Part:BBa_K2621038
CAT-Seq Ribosome Binding Site (RBS)
This part is an ribosome binding site (RBS) - a sequence of nucleotides upstream of the start codon of an mRNA transcript that is responsible for the recruitment of a ribosome during the initiation of protein translation.
This RBS was characterized using both standard methods and the high-throughput CAT-Seq system.
See how this part is used in the CAT-Seq by pressing here!
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Part Characterization (Vilnius-Lithuania Overgraduate 2018)
- 2.1 Kinetic characterization of the CAT-Seq Esterase
- 2.2 Esterase and its mutants catalytic activity determination
- 2.3 Esterase and mutants activity assessment using CAT-Seq
- 2.4 Ribosome binding site activity measurements
- 2.5 Ribosome binding site activity measurements using CAT-Seq
- 2.6 Cross-interaction measurements of Toehold Switches
- 2.7 Cross-interaction measurements of Toehold Switches using CAT-Seq
- 2.8 References
Introduction
Usage with CAT-Seq (Catalytic Activity Sequencing)
About CAT-Seq
CAT-Seq stands for Catalytic Activity Sequencing - a system designed and built for high-speed activity and interaction characterization of Catalytic and Regulatory biological parts. You can learn more about CAT-Seq [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Vilnius-Lithuania-OG by clicking this link]
Catalytic Activity Sequencing Overview
- Library preparation - A library of catalytic biomolecules is prepared.
- Library encapsulation into droplets - Every library fragment is physically separated by encapsulating them into picoliter water droplets. Also, substrate nucleotides, the targets for catalytic biomolecules, are encapsulated.
- Catalytic biomolecule production - In each droplet catalytic biomolecules are produced.
- Catalysis of the substrate conversion - Catalytic biomolecules may recognise the Substrate Nucleotides as a target for chemical reaction catalysis. Depending on biomolecule activity, a specific number of nucleotides with removed substrates (product nucleotides) is established in each droplet.
- Activity Recording
- Droplet Merging - each of prior droplet is merged with new droplet that contains DNA amplification mix and reference nucleotides. The reference nucleotides are helping to tracking the Product Nucleotide number.
- DNA amplification - DNA is amplified using the different unique catalytic biomolecule DNA in each droplet. During the amplification, the Product Nucleotides and the Reference Nucleotides are incorporated into the DNA sequence.
- Activity Reading by Nanopore Sequencing - All of the droplets are broken and the amplified DNA is sequenced. During the sequencing, biomolecule’s activity is retrieved by calculating reference and Product Nucleotides (substrate removed), together with the sequence of particular biomolecule variant.
Genetic Regulatory Part activity and cross-interaction assessment
While Catalytic Activity Sequencing began as a method for catalytic biomolecule activity recording, we have also create a way to adjust CAT-Seq to record activities of regulatory part. In addition to the activities, cross-interactions of different regulatory parts can also be measured.
When assessing the activities and sequences of libraries of catalytic biomolecules in CAT-Seq , the activity is measured and recorded as a function of Product Nucleotide that was produced in each droplet.
Yet, the activity of the catalytic biomolecule is not the only aspect that can influence the amount of Product Nucleotides that are produced. If all of the droplets would contain the same catalytic biomolecule , but each droplet would have a different concentration of that biomolecule, we would in result get different amounts of Product Nucleotides. For example, droplets with large amount of biomolecules may produce a large number of Product Nucleotides and vice-versa. The default and well-characterized Catalytic Biomolecule in CAT-Seq for regulatory part charectation would be the CAT-Seq Esterase.
Yet, the activity of the catalytic biomolecule is not the only aspect that can influence the amount of Product Nucleotides that are produced. If all of the droplets would contain the same catalytic biomolecule , but each droplet would have a different concentration of that biomolecule, we would in result get different amounts of Product Nucleotides. For example, droplets with large amount of biomolecules may produce a large number of Product Nucleotides and vice-versa. The default and well-characterized Catalytic Biomolecule in CAT-Seq for regulatory part charectation would be the CAT-Seq Esterase.
Example for RBS activity strength determination
We can now explore an example in which the CAT-Seq esterase can be used to assess the strengths of different ribosome binding site (RBS) sequences.
While keeping all the workflow from the main Catalytic Activity Sequencing design, all we need to do is to change the way we prepare the library. Firstly, instead of using a library of catalytic biomolecules, we can use a single CAT-Seq Esterase enzyme. Then, specific or random RBS sequence library can be prepared and attached to the esterase enzyme sequence. After that, every step of CAT-Seq method is the same.
After the library is encapsulated into droplets, depending on the RBS sequence strength some droplets may have different amounts of the esterase. For example, the droplets with more esterase will produce more Product Nucleotides and vice-versa. After the amplification and sequencing steps we can learn two main things about the measured library - the RBS sequence and its relative RBS strength in the form of Product Nucleotide concentration for every library variant screened.
Part Characterization (Vilnius-Lithuania Overgraduate 2018)
Kinetic characterization of the CAT-Seq Esterase
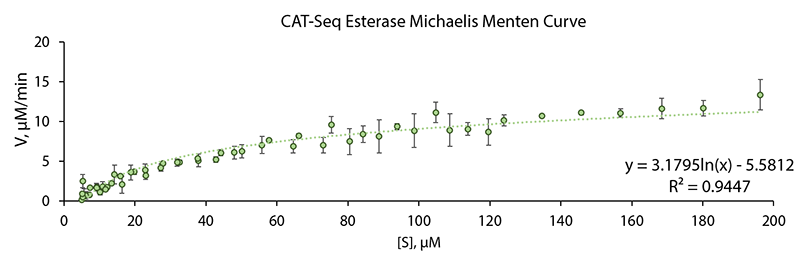
Spectrofotometic kinetic data based on decay of absorbance at 310 nm due to substrate nucleotide catalytic conversion was gathered using a range of starting substrate nucleotide concentrations. A Michelis Menten curve for the CAT-Seq esterase was plotted using the aquired data. Data shown in 1 Fig., show perfect fit (R2 = 0.9449) to a standard Michaelis Menten curve.
Michaelis Menten plot transformations were generated for CAT-Seq esterase enzyme (BBa_K2621000). 2 Fig., display Lineweaver-Burk and Hanes-Woolf transformation plot. Based on the equation koeficients in the Hanes-Woolf transformation, the expermentally determined Vmax value is 17.2 µM/min, Km value is 86 µM.

Esterase and its mutants catalytic activity determination
The 10 esterase mutants housing mutations at bioinformatically predicted sites were created. To see why and how mutations were designed in-silico, [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Vilnius-Lithuania-OG/Model please click this link]. Each of the mutant was constructed utilizing PCR and synthesized using In vitro transcription and translation kit and their catalytic activity towards N4-benzoyl-2'-deoxycytidine triphosphate were tested.

The reaction kinetics were measured using the spectrophotometer as a decrease of absorbance. Figure 3 displays the relative hydrolysis speed of each mutant generated. As seen from these results, a variety of mutants, showing different catalysis speeds were produced. Some of the amino acids changes affected the activity drastically, for example Trp224 to Tyr, Lys227 to Arg or Glu509 to Lys. Other mutations only modulated the activity Asn107 to Asp or Glu194 to Ala. Additionally, large 8 amino acid deletion at position Pro348-Hy356 caused only a moderate decrease in enzymes activity.
Esterase and mutants activity assessment using CAT-Seq
The constructed in silico designed mutant library was subjected to catalytic activity sequencing. By applying the data preparation and analysis pipeline, the mean methylation scores arising from different ratios of catalytically converted and reference nucleotides for each barcoded mutant DNA template were filtered and extracted from the DNA embedded with catalytic activity information (in a form of incorporated reference to catalytically converted nucleotide ratio). The collected data was normalized over Wild Type Esterase and K227R mutant (lowest activity).

The relative methylation score (reference nucleotide count) of each mutant read corresponds to the activity of the enzyme it encodes. The higher the activity of the expressed enzyme, the lower methylation score are assigned, due to catalytic conversion of substrate nucleotides. The comparison of the results, gathered with CAT-Seq catalytic activity sequencing method and in standard sized reactions (in bulk) spectrophotometric data (Fig 1.) conclude the viability of CAT-Seq approach. The activity reading, extracted from the DNA sequence correlates with the in bulk measurement data perfectly. The activity of the each Esterase mutant is measured accurately and is assigned to the corresponding DNA sequence.
Ribosome binding site activity measurements
The three ribose binding sites (BBa_B0030, BBa_B0032, BBa_B0034) already found in biobrick registry and a new CAT-Seq RBS BBa_K2621038 were place upstream the CAT-Seq esterase gene. The strength of each ribosome binding site was investigated by expressing the esterase enzyme using the In vitro transcription and translation kit and spectrophotometrically measuring the as a decrease of absorbance due to the hydrolysis of substrate nucleotides.

Figure 4 displays the relative hydrolysis speed (normalized to BBa_B0034) of CAT-Seq esterase expressed using 4 different ribosome binding sites. Based on the fact that the same enzyme and substrate nucleotide concentration are used, the difference in activity corresponds to difference in synthesised biomolecule concentrations. The expression of an enzyme depends on the particular strength of used ribosome binding sites.
Taking this into consideration, the measured relative activity corresponds to strength of ribosome binding sites.
Ribosome binding site activity measurements using CAT-Seq
The constructed Ribosome Binding site library (BBa_B0030, BBa_B0032, BBa_B0034, BBa_K2621038 with a downstream CAT-Seq esterase gene BBa_K2621000) was subjected to catalytic activity sequencing method. The mean methylation scores (reference nucleotide count) for each barcoded DNA template, housing different RBS were filtered and extracted from the DNA embedded with catalytic activity information (in a form of incorporated reference to catalytically converted nucleotide ratio). The collected activity data was normalized to BBa_B0034 data and is shown in Fig. 2.

Stronger ribosome binding sites increase the yield of translated proteins and in turn increase the number of catalytically converted substrate nucleotides. This increase is inversely proportional to the assigned mean methylation score. Based on this fact, the activity results can be extracted from mean methylation scores (reference nucleotide count) and correspond to ribosome binding site strength. The catalytic activity sequencing results were compared to earlier measured in bulk RBS strength results.
The comparison once again concludes the viability of CAT-Seq approach. The ribosome binding site strength, extracted from the DNA sequence reference nucleotide count correlates with the in bulk measurement data. These results display the validity of CAT-Seq as a method for screening the strength of regulatory sequences and its ability to assign accurate phenotype to genotype linkage.
Cross-interaction measurements of Toehold Switches
The 9 library members, composed of 3 unique Toehold Switch sequences and 3 unique activating RNA sequences, termed Trigger RNA, were designed to test the orthogonality and regulatory characteristics of each part.
Each of the regulatory part, consisting of one toehold sequence upstream of the CAT-Seq esterase gene (BBa_K2621000) and one trigger sequence were constructed. First of all, the orthogonality of each toehold:activating RNA pair and they regulatory characteristic have been tested in bulk.
The constructed library members were synthesized using In vitro transcription and translation kit and their catalytic activity towards N4-benzoyl-2'-deoxycytidine triphosphate were tested. The reaction kinetics were measured using the spectrophotometer as a decrease of absorbance due tue hydrolyzed substrate nucleotide.

Figure 5 displays the relative hydrolysis speed of each regulatory part variant in a form of matrix. The decrease of absorbance shown in Y axis corresponds to the catalytic conversion of substrate nucleotides. As seen from control experiment, in which standard esterase was expressed, the decline of absorbance over time is seen.
Taking these results into consideration, the same decrease of absorbance is only seen in the diagonal of the matrix. This means, that active catalytic molecules is expressed only when both regulatory molecules of the same group are present - Toehold1 (BBa_K2621011) with Trigger1 (BBa_K2621014), Toehold2 (BBa_K2621012) with Trigger2 (BBa_K2621015) and Toehold3 (BBa_K2621013) with Trigger3 (BBa_K2621016). None of the regulatory sequences show any cross talk with the other group. These results conclude the generation of working toehold riboswitches control library for regulatory sequences parameter and orthogonality screening.
Cross-interaction measurements of Toehold Switches using CAT-Seq
In addition to ribosome binding sites, we have constructed Toehold regulatory sequence library constituted of different toehold and triggers pairs was constructed subjected to catalytic activity sequencing method:
- BBa_K2621011 - Toehold Switch 1
- BBa_K2621012 - Toehold Switch 2
- BBa_K2621013 - Toehold Switch 3
- BBa_K2621014 - Trigger RNA 1
- BBa_K2621015 - Trigger RNA 2
- BBa_K2621016 - Trigger RNA 3
The mean methylation scores (reference nucleotide count) for each barcoded DNA template, housing different regulatory sequence were filtered and extracted from the DNA embedded with catalytic activity information (in a form of incorporated reference to catalytically converted nucleotide ratio).

The graph displays the mean methylation (reference nucleotide) scores assigned to each barcoded toehold-trigger construct read. Based on the results, low methylation score are only assigned when both Toehold and trigger sequences from the same group are present, due tue esterase being expressed. These results correlate perfectly to the standard (not in droplet) measurement results, carried out earlier.
Based on this fact it can be concluded that CAT-Seq activity sequencing method can be utilized as a precise and accurate way to screen and assign the activity and orthogonality of regulatory sequences.
References
| None |





