Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa J23101"
KalenClifton (Talk | contribs) (→Baltimore Biocrew 2019 Characterization) |
KalenClifton (Talk | contribs) (→Baltimore Biocrew 2019 Characterization) |
||
| Line 127: | Line 127: | ||
</tr> | </tr> | ||
</table> | </table> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <strong>Conclusion</strong><br> | ||
| + | After redoing our protocol many times and trying to compare our results to 2006 Berkeley iGEM team we concluded that our data doesn’t quite match theirs. The different results in strengths could be caused by many different factors while doing our protocols. However, we have succeeded in characterizing the different strength Andersons promoters (J23100, J23101, J23103, J23105, J23118) by measuring RNA using Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR). In conclusion, we successfully reached our goal in bringing new data to the characterizations of 5 different Andersons Promoters. In the future, it would be good for other iGEM teams to try to measure RNA as well so there will be a standard qPCR protocol for iGEM. | ||
Revision as of 05:25, 20 October 2019
constitutive promoter family member
For video explanation on this promoter family and its use, visit [http://www.synbiotrails.org/#!/trail?id=org.clothocad.trails.youtube.TranscriptionModels here].
Variant RFP (au) J23112 1 J23103 17 J23113 21 J23109 106 J23117 162 J23114 256 J23115 387 J23116 396 J23105 623 J23110 844 J23107 908 J23106 1185 J23108 1303 J23118 1429 J23111 1487 J23101 1791 J23104 1831 J23102 2179 J23100 2547 |
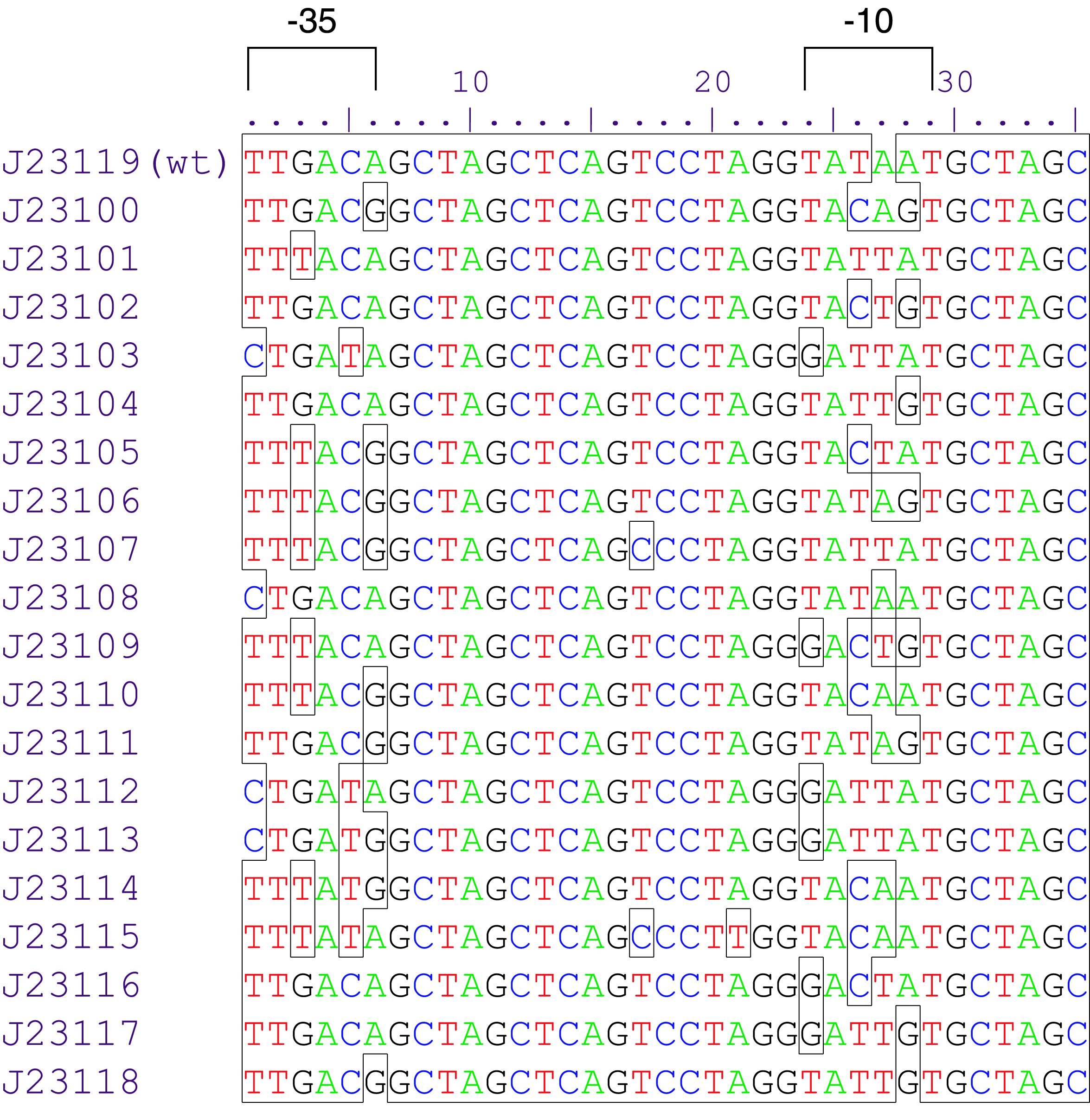
Constitutive promoter family
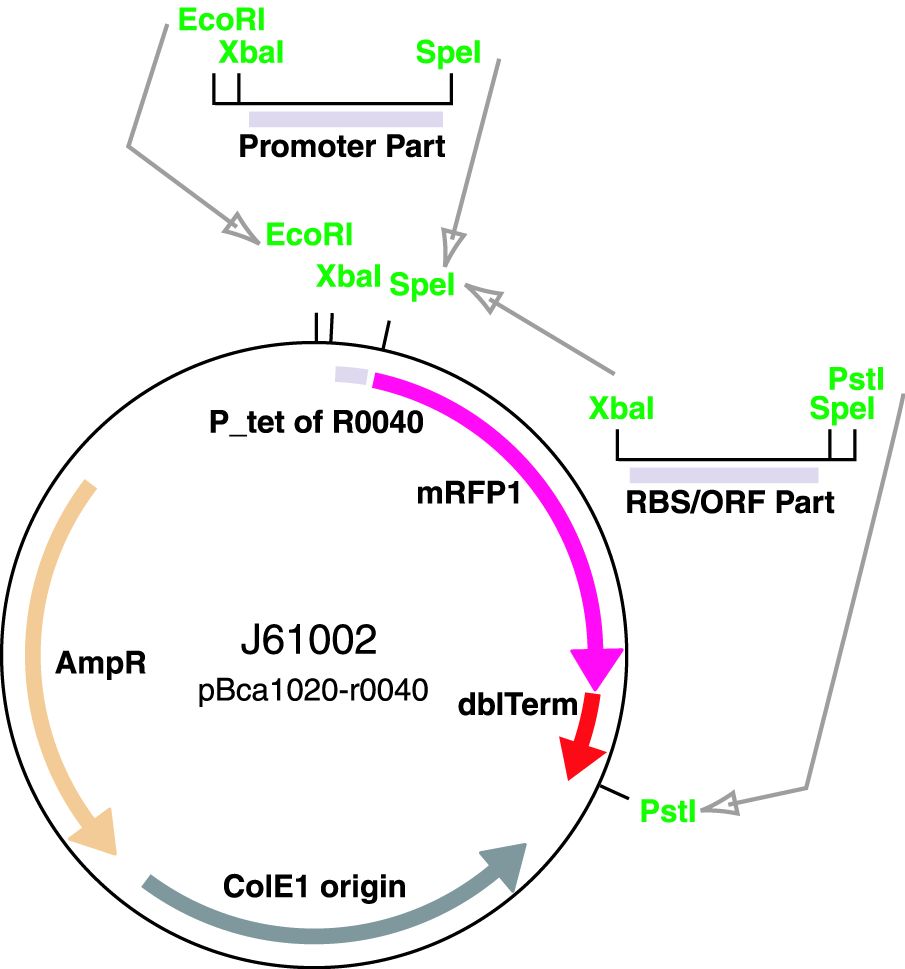
Parts J23100 through J23119 are a family of constitutive promoter parts isolated from a small combinatorial library. J23119 is the "consensus" promoter sequence and the strongest member of the family. All parts except J23119 are present in plasmid J61002. Part J23119 is present in pSB1A2. This places the RFP downstream of the promoter. Reported activities of the promoters are given as the relative fluorescence of these plasmids in strain TG1 grown in LB media to saturation. See part BBa_J61002 for details on their use.
These promoter parts can be used to tune the expression level of constitutively expressed parts. The NheI and AvrII restriction sites present within these promoter parts make them a scaffold for further modification. JCAraw
Contribution
Group: Valencia_UPV iGEM 2018
Author: Adrián Requena Gutiérrez, Carolina Ropero
Summary: We adapted the part to be able to assemble transcriptional units with the Golden Gate assembly method
Documentation:
In order to create our complete [http://2018.igem.org/Team:Valencia_UPV/Part_Collection part collection] of parts compatible with the Golden Gate assembly method, we made the part BBa_K2656007 which is this part adapted to the Golden Gate technology.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
USTC_2009's MEASUREMENT
Characterization by GreatBay_China 2018
Team GreatBay_China 2018 characterized J23119Part:BBa_J23119, Part:BBa_J23105, and Part:BBa_J23101 by assembling them with Part:BBa_B0034 and a sfGFP Part:BBa_I746916 on three vectors: pUC20 (copy number about 500/cell), pR6K (copy number about 15/cell), pSC101 (copy number about 2/cell). Then we measured the fluorescence by Flow Cytometry as a reference for the TALE stabilized promoter library.
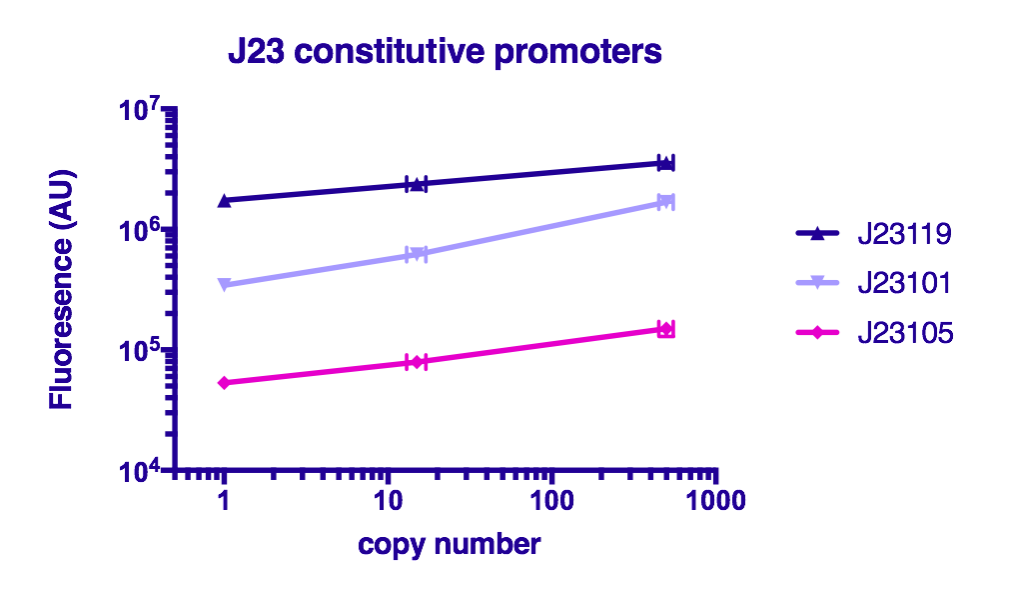
The result indicate that the strength of J23119, J23105, and J23101 are about the same as described by team iGEM2006_Berkeley, and the fluorescence increases as the copy number of the vector increases
Baltimore Biocrew 2019 Characterization
Goal
We, the Baltimore Biocrew, decided to characterize some of the Anderson promoters. These promoters are highly used by iGEM but the relative expression of these promoters have been routinely determined by measuring the fluorescence of a reporter protein. However, the function of a promoter is to start transcription of a gene so it may be more informative to measure the amount of RNA (instead of protein) produced by a reporter gene. Therefore, we decided to further characterize a selection of the Anderson promoters (J23100, J23101, J23103, J23105, J23118) by measuring RNA using Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR).
Results
We did data analysis using the Livak Method (a standard, comparative method) to determine the relative strength of the promoters from the qPCR data using rrSD as our reference gene, RFP as our target gene, and J23100 as our calibrator sample.
Example:
ΔCT(J23101) = CT(RFP, J23101) – CT(rrSD, J23101)
ΔΔCT(J23101) = ΔCT(J23101) – ΔCT(J23100)
2^(–ΔΔCT) = relative expression ratio
In our first trial of qPCR (8/03/19), we were able to measure the relative strengths for J23100, J23101, J23103, and J23105 which were 1.00, 0.00, 0.81, and 1.93, respectively. Since these strengths did not match the relative expression levels reported by iGEM2006_Berkeley, we repeated the qPCR (8/10/19) with the same cDNA. The strengths from this second trial were 1.00, 0.00, 0.37, and 0.20. We repeated it again and the relative strengths that we got on 10/12/19 for J23100, J23101, J23103, and J23103 were 1, 0, 2.91, and .32. Next, we made new cDNA by growing new liquid cultures, extracting RNA again, and repeating reverse transcription. From the new cDNA, we repeated the qPCR procedure two more times. The relative strengths for that we got on 9/28/19 for J23100, J23101, J23103, J23105, and J23118 were 1, 24.63, .36, 1.76, and .25. The relative strengths that we got on 10/12/19 for J23100, J23101, J23103, and J23105 were 1, 45.97, 3.20, and 1.26. In addition we measured promoter J23118 twice and got the strengths 1.13 and 1.32.
Here is the relative promoter strengths that we got from the qPCR. Baltimore BioCrew in blue compared to the 2006 Berkeley iGEM in orange.
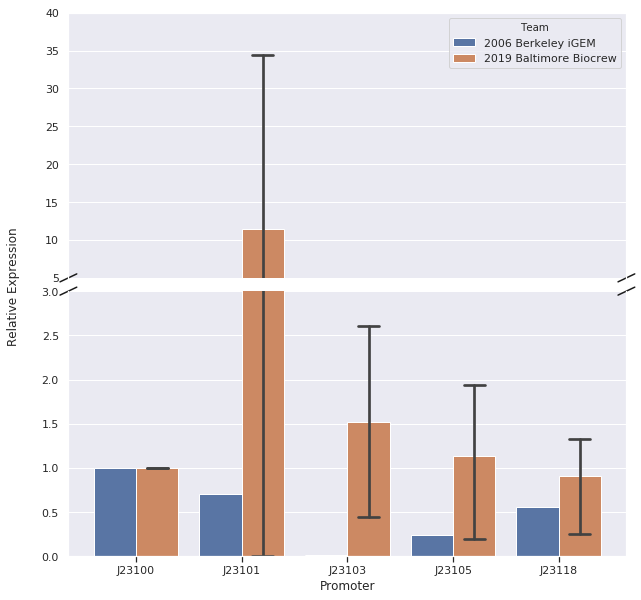
To support our RNA measurements we also measured fluorescence of the liquid cultures we used to extract RNA. The cultures were grown overnight so we expected the bacteria to be at the stationary phase, but we measured OD to normalize any differences in growth.
| Promoter | OD | fluorescence | fluorescence divided by OD | corrected relative expression | reported relative expression |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_J23100 | 0.876 | 250 | 285.38 | 1 | 1 |
| BBa_J23101 | 0.674 | 255 | 378.33 | 1.33 | 0.7 |
| BBa_J23103 | 1.1 | 230 | 209.09 | 0.73 | 0.01 |
| BBa_J23105 | 1.08 | 215.74 | 209.09 | 0.76 | 0.24 |
| BBa_J23118 | 1.04 | 238 | 228.84 | 0.80 | 0.56 |
After redoing our protocol many times and trying to compare our results to 2006 Berkeley iGEM team we concluded that our data doesn’t quite match theirs. The different results in strengths could be caused by many different factors while doing our protocols. However, we have succeeded in characterizing the different strength Andersons promoters (J23100, J23101, J23103, J23105, J23118) by measuring RNA using Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction (qPCR). In conclusion, we successfully reached our goal in bringing new data to the characterizations of 5 different Andersons Promoters. In the future, it would be good for other iGEM teams to try to measure RNA as well so there will be a standard qPCR protocol for iGEM.