Part:BBa_K2549039
VP64-dNLS-ZF21.16
This part is one of the downstream elements of our amplifier. It is constructed by fusing VP64 (Part:BBa_K2549057), dNLS (Part:BBa_K2549056) and ZF21.16 (Part:BBa_K2549046), from N terminal to C terminal. VP64 is a tetrameric VP16 transcription activator which shows ultrahigh transcription activation function. dNLS, which is short for destroyable nuclear localization sequence, is able to guide the fusion protein to be located to the nucleus without TEV protease. It is cleaved and unable to guide the fusion protein when TEV protease exist. Thus when coexpressed with NLS-TEVp (Part:BBa_K2549041), it is cleaved and the transcription activation function cannot be conducted.
Biology
TEV protease-based transcription regulation or proteolysis-only activity
TEV protease is widely used in synthetic biology for its high cleavage specificity (targetting amino acids sequence ENLYFQG/S between QG or QS)[1] and cleaves and high efficiency (optimized by RB Kapust et al to remove autolysis)[2]. Rossner MJ et al have demonstrated the TEV activity-dependent activation of several reporters[3]. In our system, we set the TEV protease specific cleavage site into the spacer region of the nuclear localization sequence[4], which is the core design of the TEV protease-based complex logic gates.
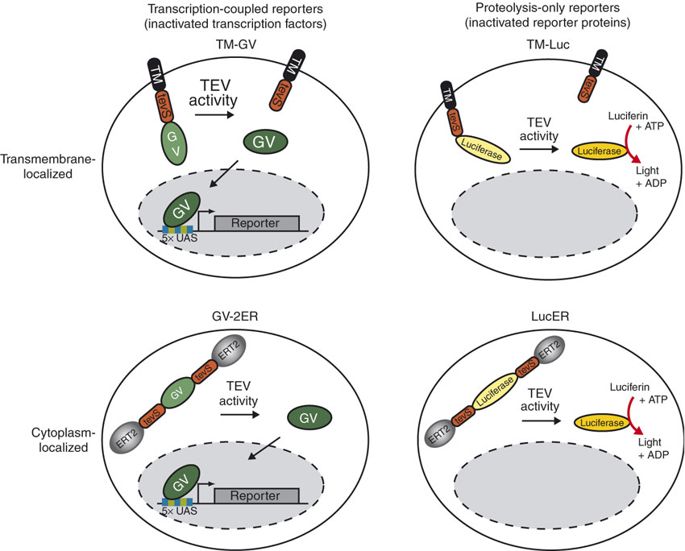
For more details about TEV protease, please refer to our TEVp (Part:BBa_K2549013).
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 502
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
References
- ↑ Release of proteins and peptides from fusion proteins using a recombinant plant virus proteinase. Parks TD, Leuther KK, Howard ED, Johnston SA, Dougherty WG. Anal Biochem, 1994 Feb;216(2):413-7 PMID: 8179197; DOI: 10.1006/abio.1994.1060
- ↑ Tobacco etch virus protease: mechanism of autolysis and rational design of stable mutants with wild-type catalytic proficiency. Kapust RB, Tözsér J, Fox JD, ..., Copeland TD, Waugh DS. Protein Eng, 2001 Dec;14(12):993-1000 PMID: 11809930
- ↑ Monitoring regulated protein-protein interactions using split TEV. Wehr MC, Laage R, Bolz U, ..., Nave KA, Rossner MJ. Nat Methods, 2006 Dec;3(12):985-93 PMID: 17072307; DOI: 10.1038/nmeth967
- ↑ Two interdependent basic domains in nucleoplasmin nuclear targeting sequence: identification of a class of bipartite nuclear targeting sequence. Robbins J, Dilworth SM, Laskey RA, Dingwall C. Cell, 1991 Feb;64(3):615-23 PMID: 1991323
//proteindomain/binding
//proteindomain/localization
| None |
