Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1073024"
PeterGockel (Talk | contribs) |
PeterGockel (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 35: | Line 35: | ||
<h3>Usage and Biology</h3> | <h3>Usage and Biology</h3> | ||
<hr class="head"> | <hr class="head"> | ||
| − | + | <br></br> | |
<p> | <p> | ||
| − | Improved version: | + | Improved version: <a |
| + | href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1758100" | ||
| + | target="_blank"> BBa_K1758100</a> | ||
| + | <br></br> | ||
The part was improved in terms of its expression level, based on the insertion of a 5’-untranslated region (5’-UTR) upstream of the coding sequence. This 5'-UTR was adapted from iGEM Bielefeld 2015 ( <a | The part was improved in terms of its expression level, based on the insertion of a 5’-untranslated region (5’-UTR) upstream of the coding sequence. This 5'-UTR was adapted from iGEM Bielefeld 2015 ( <a | ||
href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1758100" | href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1758100" | ||
Revision as of 19:47, 18 October 2019
Constitutively expressed chromoprotein amilGFP
This device is an enhanced construct of 2012 Uppsala's BBa_K592010. It consists of a strong promoter (BBa_J23100) combined with a RBS (BBa_B0032) and the encoding region of the chromoprotein amilGFP (BBa_K592010). This results in a constitutively high expression of amilGFP.
Usage and Biology
During cultivation, the chromoprotein amilGFP is expressed and stored intracellularly. The yellow color of the protein can be seen by the naked eye, thus the chromoprotein can be used as a reporter or selection marker to distinguish cells easily.
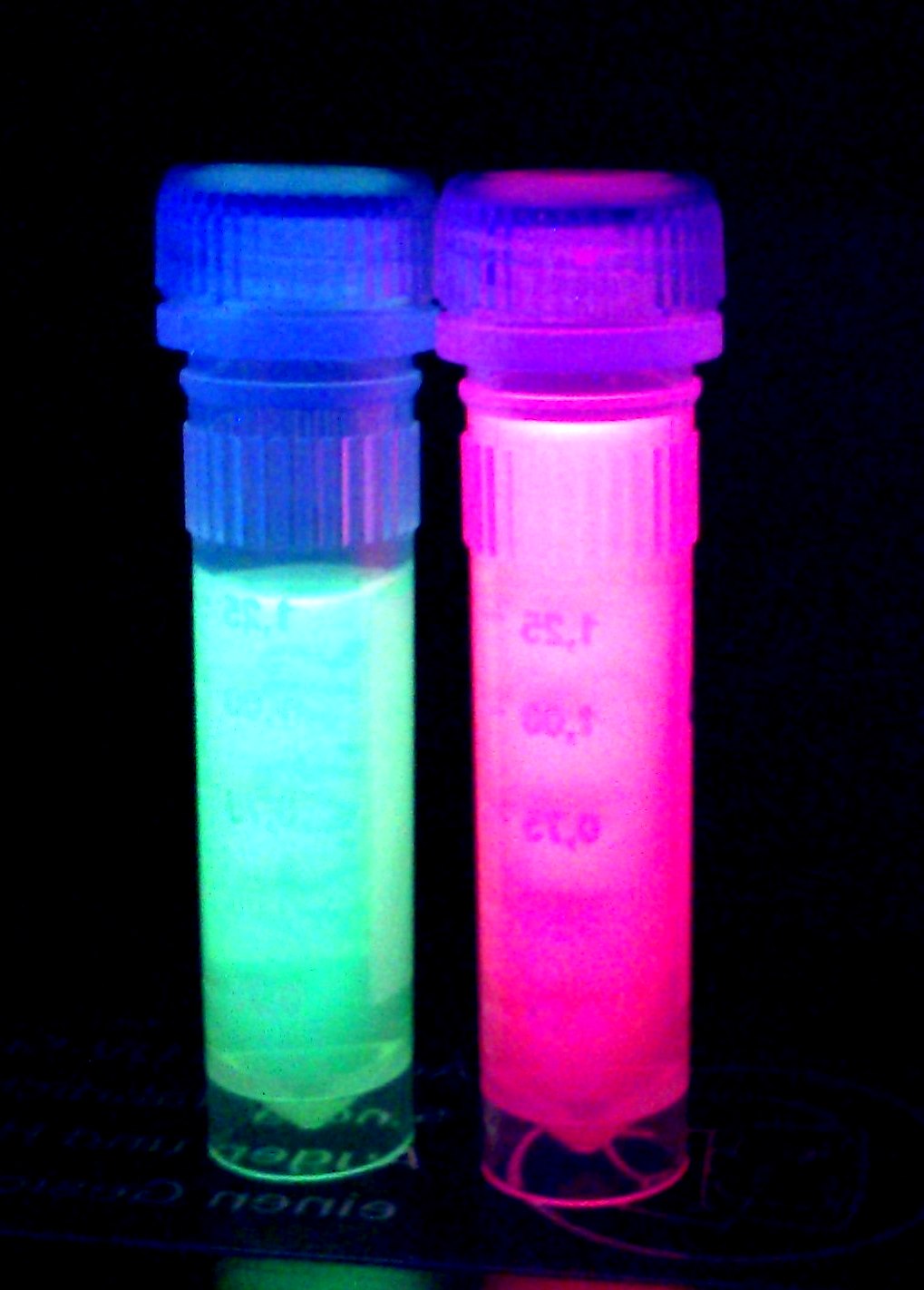
iGEM Team Braunschweig 2013:
Left: Liquid cultures of E. coli XL1 expressing chromoproteins amilGFP , eforRed (BBa_K1073022) and aeBlue (BBa_K1073020).
Right: Cell pellet of E. coli XL1 expressing amilGFP.
The yellow color of amilGFP can be seen by the naked eye. The chromoprotein also fluoresce when excited. Thus it can be used to identify cells with fluorescence microscopy or flow cytometry. For further information as well as absorption and emission spectra see experience page.
iGEM Team Braunschweig 2013: Supernatant after cell disruption containing chromoproteins of eforRed (BBa_K1073022) and amilGFP. Both chromoproteins fluoresce when excited by UV-light.
Translation Enhancing 5'-UTR (Improvement by iGEM TU_Darmstadt 2019)
Usage and Biology
Improved version: BBa_K1758100
The part was improved in terms of its expression level, based on the insertion of a 5’-untranslated region (5’-UTR) upstream of the coding sequence. This 5'-UTR was adapted from iGEM Bielefeld 2015 ( BBa_K1758100) and is based on the research of Olins et al
[1]
and Takahashi et al.
[2]
.
It contains the strong ribosomal binding site (RBS) g10-L from the T7 bacteriophage and a sequence that plays a role in the regulation of mRNA binding to and release from the 30S ribosomal subunit. The 5'-UTR therefore enhances the translation efficiency of the following coding sequence (CDS) (Fig. 1).
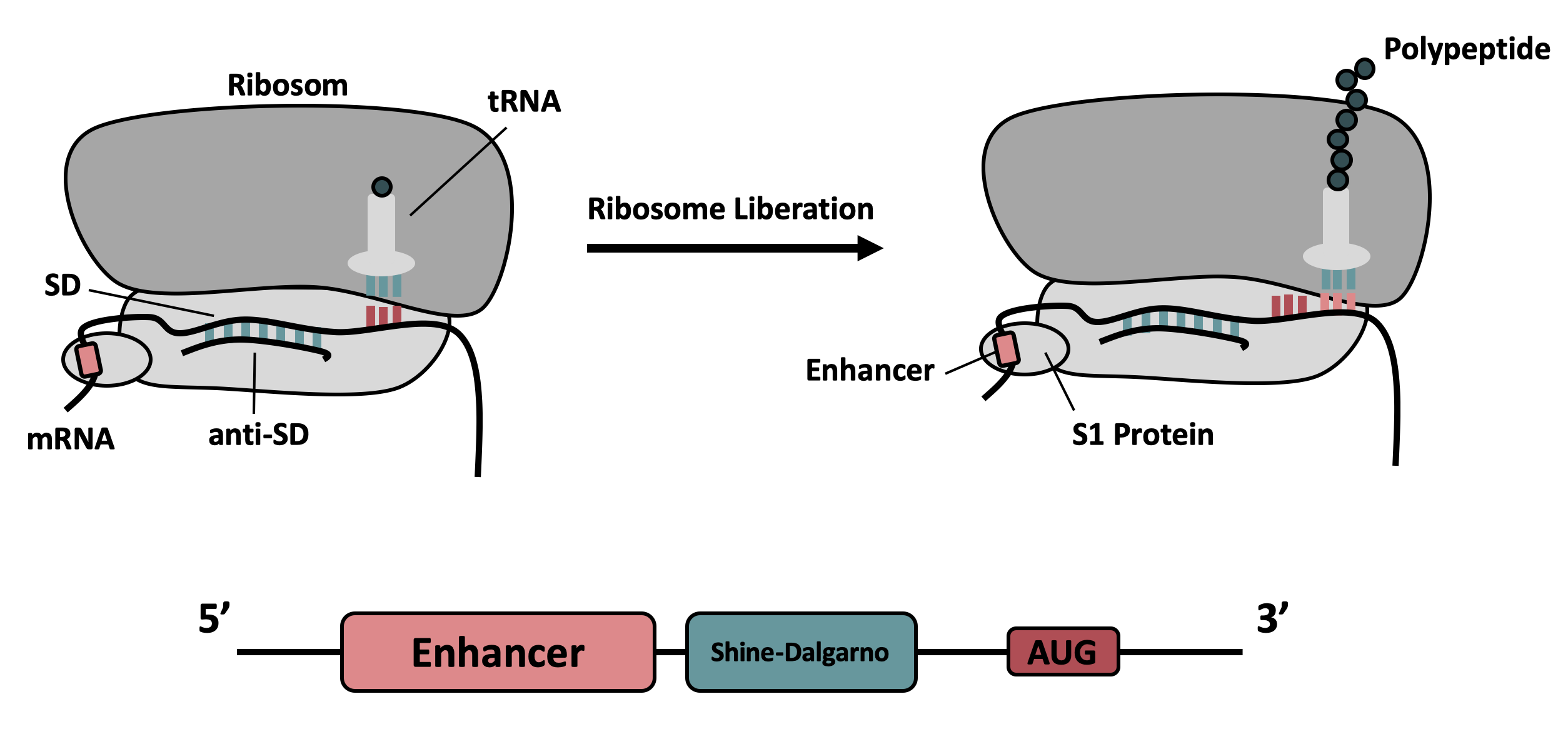
The sequence of the translation enhancing 5’-UTR can be divided into the four main features listed below:

| Sequence | Function |
|---|---|
|
AATAATTTTGTT TTAACTTTAA |
The T7 g10 leader sequence (first described by Olins et al [1] )increases the efficiency of translation initiation. This sequence contains the epsilon motif TTAACTTTA which enhances the binding of the mRNA to the 16S rRNA. |
| poly-A | Referring to Takahashi et al. [2] a spacer between the epsilon motive and the RBS improves the translation rate. |
| GAAGGAG | According to Karig et al. [3] and Lentini et. al [4] a distance of 4-9 bases between RBS and start codon increases the translation efficiency. |
| AATAATCT | According to Lentini et. al [4] an AT-rich composition between the RBS and the start codon results in the best expression results. |
Results
Fig. 1 shows the original version of the part (left) and the improved version (right) after overnight cultivation on an agar plate and after cultivation for 24 h in M9 minimal medium for better visualization of the emitted light at 512 nm [5] . Both the agar plate and the liquid culture were supplemented with chloramphenicol according to the cmp resistance on the pSB1C3 backbone. Both pictures were taken using a dark reader (Dark Reader Clare Chemical Research) for better visualization of the yellow color.
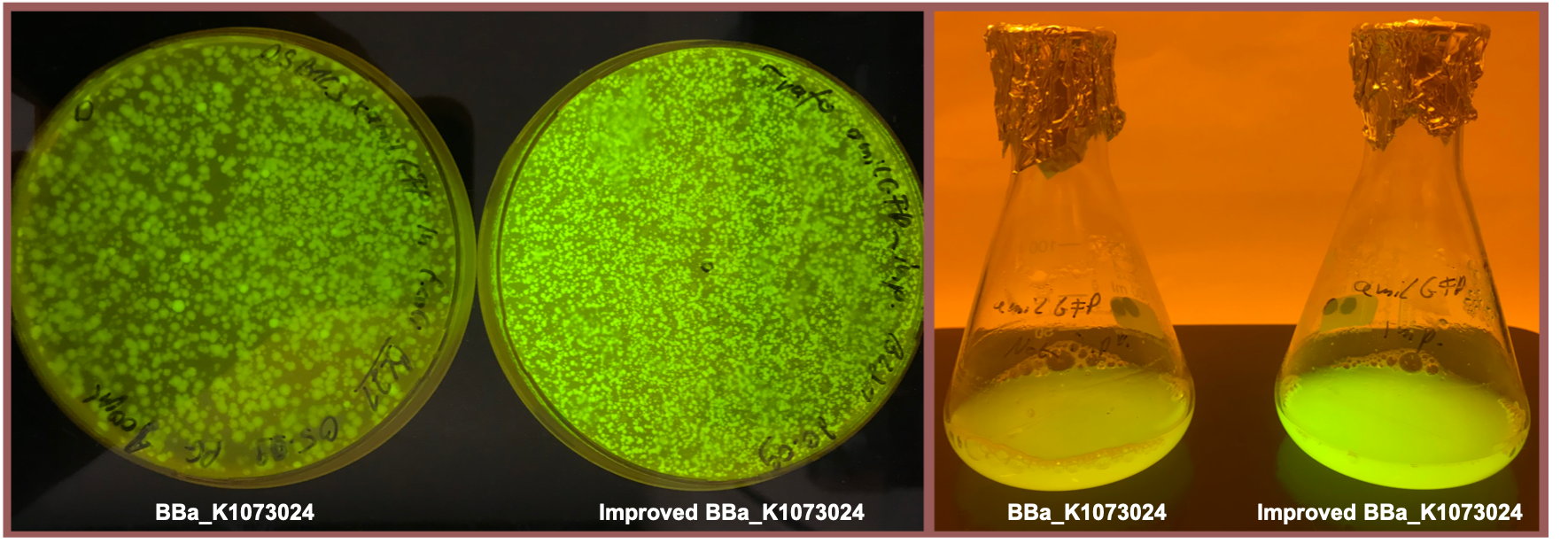
Both the agar plate and the liquid culture show an enhanced expression of the amilGFP gene after the upstream insertion of the translation enhancing 5’-UTR.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]