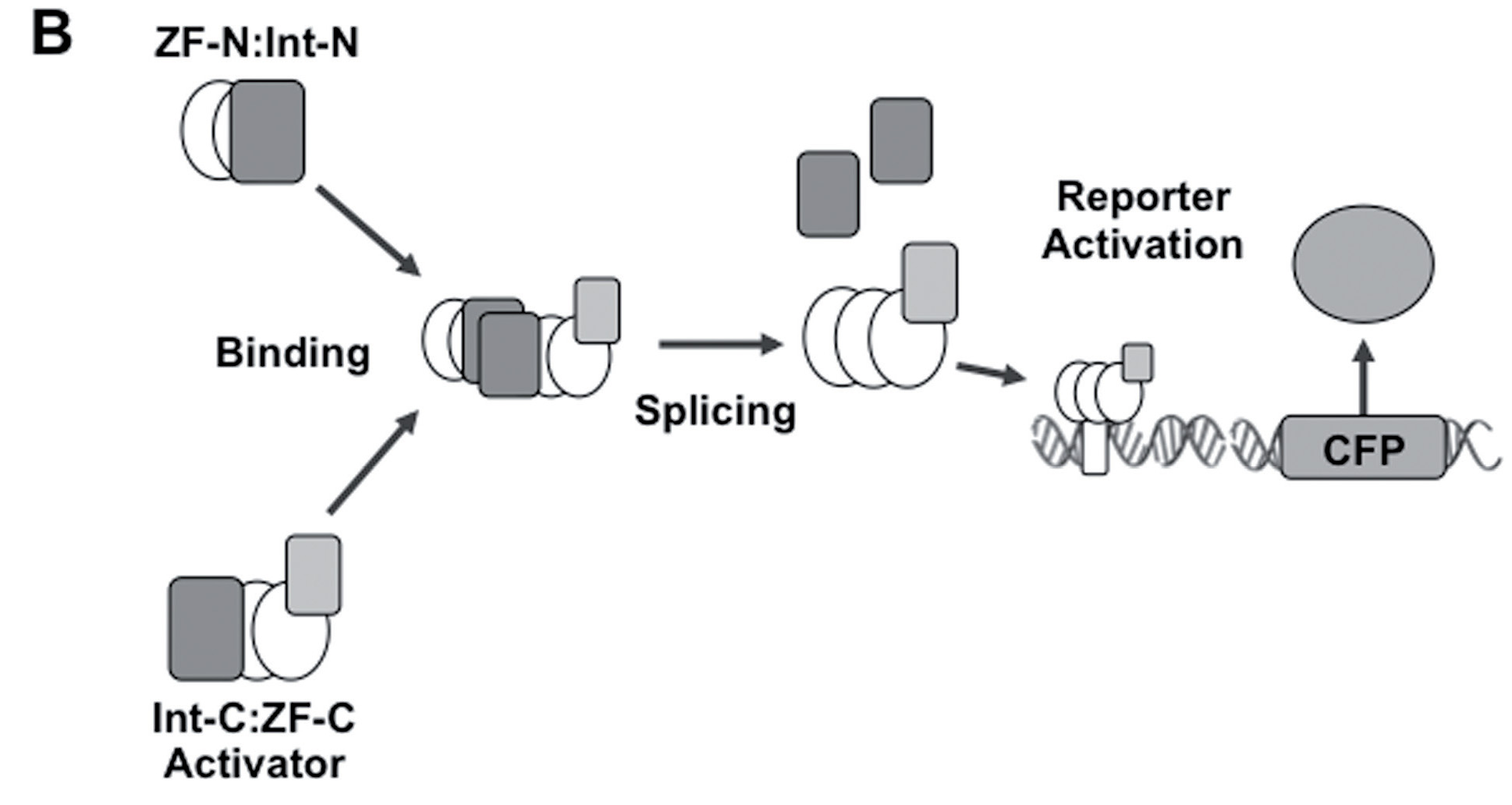
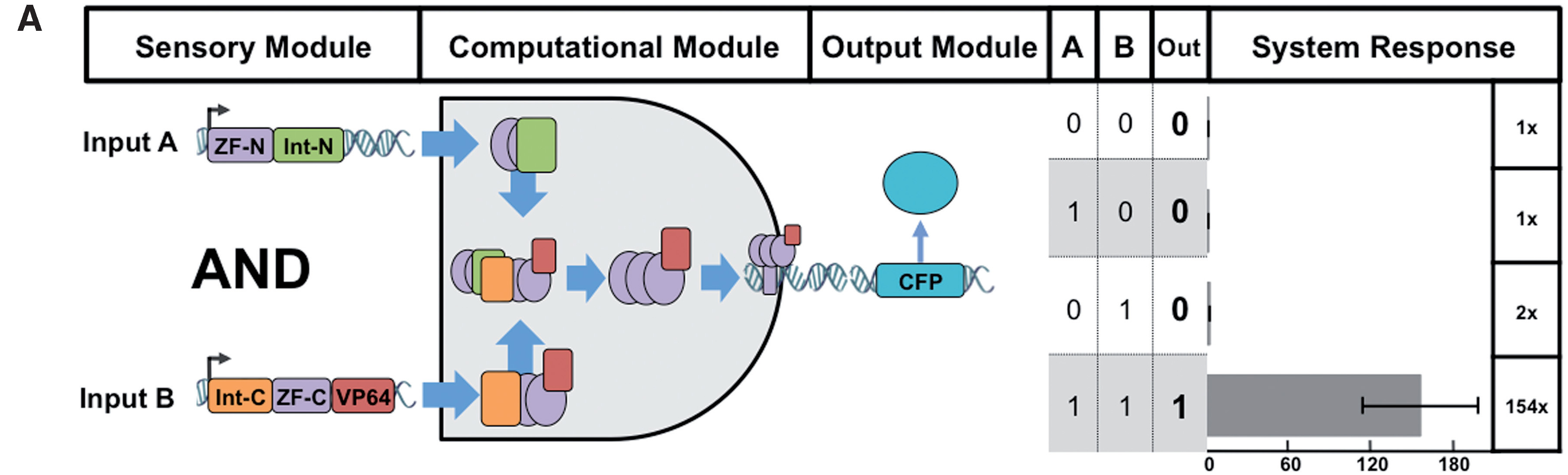
This part is one of the downstream elements of our amplifier. It is constructed by fusing VP64 (Part:BBa_K2549057), G4S linker (Part:BBa_K2549053), ZF21.16N (Part:BBa_K2549011) and CfaN (Part:BBa_K2549009), from N terminal to C terminal. VP64 is a tetrameric VP16 transcription activator which shows ultrahigh transcription activation function. G4S is a glycine-rich peptide linker whose sequence is GGGGS. ZF21.16N is the N-terminal fragment of the zinc finger whose recognition helices for three-finger arrays are substituted by the reported synthetic zinc finger 21.16 residues on the basis of the BCR_ABL-1 artificial zinc finger[1]. CfaN is the N-terminal fragment of Cfa which is a consensus sequence from an alignment of 73 naturally occurring DnaE inteins that are predicted to have fast splicing rates. When coexpressed with CfaC-ZF21.16C-NLS (Part:BBa_K2549038) in the same cell, both fusions will be produced and a transcription activating function will be executed.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Biology
Boolean logic gates via split zinc finger-based transcription factors
Lohmueller JJ et al have demonstrated the split ZF-TF reconstitution process. Please note that we used Cfa split intein (Part:BBa_K2549009 and Part:BBa_K2549010) but not dnaB reported below.
Characterization
It works as we designed
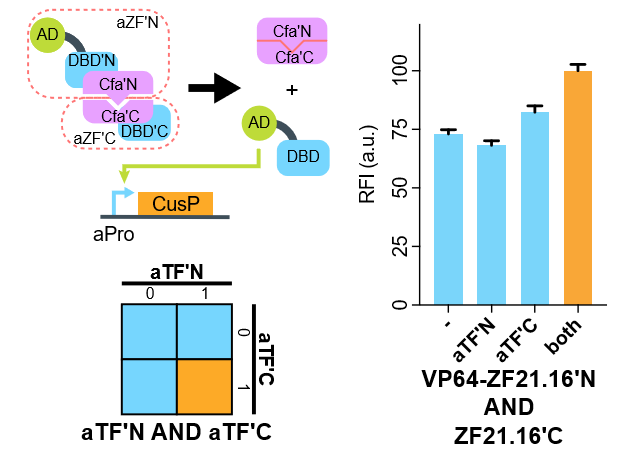
Flow cytometry results suggest that when coexpressed with CfaC-ZF21.16C-NLS, the expression level of d2EGFP is relatively turned up compared to none of them exists or only one of them exists.
References
- ↑ A tunable zinc finger-based framework for Boolean logic computation in mammalian cells. Lohmueller JJ, Armel TZ, Silver PA. Nucleic Acids Res, 2012 Jun;40(11):5180-7 PMID: 22323524; DOI: 10.1093/nar/gks142
//proteindomain/binding
//proteindomain/internal/special
| None |