Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K863005"
SarahatBUGSS (Talk | contribs) m (→Usage and Biology) |
SarahatBUGSS (Talk | contribs) m (→Usage and Biology) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
[1] Susana Rodríguez Couto & José Luis Toca Herrera;Industrial and biotechnological applications of laccases: A review; 2006; Biotechnology Advances 24 500–513 | [1] Susana Rodríguez Couto & José Luis Toca Herrera;Industrial and biotechnological applications of laccases: A review; 2006; Biotechnology Advances 24 500–513 | ||
| − | The Baltimore Biocrew 2017 team discovered that proteins generated through biobrick parts can be evaluated for allergenicity. This information is important to the people using these parts in the lab, as well as when considering using the protein for mass production, or using in the environment. The allergenicity test permits a comparison between the sequences of the biobrick parts and the identified allergen proteins enlisted in a data base.The higher the similarity between the biobricks and the proteins, the more likely the biobrick is allergenic cross-reactive. In the full-length alignments by FASTA, 30% or more amount of similarity signifies that the biobrick has a Precaution Status meaning there is a potential risk with using the part. A 50% or more amount of identity signifies that the biobrick has a Possible Allergen Status. In the sliding window of 80 amino acid segments, greater than 35% signifies similarity to allergens. The percentage of similarity implies the potential of harm biobricks’ potential negative impact to exposed populations. For more information on how to assess your own biobrick part please see the | + | Allergen characterization of BBa_K863005. |
| + | The Baltimore Biocrew 2017 team discovered that proteins generated through biobrick parts can be evaluated for allergenicity. This information is important to the people using these parts in the lab, as well as when considering using the protein for mass production, or using in the environment. The allergenicity test permits a comparison between the sequences of the biobrick parts and the identified allergen proteins enlisted in a data base.The higher the similarity between the biobricks and the proteins, the more likely the biobrick is allergenic cross-reactive. In the full-length alignments by FASTA, 30% or more amount of similarity signifies that the biobrick has a Precaution Status meaning there is a potential risk with using the part. A 50% or more amount of identity signifies that the biobrick has a Possible Allergen Status. In the sliding window of 80 amino acid segments, greater than 35% signifies similarity to allergens. The percentage of similarity implies the potential of harm biobricks’ potential negative impact to exposed populations. For more information on how to assess your own biobrick part please see the “Allergenicity Testing Protocol” in the following page http://2017.igem.org/Team:Baltimore_Bio-Crew/Experiments | ||
For the biobrick Part:BBa_K863005, there was a 27.1 % of identity match and 54.3% similarity match to the top allergen in the allergen database. This means that the biobrick part is NOT of potential allergen status. In 80 amino acid alignments by FASTA window, no matches found that are greater than 35% for this biobrick. This also means that there is NOT of potential allergen status. | For the biobrick Part:BBa_K863005, there was a 27.1 % of identity match and 54.3% similarity match to the top allergen in the allergen database. This means that the biobrick part is NOT of potential allergen status. In 80 amino acid alignments by FASTA window, no matches found that are greater than 35% for this biobrick. This also means that there is NOT of potential allergen status. | ||
Latest revision as of 23:52, 1 November 2017
ecol laccase from E. coli with T7 promoter, RBS and His-tag
E.coli laccase ORF with T7, RBS and HIS tag
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Usage and Biology
In the last few years a lot of attention has been drawn to laccases due to their ability to oxidize both phenolic and nonphenolic lignin related compounds as well as highly recalcitrant environmental pollutants. This makes them very useful for applications concerning several biotechnological processes. This includes the detoxification of industrial effluents, for example from the paper and pulp, textile and petrochemical industries. Laccases are also valuable as a tool as a tool for medical diagnostics and as a bioremediation agent to clean up herbicides, pesticides and certain explosives in soil. Furthermore these enzymes are also used as catalysts for the manufacture of anti-cancer drugs and even as ingredients in cosmetics[1].
Their capacity to remove xenobiotic substances and produce polymeric products makes them a useful tool for bioremediation purposes. In our project laccases are used as cleaning agents for a water purification system.
Laccases are copper-containing polyphenol oxidase enzymes (EC 1.10.3.2) that can be found in many plants, insects, microorganisms and mainly in fungi. These enzymes fulfill several functions in different metabolic pathways.
Laccases are able to oxidize a broad range of substrates due to the contained copper-cluster, by reducing oxygen to water. The active site of the enzyme includes a four-copper-ion-cluster, which can be distinguished by spectroscopic analyses. This cluster consists of one blue copper-ion (type 1), one type 2 and two type 3 copper-ions. Because of the blue copper-ion, the laccases belong to the big family of the blue copper proteins. This specific blue copper ion is essential for the enzyme mediated radical oxidation of the phenolic groups. In this reaction the electron from the oxidation is transferred to the other three copper ions. These ions form a trinuclearic cluster, which transfers electrons to the terminal electron acceptor oxygen. By receiving four electrons the molecular oxygen is finally reduced to water.
[1] Susana Rodríguez Couto & José Luis Toca Herrera;Industrial and biotechnological applications of laccases: A review; 2006; Biotechnology Advances 24 500–513
Allergen characterization of BBa_K863005. The Baltimore Biocrew 2017 team discovered that proteins generated through biobrick parts can be evaluated for allergenicity. This information is important to the people using these parts in the lab, as well as when considering using the protein for mass production, or using in the environment. The allergenicity test permits a comparison between the sequences of the biobrick parts and the identified allergen proteins enlisted in a data base.The higher the similarity between the biobricks and the proteins, the more likely the biobrick is allergenic cross-reactive. In the full-length alignments by FASTA, 30% or more amount of similarity signifies that the biobrick has a Precaution Status meaning there is a potential risk with using the part. A 50% or more amount of identity signifies that the biobrick has a Possible Allergen Status. In the sliding window of 80 amino acid segments, greater than 35% signifies similarity to allergens. The percentage of similarity implies the potential of harm biobricks’ potential negative impact to exposed populations. For more information on how to assess your own biobrick part please see the “Allergenicity Testing Protocol” in the following page http://2017.igem.org/Team:Baltimore_Bio-Crew/Experiments
For the biobrick Part:BBa_K863005, there was a 27.1 % of identity match and 54.3% similarity match to the top allergen in the allergen database. This means that the biobrick part is NOT of potential allergen status. In 80 amino acid alignments by FASTA window, no matches found that are greater than 35% for this biobrick. This also means that there is NOT of potential allergen status.
Contents
- 1 Usage and Biology
- 2 Cultivation, Purification and SDS-PAGE
- 2.1 Shaking Flask Cultivations
- 2.2 3 L Fermentation E. coli KRX with BBa_K863005
- 2.3 Purification of ECOL
- 2.4 SDS-PAGE of ECOL purification
- 2.5 6 L Fermentation of E. coli KRX with BBa_K863005
- 2.6 Purification of ECOL
- 2.7 SDS-PAGES of ECOL purification
- 2.8 Since Regionals: 12 L Fermentation E. coli KRX with BBa_K863005
- 2.9 Purification of ECOL
- 2.10 SDS-Page of protein purification
- 3 Activity Analysis of ECOL
- 3.1 Initial activity tests of purified fractions
- 3.2 ECOL CuCl2 concentration
- 3.3 ECOL activity depending on different ABTS concentrations
- 3.4 Impact of MeOH and acetonitrile on ECOL
- 3.5 Since regionals: Searching for substrate saturation of ECOL
- 3.6 Since regionals: ECOL pH optimum
- 3.7 ECOL activity at different temperatures
- 4 MALDI-TOF Analysis of ECOL
- 5 Substrate Analysis
- 6 Immobilization
- 7 Visulization
Cultivation, Purification and SDS-PAGE
Shaking Flask Cultivations
The first trials to produce ECOL were produced in shaking flask with various designs (from 100 mL-1 to 1 L flasks, with and without baffles) and under different conditions. The parameters tested during our screening experiments were temperature (27 °C,30 °C and 37 °C), concentrations of chloramphenicol (20-170 µg mL-1), various induction strategies ([http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Autoinduction_medium autoinduction] and manual induction) and cultivation time (6 - 24 h). Furthermore it was cultivated with and without 0.25 mM CuCl2 to provide a sufficient amount of copper, which is needed for the active center of the laccase. Based on the screening experiments we identified the best conditions under which ECOL was expressed. The addition of CuCl2 did not increase the activity, so it was omitted.
- flask design: shaking flask without baffles
- medium: [http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Autoinduction_medium autoinduction medium]
- antibiotics: 60 µg mL-1 chloramphenicol
- temperature: 37 °C
- cultivation time: 12 h
The reproducibility of the measured data and results were investigated for the shaking flask and bioreactor cultivation.
3 L Fermentation E. coli KRX with BBa_K863005
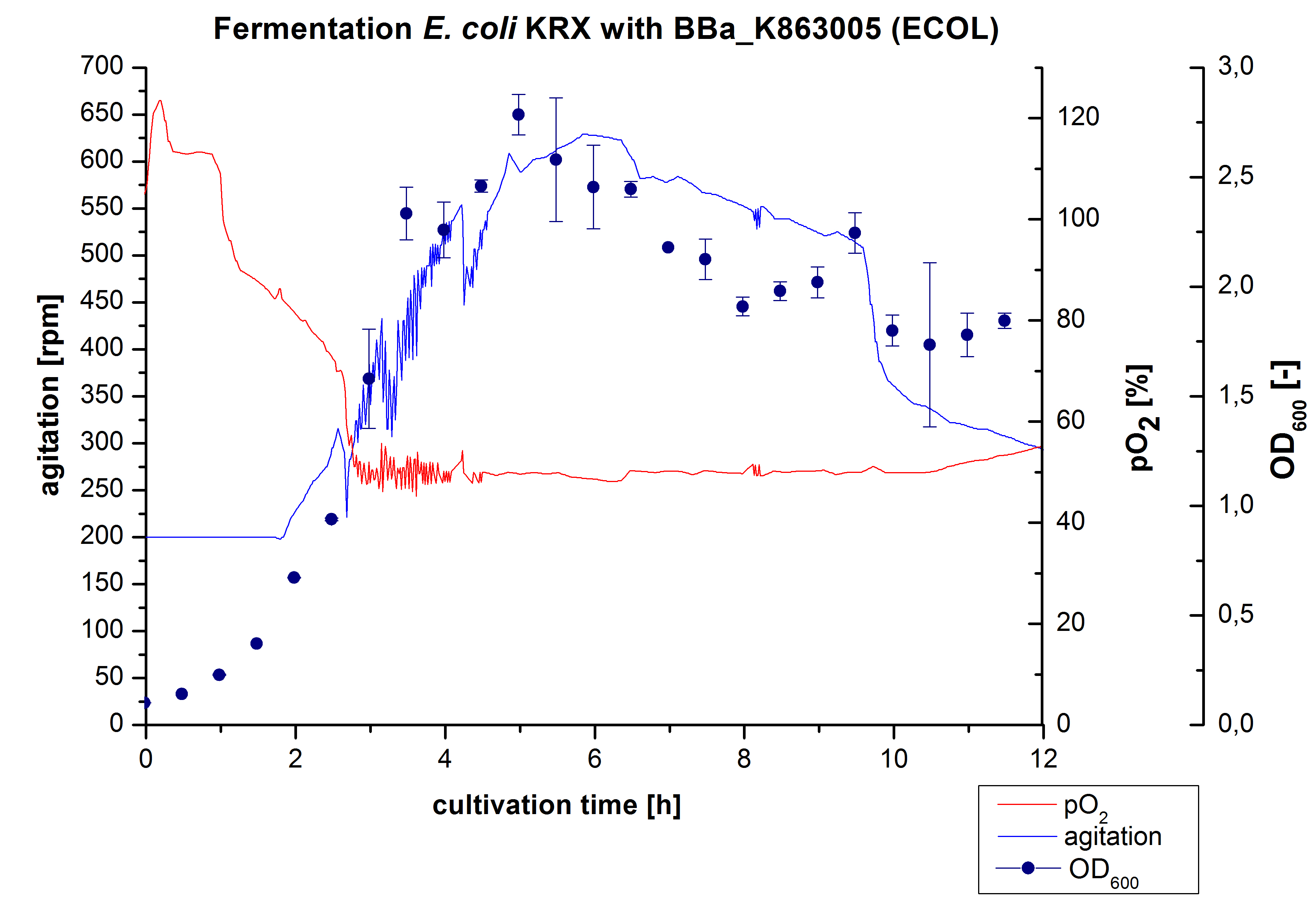
After the positive measurement of activity of ECOL we made a scale-up and fermented E. coli KRX with BBa_K863005 in an Infors Labfors fermenter with a total volume of 3 L. Agitation speed, pO2 and OD600 were determined and illustrated in Figure 1. The exponential phase started after 1.5 hours of cultivation. The cell growth caused a decrease in pO2. After 2 hours of cultivation the agitation speed increased up to 629 rmp (5.9 hours) to hold the minimal pO2 level of 50 %. Then, after 4 hours there was a break in cell growth due to induction of protein expression. The maximal OD600 of 2.78 was reached after 5 hours. In comparison to E. coli KRX (OD600,max =4.86 after 8.5 hours) and to E. coli KRX with BBa_K863000 (OD600,max =3.53 after 10 hours, time shift due to long lag phase) the OD600 max is lower. In the following hours, the OD600 and the agitation speed decreased and the pO2 increased, which indicates the death phase of the cells. This is caused by the cell toxicity of ECOL (reference: [http://www.dbu.de/OPAC/ab/DBU-Abschlussbericht-AZ-13191.pdf DBU final report]). Hence, cells were harvested after 12 hours.
Purification of ECOL
The harvested cells were resuspended in [http://2012.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Buffers_for_His-Tag_affinity_chromatography Ni-NTA- equilibration buffer], mechanically disrupted by [http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Production#Mechanical_lysis_of_the_.28bio-reactor.29_cultivation homogenization] and cell debris were removed by centrifugation. The supernatant of the cell lysate was loaded on the Ni-NTA column (15 mL Ni-NTA resin) with a flow rate of 1 mL min-1 cm-2. Then the column was washed with 10 column volumes (CV) [http://2012.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Buffers_for_His-Tag_affinity_chromatography Ni-NTA equilibration buffer]. The bound proteins were eluted by an increasing [http://2012.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Buffers_for_His-Tag_affinity_chromatography Ni-NTA elution buffer] step elution from 5 % (equates to 25 mM imidazol) with a length of 50 mL, to 50 % (equates to 250 mM imidazol) with a length of 60 mL, to 80 % (equates to 400 mM imidazol) with a length of 40 mL and finally to 100 % (equates to 500 mM imidazol) with a length of 80 mL. This strategy was chosen to improve the purification caused by a step by step increasing Ni-NTA-elution buffer concentration. The elution was collected in 10 mL fractions. Due to the high UV-detection signal of the loaded samples and to simplify the illustration of the detected product peak only the UV-detection signal of the wash step and the elution are shown. A typical chromatogram of purified laccases is illustrated here. The chromatogram of the ECOL elution is shown in Figure 2:
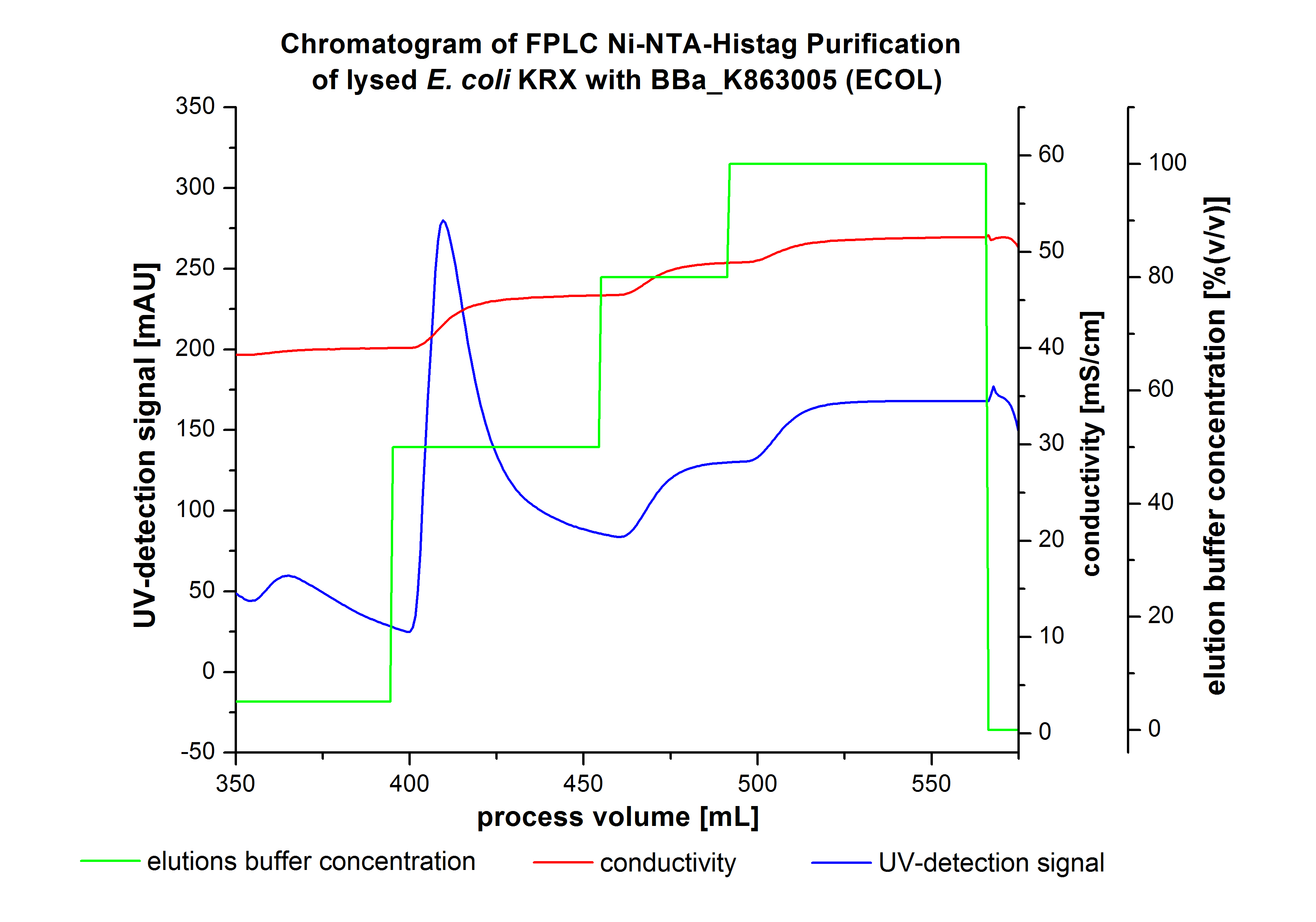
The chromatogram shows two distinguished peaks. The first peak was detected at a [http://2012.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Buffers_for_His-Tag_affinity_chromatography Ni-NTA-equilibration buffer] concentration of 5 % (equates to 25 mM imidazol) and resulted from the elution of weakly bound proteins. After increasing the Ni-NTA elution buffer concentration to 50 % (equates to 250 mM imidazol), an UV-detection signal peak of 292 mAU was measured. The area of this peak indicates that a high amount of protein was eluted. The corresponding fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE to detect ECOL. There were no further peaks detectable. The following increasing UV detection signal results from the rising imidazol concentration of the Ni-NTA elution buffer. The corresponding SDS-PAGES are shown in Figure 3.
SDS-PAGE of ECOL purification
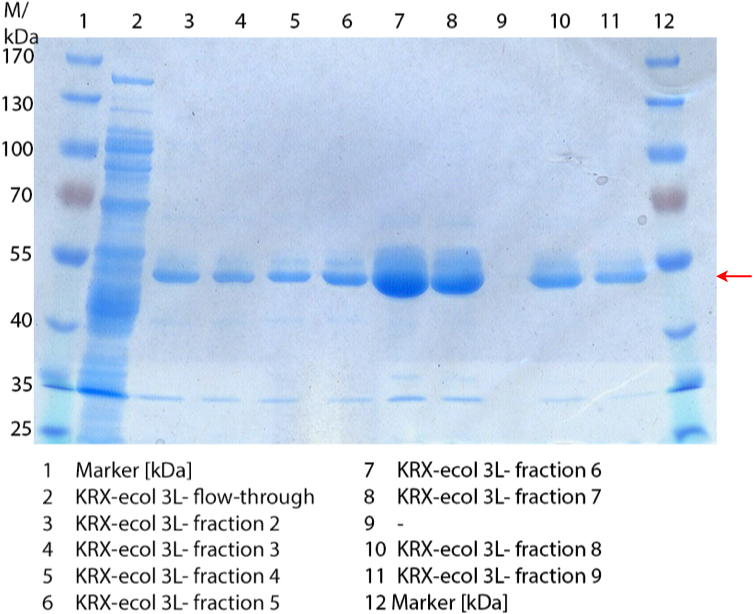
In Figure 3 the SDS-PAGE of the Ni-NTA His tag purification of the lysed culture (E. coli KRX containing BBa_K863005) is shown including the flow-through and the fractions 2 to 9. The red arrow indicates the band of ECOL with a molecular weight of 53.4 kDa, which appears in all fractions. The strongest bands appear in fractions 6 and 7. These were the first two fractions (each 10 mL) eluted with 50 % Ni-NTA elution buffer (equates to 250 mM imidazol), in which the distinguished peak appeared.
These bands were analyzed by [http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Analytics#MALDI MALDI-TOF] and identified as CueO (ECOL). In contrast, the second, faint band with a lower molecular weight could not be identified.
6 L Fermentation of E. coli KRX with BBa_K863005
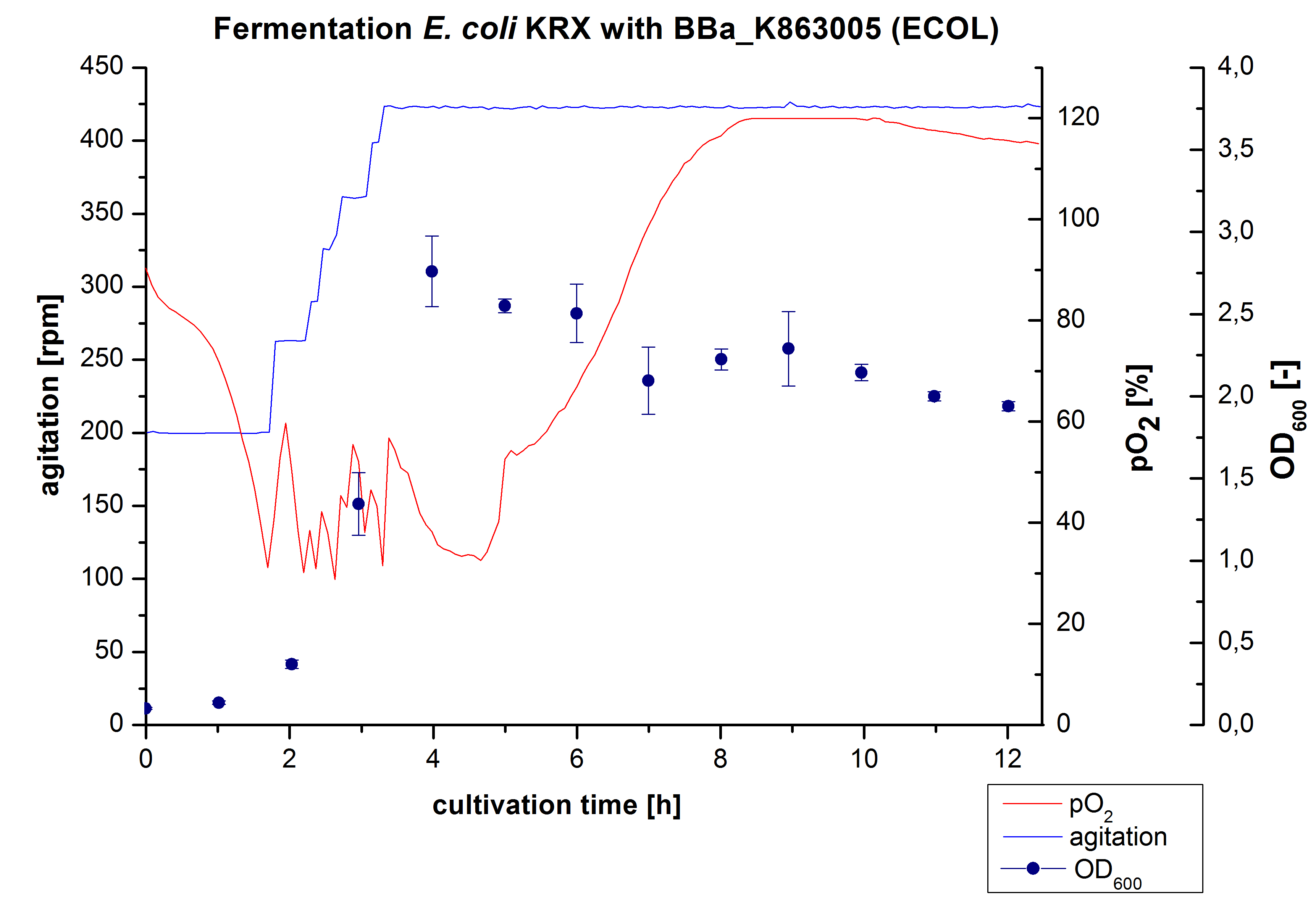
Another scale-up of the fermentation of E. coli KRX with BBa_K863005 was made up to a final working volume of 6 L in a Bioengineering NFL 22 fermenter. Agitation speed, pO2 and OD600 were determined and illustrated in Figure 4. There was no noticeable lag phase and the cells immediately began to grow. The cells were in an exponential phase between 2 and 4 hours of cultivation, which results in a decrease of pO2 value and therefore in an increase of agitation speed. After 4 hours of cultivation the maximal OD600 of 2.76 was reached, which is comparable to the 3 L fermentation of E. coli KRX with BBa_K863005. Due to induction of protein expression there is a break in cell growth. The death phase started, which is indicated by an increasing pO2 and a decreasing OD600. This demonstrates the cytotoxicity of the laccase for E. coli, which was reported by the [http://www.dbu.de/OPAC/ab/DBU-Abschlussbericht-AZ-13191.pdf DBU]. In comparison to the fermentation of E. coli KRX with BBa_K863000 under the same conditions (OD600,max= 3.53), the OD600,max was lower. Cells were harvested after 12 hours.
/sub
Purification of ECOL
The harvested cells were resuspended in [http://2012.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Buffers_for_His-Tag_affinity_chromatography Ni-NTA-equilibration buffer], mechanically disrupted by [http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Production#Mechanical_lysis_of_the_.28bio-reactor.29_cultivation homogenization] and cell debris were removed by centrifugation. The supernatant of the cell lysate was loaded on the Ni-NTA column (15 mL Ni-NTA resin) with a flow rate of 1 mL min-1 cm-2. The column was washed by 10 column volumes (CV) [http://2012.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Buffers_for_His-Tag_affinity_chromatography Ni-NTA- equilibration buffer]. The bound proteins were eluted by an increasing [http://2012.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Buffers_for_His-Tag_affinity_chromatography Ni-NTA- elution buffer] gradient from 0 % to 100 % with a length of 200 mL and the elution was collected in 10 mL fractions. Due to the high UV-detection signal of the loaded samples and to simplify the illustration of the detected product peak only the UV-detection signal of the wash step and the eluate are shown. A typical chromatogram of purified laccases is shown here. The chromatogram of the ECOL elution is shown in Figure 5:
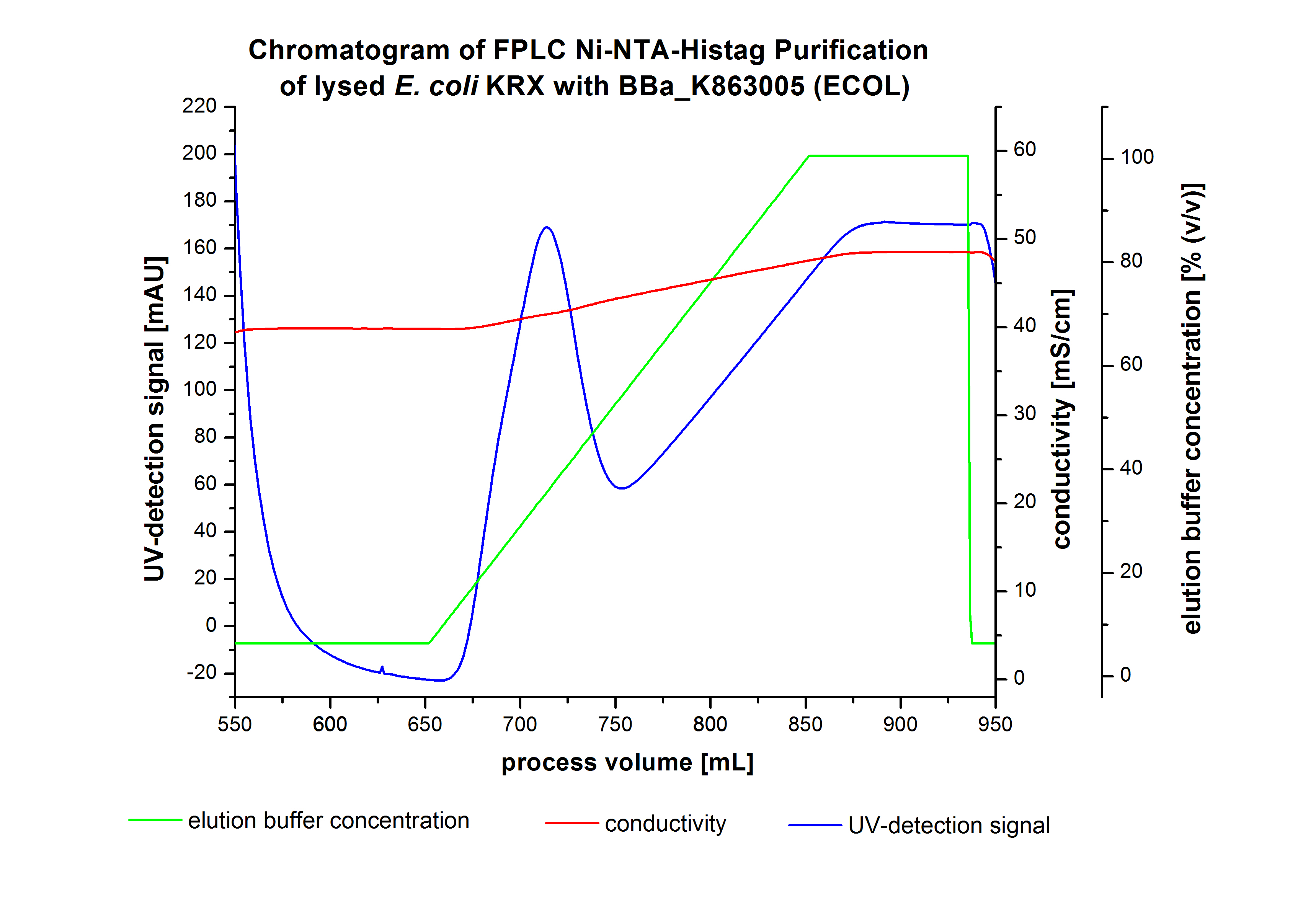
After washing the column with 10 CV [http://2012.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Buffers_for_His-Tag_affinity_chromatography Ni-NTA-elution buffer] the elution process was started. At a process volume of 670 mL to 750 mL the chromatogram shows a remarkable widespread peak (UV-detection signal 189 mAU) caused by the elution of a high amount of proteins. The run of the curve show a fronting. This can be explained by the elution of weakly bound proteins, which elutes at low imidazol concentrations. A better result could be achieved with a step elution strategy ([http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Results/Summary#Purification_of_ECOL see purification of the 3 L Fermentation above]). To detect ECOL the corresponding fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE.
SDS-PAGES of ECOL purification
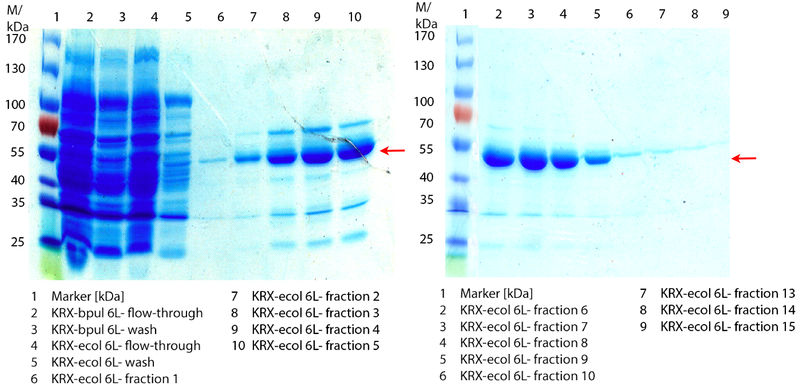
In Figure 6 the SDS-PAGE of the Ni-NTA His tag purification of the lysed culture E. coli KRX containing BBa_K863005 (6 L fermentation) including the flow-through, wash and the fractions 1 to 15 (except from fraction 11/12) is shown. The red arrow indicates the band of ECOL with a molecular weight of 53.4 kDa, which appears in all fractions. The strongest bands appear from fractions 3 and 8 with a decreasing amount of other non-specific bands. In summary, the scale up was successful, improving protein production and purification once again.
Since Regionals: 12 L Fermentation E. coli KRX with BBa_K863005
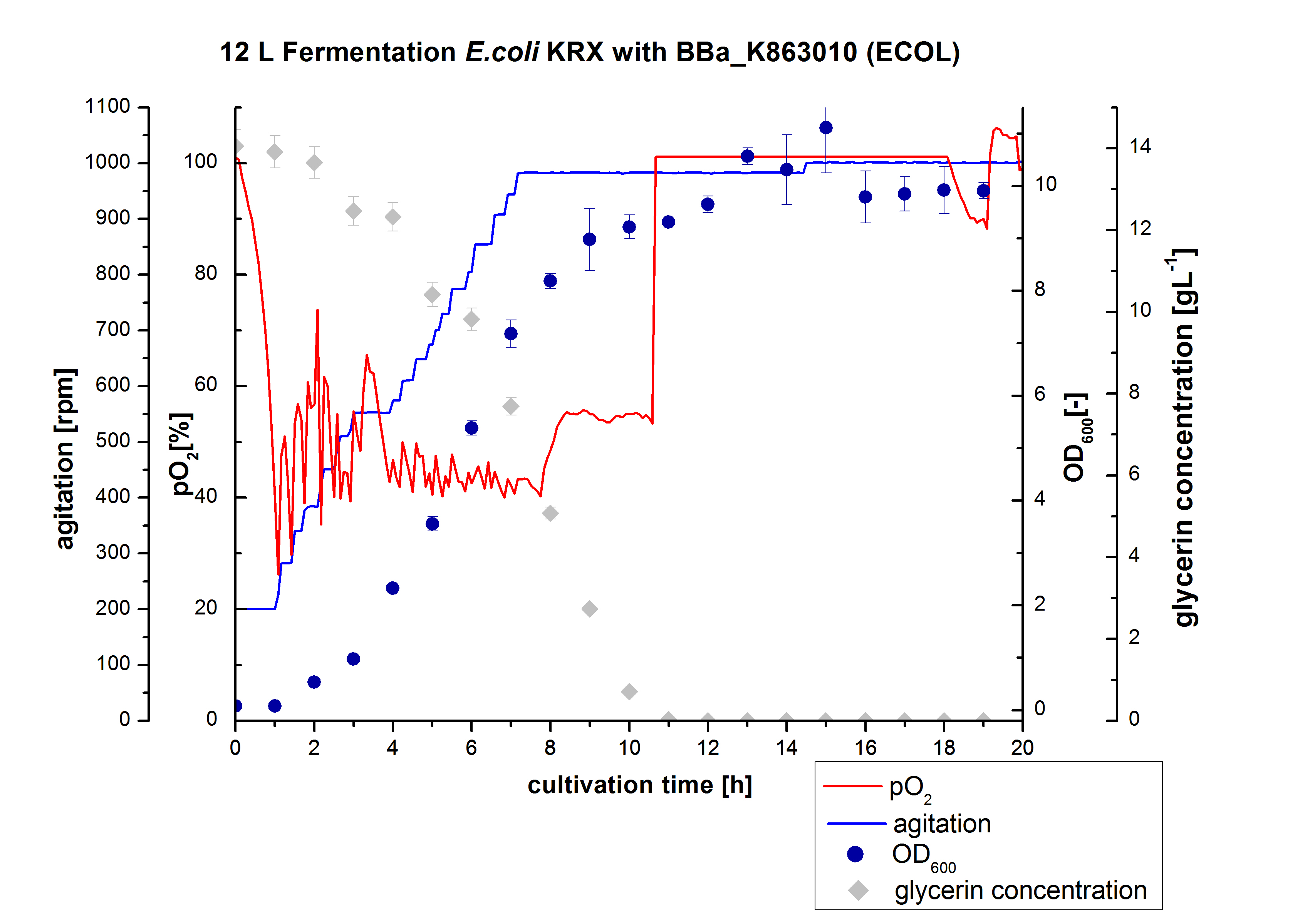
<p align="justify"> Finally another scale-up was made and E. coli KRX with BBa_K863005 was fermented in an Bioengineering NLF 22 fermenter with a total volume of 12 L to produce a high amount of the enzyme for further characterizations. This time [http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#HSG_Autoinduction_medium HSG autoinduction medium] was used to get a higher biomass. Agitation speed, pO2 and OD600 were determined and the glycerin concentration of the samples analyzed. The data are illustrated in Figure 7. For adaption to the medium, there was a lag phase of one hour. Between the 3 and 8 hours of cultivation the cells were in the exponential phase. During this phase the cells consumed O2, so that the agitation speed was increased automatically, as well as glycerin. After 11 hours of cultivation the pO2 increased, the glycerin was completely consumed and the cells were in the stationary phase. The maximal OD600 of 11.1 was reached after 15 hours of cultivation. The cells were harvested after 19 hours of cultivation.
Purification of ECOL
The harvested cells were resuspended in [http://2012.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Buffers_for_His-Tag_affinity_chromatography Ni-NTA- equilibration buffer], mechanically disrupted by [http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Production#Mechanical_lysis_of_the_.28bio-reactor.29_cultivation homogenization] and cell debris were removed by centrifugation, microfiltration as well as diafiltration to concentrate the protein concentration in the cell lysate solution. This solution of the cell lysate was loaded on the Ni-NTA column (15 mL Ni-NTA resin) with a flow rate of 1 mL min-1 cm-2. Then the column was washed with 10 column volumes (CV) [http://2012.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Buffers_for_His-Tag_affinity_chromatography Ni-NTA equilibration buffer]. The bound proteins were eluted by an increasing [http://2012.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Buffers_for_His-Tag_affinity_chromatography Ni-NTA elution buffer] step elution from 5 % (equates to 25 mM imidazol) with a length of 40 mL, to 50 % (equates to 250 mM imidazol) with a volume of 80 mL, to 80 % (equates to 400 mM imidazol) and finally to 100 % (equates to 500 mM imidazol) with a volume of 80 mL. This strategy was chosen to improve the purification caused by a step by step increasing Ni-NTA-elution buffer concentration. The elution was collected in 10 mL fractions. In Figure 8 only the UV-detection signal of the wash step and the elution are shown, this is because of the high UV-detection signal of the loaded samples and to simplify the illustration of the detected product peak. A typical chromatogram of purified laccases is illustrated here. The chromatogram of the ECOL elution is shown in Figure 8.
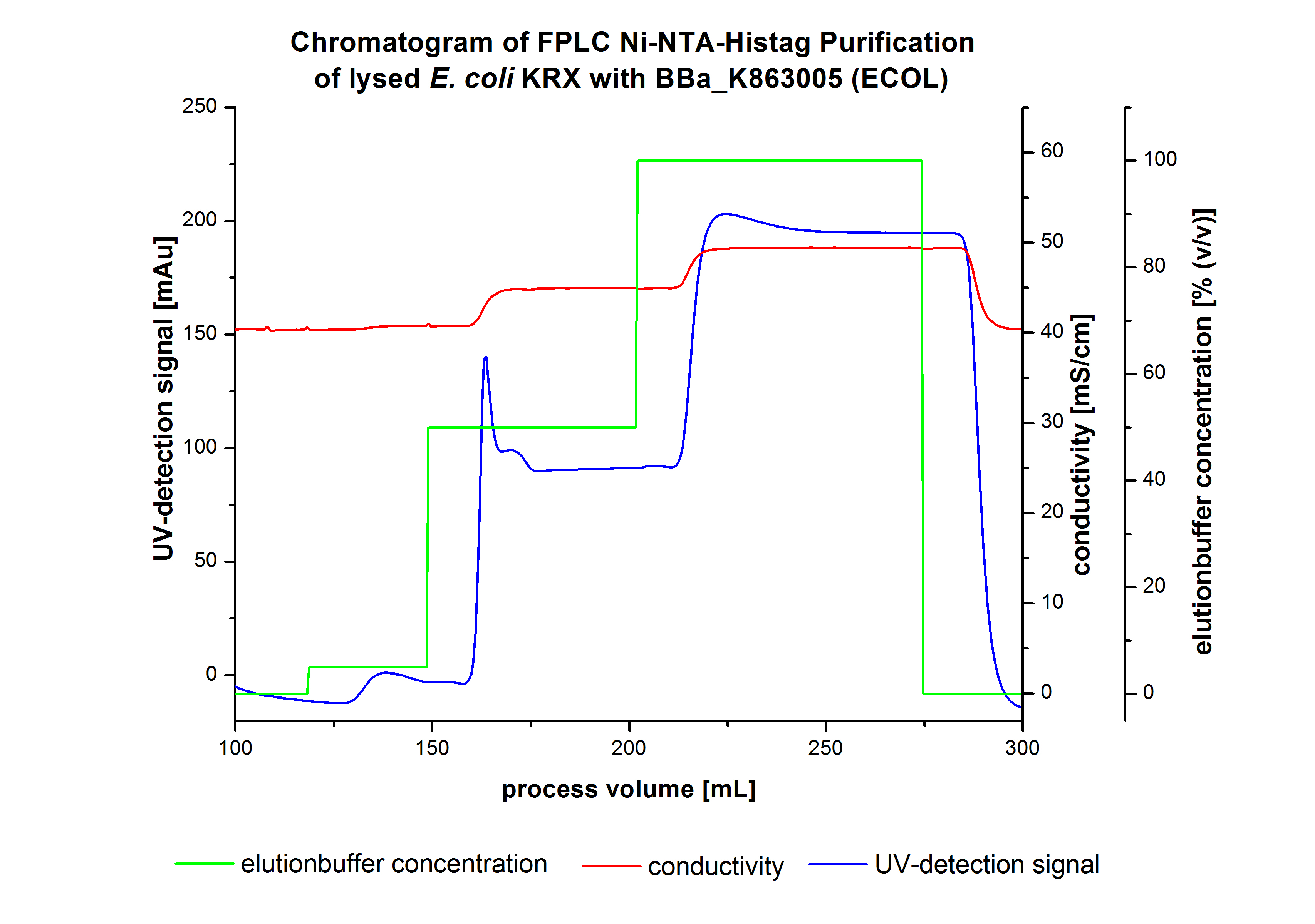
The chromatogram shows two distinguished peaks. The first peak was detected at a [http://2012.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Buffers_for_His-Tag_affinity_chromatography Ni-NTA-equilibration buffer] concentration of 5 % (equates to 25 mM imidazol) and resulted from the elution of weakly bound proteins. After increasing the Ni-NTA elution buffer concentration to 50 % (equates to 250 mM imidazol), an UV-detection signal peak of 140 mAU was measured. The area of this peak indicates that a high amount of protein was eluted. In addition, a second peak right behind the first peak can be detected. At this point it is not clear which peak contains our product and which peak is caused by impurities. The corresponding fractions were analyzed by SDS-PAGE to detect ECOL. A last peak can be detected after increasing the elution buffer concentration to 100 % (equates to 500 mM imidazol). This peak could be explained by impurities which were strongly bound on the Ni-NTA-resin. All corresponding fractions with an UV-signal were analyzed by SDS-PAGES. The Results are shown in Figure 8.
SDS-Page of protein purification
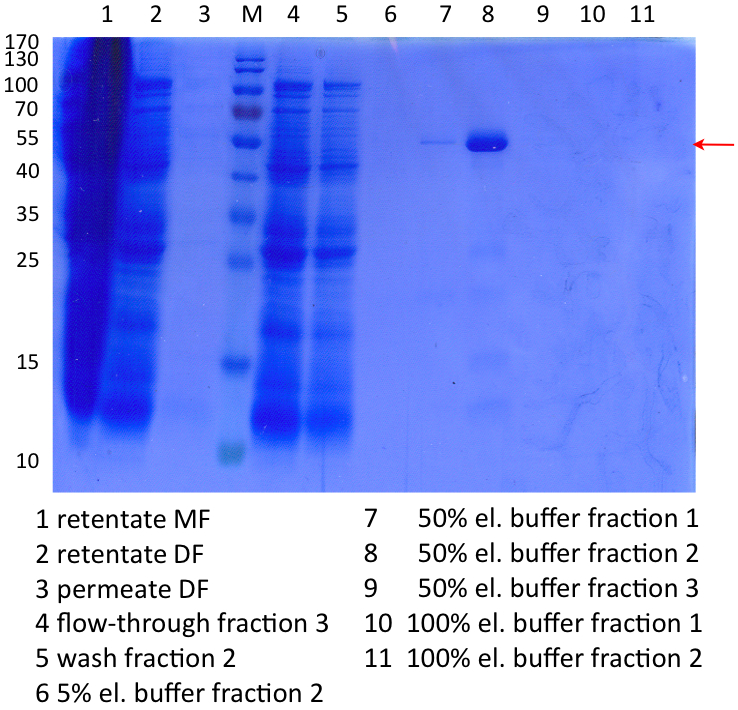
In Figure 9 the SDS-PAGE of the Ni-NTA purification of the lysed E.coli KRX culture containing BBa_K863005 is illustrated. It shows the permeate and retentate of microfiltration and diafiltration respectively, several fractions of flow-through, wash and the elutions with different buffer concentrations respectively. The selected samples were taken where peaks were seen in the chromatogram. The His-tagged BPUL has a molecular weight of 53.4 kDa. The red arrow shows ECOL. Unfortunately it could not be identified because the MALDI was broken-down for the last two weeks.
Activity Analysis of ECOL
Initial activity tests of purified fractions
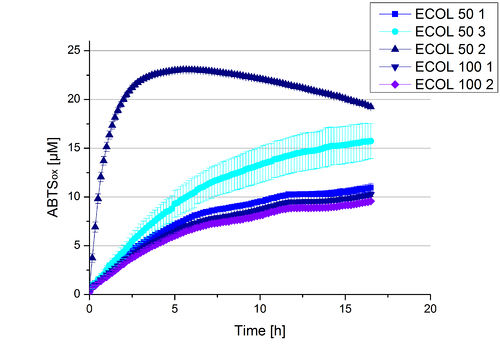
A cultivation of ECOL has been done and the fractions of the purification were analyzed further on protein content and re-buffered subsequently into deionized H2O. To determine the protein content afterwards because of loss of proteins through re-buffering, another [http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Amsterdam/Labjournal#Tuesday_October_17th/ protein concentration measurement] has been done. The re-buffered fractions have been incubated with 0.4 mM CuCl2 to gain higher activity of the laccases, because they are copper-dependent. Standard activity tests were done with all ECOL fractions with adjusted protein content for comparison. The experimental setup included the ECOL fractions, Britton-Robinson buffer (pH 5) and 0.1 mM ABTS. Measurements were done at 25 °C. Resulting, one fraction showed very high activity in comparison to the other fractions (see Fig. 10). This fraction, fraction 50% 2, oxidized up to 23 µM ABTS after 5 hours. The first number of the sample indicates the percentage of used elution buffer, whereas the second number stands for the fraction number of this elution. This fraction was set as containing 90 % ECOL laccase of the whole protein content. Therefore a ECOL concentration of 63,9 µg mL-1 was gained. This fraction was analyzed further on pH optimum, temperature dependency and ABTS saturation.
ECOL CuCl2 concentration
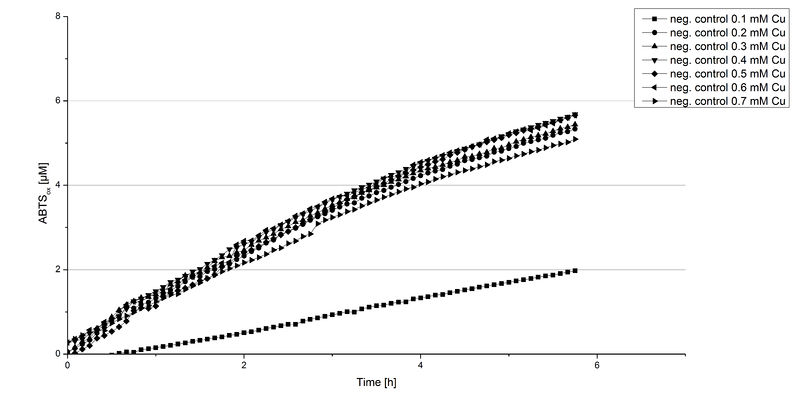
Another test of ECOL was done to survey the best CuCl2 concentration for the activity of the purified ECOL laccase. 0.03 mg mL-1 protein were incubated with different CuCl2 concentration ranging from 0 to 0.7 mM CuCl2. Activity tests were performed with the incubated samples, in 100 mM sodium actetate buffer (pH 5), 0.1 mM ABTS, to a final volume of 200 µL. The activity was measured at 420 nm, 25°C and over a time period of 10 hours. As expected the saturation takes place after 5 hours (see Figure 11). The differences in the activity of ECOL laccase incubated in different CuCl2 differ minimal. The highest activity of ECOL laccase is observed after incubation with 0.4 mM CuCl2 (42% of added ABTS). With a higher concentration of 0.7 mM CuCl2 the activity seems to be reduced (only 41% ABTS got oxidized). This leads to the assumption that CuCl2 supports the ECOL laccase activity but concentrations exceeding this value of CuCl2 may have a negative impact on the ability of oxidizing ABTS. Without any CuCl2 application ECOL laccase show less activity in oxidizing ABTS (see Figure 12). This fits the expectations as laccases are copper reliant enzymes and gain their activity through the incorporation of copper. Additionally negative controls were done using the tested concentrations of CuCl2 but no laccase was added to detect the oxidization of ABTS through copper (see Figure 12). The more CuCl2 was present, the more ABTS was oxidized after 5 hours. Still the maximal change accounts only for ~6% oxidized ABTS after 5 hours.
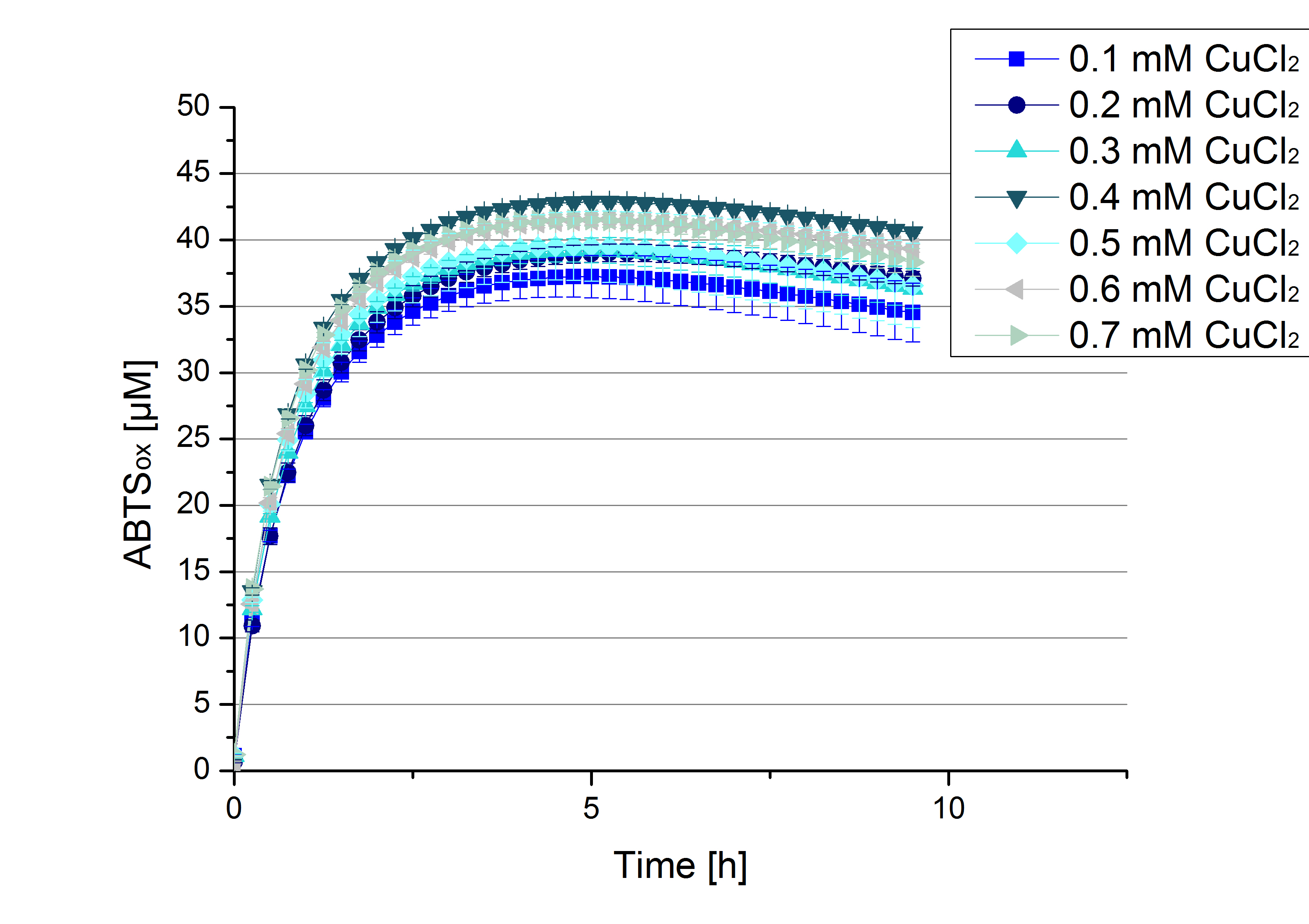
In relation to apply the laccase in waste water treatment plants it is beneficial knowing, that small amounts of CuCl2 are enough to activate the enzymes. This reduces the cost factor for the needed CuCl2 to incubate the laccases before application.
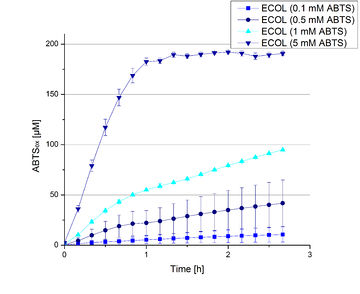
ECOL activity depending on different ABTS concentrations
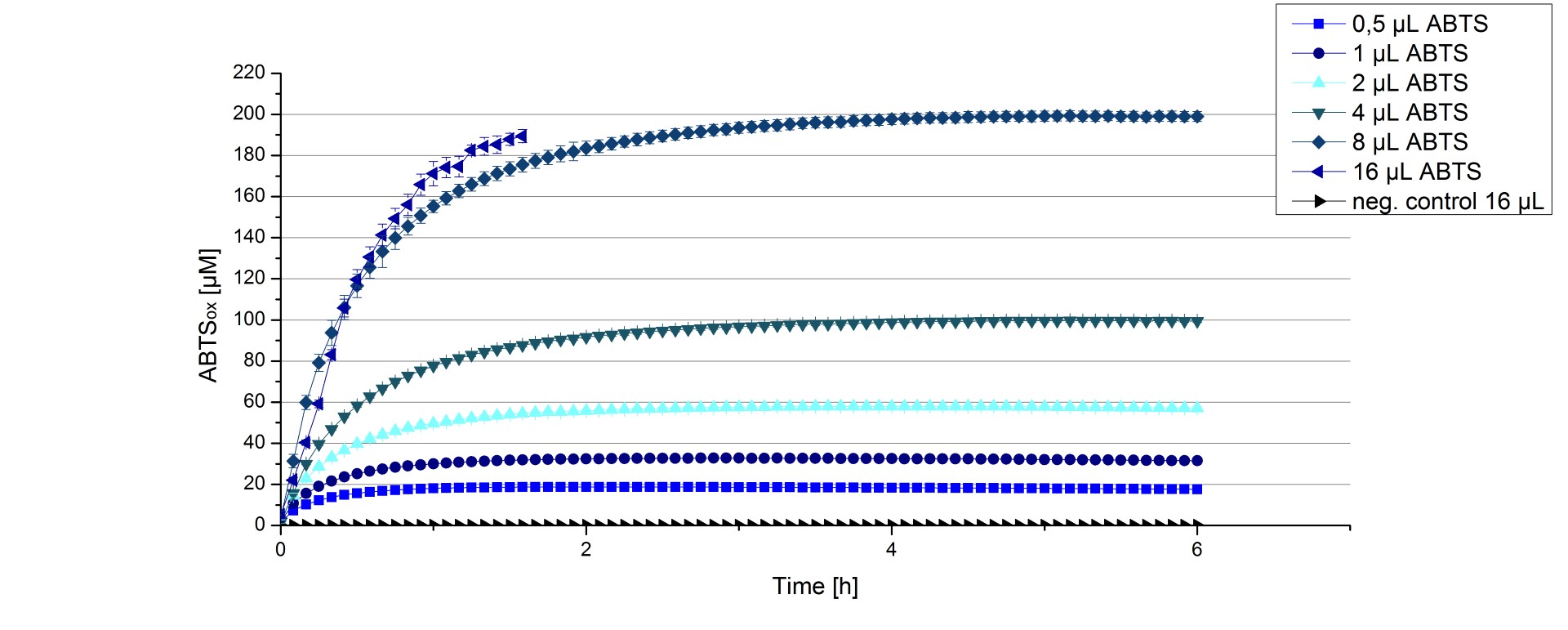
Furthermore ECOL laccase were tested using different amounts of ABTS to calculate KM and Kcat values. The same measurement setup as described above was used only with different amounts of ABTS. As anticipated the amount of oxidized ABTS increased in dependence of the amount of ABTS used (Figure 13). The results of the measurements of the samples tested with 16 µL could not be detected longer than 1.5 h because the values were higher than the detection spectrum of the device used ([http://2012.igem.org/Team:Bielefeld-Germany/Protocols/Materials#Tecan_Infinite_Microplate_Reader TecanReader]).
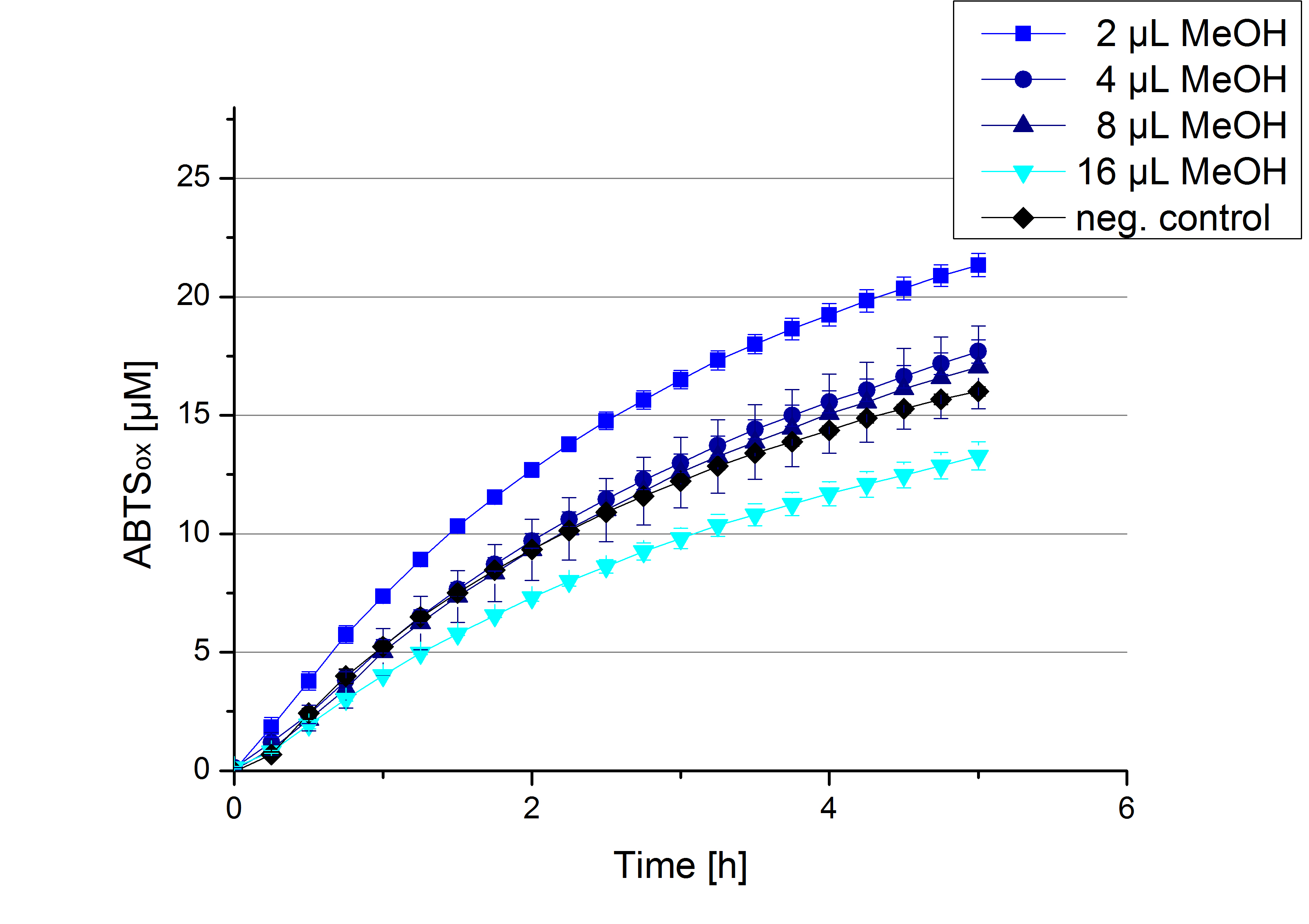
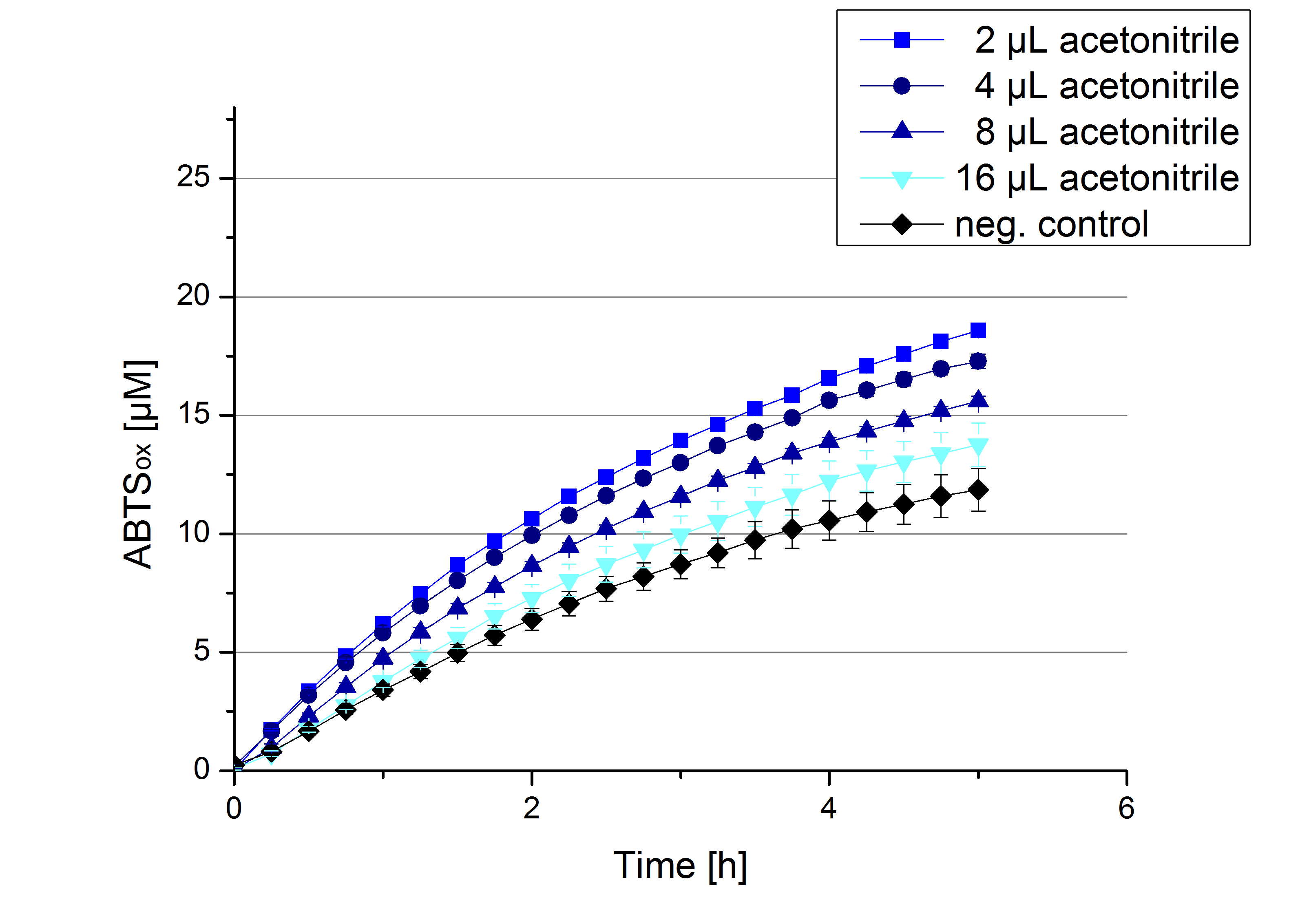
Impact of MeOH and acetonitrile on ECOL
For substrate analytic tests the influence of MeOH and acetonitrile on ECOL laccase had to be determined, because substrates have to be dissolved in these reagents. The experiment setup included 0.03 mg mL-1 ECOL laccase, 100 mM sodium acetate buffer, different amounts of MeOH (Figure 14) or acteonitrile (Figure 15), 0.1 mM ABTS, to a final volume of 200 µL. The activity of ECOL was found to be increased in presence of low concentrations (1 % v/v) of either MeOH or acetonitrile resulting in an higher amount of oxidized ABTS after 5 hours. Increasing concentrations of either substance decrease this positive effect, resulting in a significantly decreased laccase activity in presence of 8 % (v/v) MeOH. These results indicate that for further measurements in substrate analytics it is recommended not to use high concentrations of MeOH or acetonitrile to ensure the functionality of ECOL.
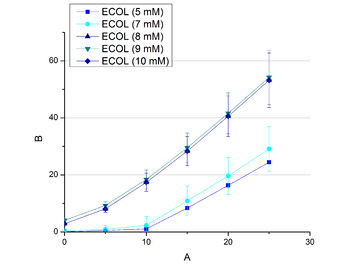
Since regionals: Searching for substrate saturation of ECOL
To calculate the activity in Units mg-1, measurements had to be done under substrate saturation. With this the comparison of Units mg-1 with other laccase activities and the literature is possible. To find the optimal substrate saturation ABTS concentrations ranging from 0.1 mM to 8 mM were applied in an experimental setup containing Britton Robinson buffer (pH 5) and temperature conditions of 25 °C. For measurements with 0.1 mM to 5 mM ABTS, 616 ng BHAL laccase were used (see Fig. 16). For measurements with 5 mM to 8 mM ABTS only 308 ng BHAL laccase were applied (see Fig. 17). The amount of oxidized ABTS increased according to the increase of ABTS concentration. To make sure that the substrate saturation is given, 9 mM ABTS have been used in further tests.
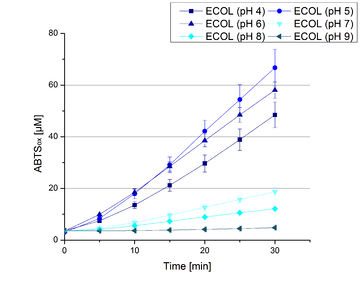
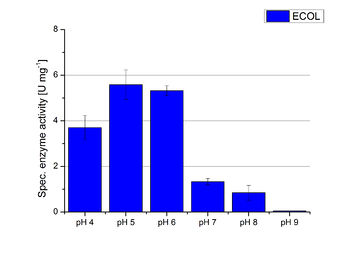
Since regionals: ECOL pH optimum
Activity assay measurements for ECOL laccases were done to find the optimal pH for further analysis. Britton Robinson buffer, adjusted to pHs ranging from pH 4 to pH 9, was used with 9 mM ABTS to detect the change in OD420. The measurements were done with 308 ng ECOL laccase for each sample. The highest activity was reached when measured in Britton Robinson buffer at pH 4 and pH 5 (see Fig. 18, Fig. 19 and Fig. 20). More than 5 U mg-1 of specific enzyme activity have calculated for these pHs (see Fig. 20). When testing the activity under basic conditions, the enzyme activity decreases. At pH 7 about 1 U mg-1 was determined. This makes an application of the ECOL not feasible since the water in the waste water treatment plants is in average of pH 6.9.
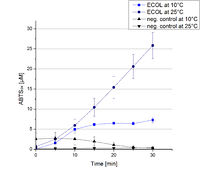
ECOL activity at different temperatures
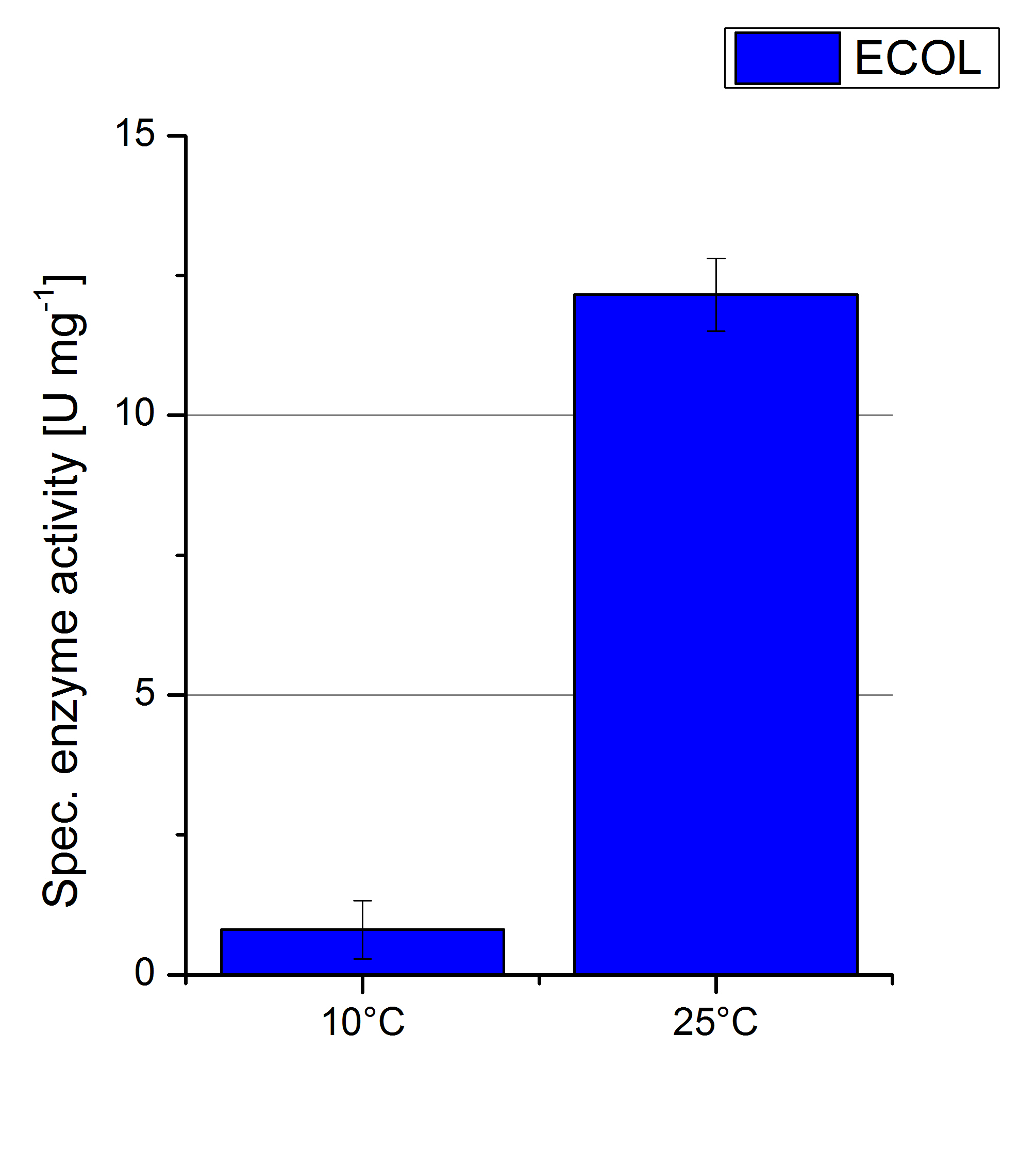
To investigate the activity of ECOL at temperatures that will apply at a waste water treatment plant throughout the year, activity tests were performed at 10 °C and 25 °C as described above. The measurements were conducted for 30 minutes. The obtained results reveal a lower activity of ECOL at 10 °C in comparison to 25 °C (see Fig. 21). The received values were used to calculate the specific enzyme activity which was between 1 and 12 U mg-1 , respectively (see Fig. 22). The negative control without ECOL but 0.4 mM CuCl2 at 10 °C and 25 °C show a negligible oxidation of ABTS. The activity of ECOL is decreased to about 90% at 10 °C. An application of ECOL at warm temperatures is therefore possible but during the cold seasons a more cryo stable enzyme would be preferable.
MALDI-TOF Analysis of ECOL
The E. coli laccase was identified using the following software
- FlexControl
- Flexanalysis and
- Biotools
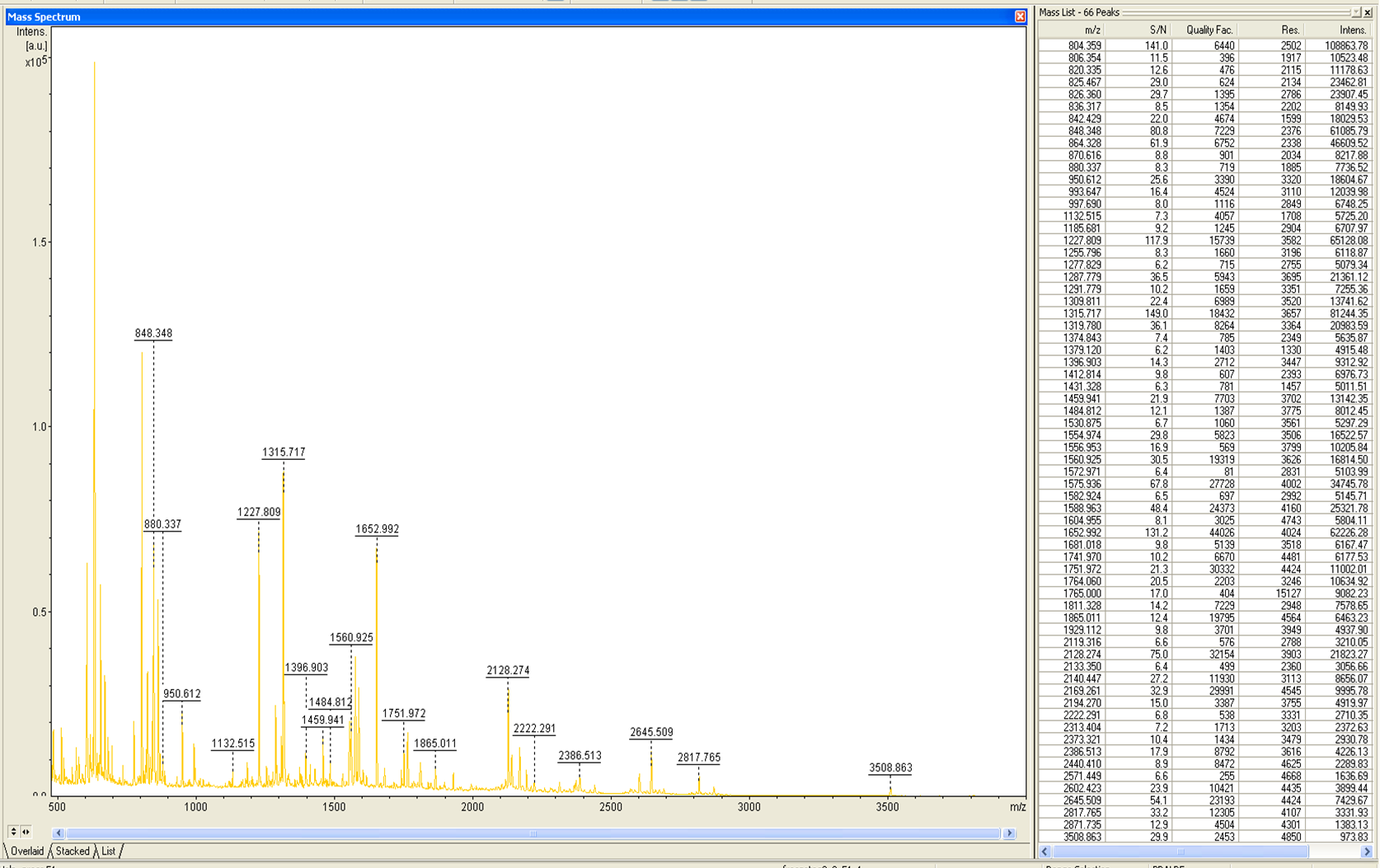
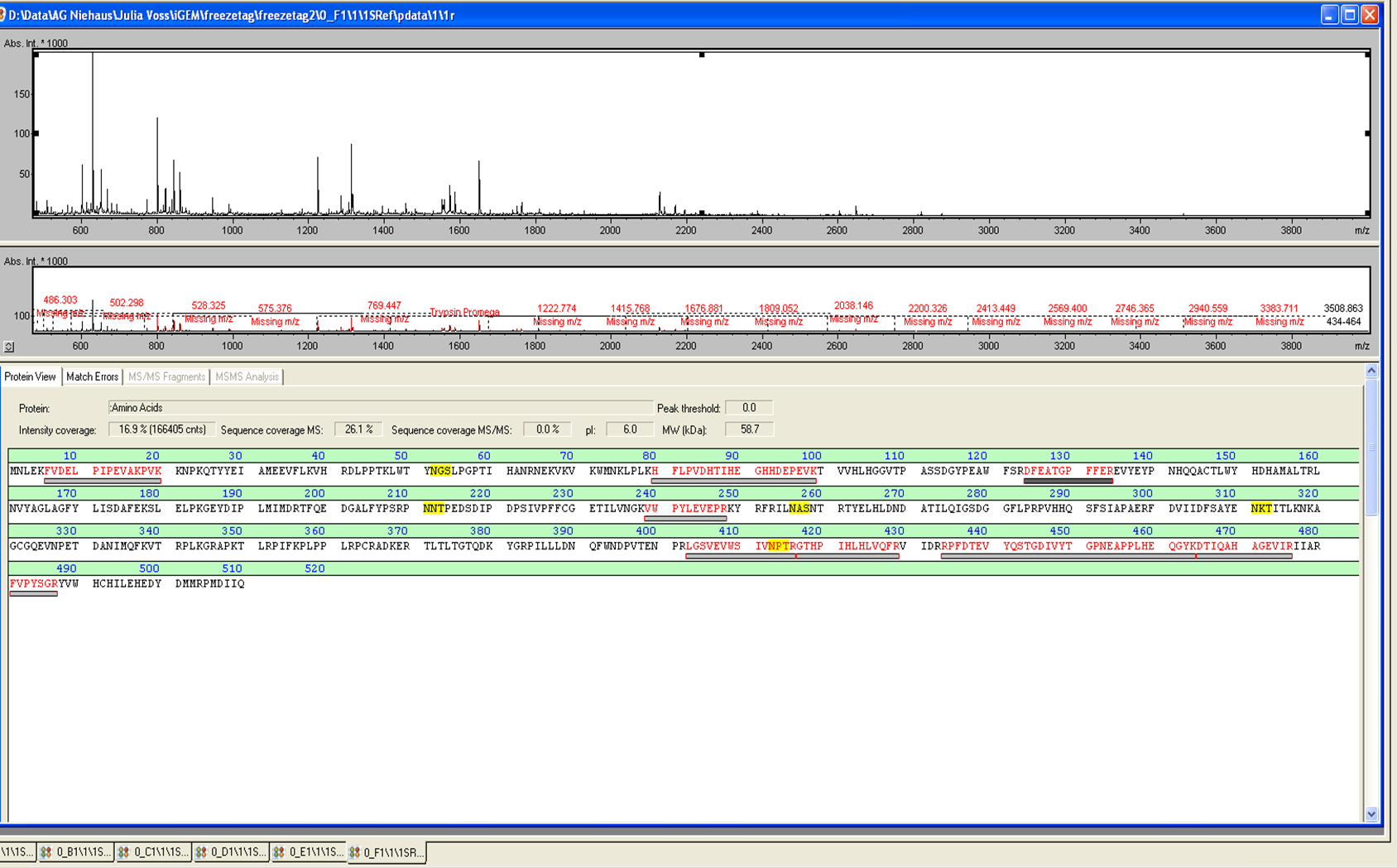
from Brunker Daltronics. TheE. coli laccase P36649 was identified with a mascot-score of 108 with an automatic run. In Figure 23 and 24 the chromatogram of the peptid mass fingerprint and the single masses are shown with a sequence coverage of 26,1%. It can be assumed that the isolated protein is ECOL.
Substrate Analysis
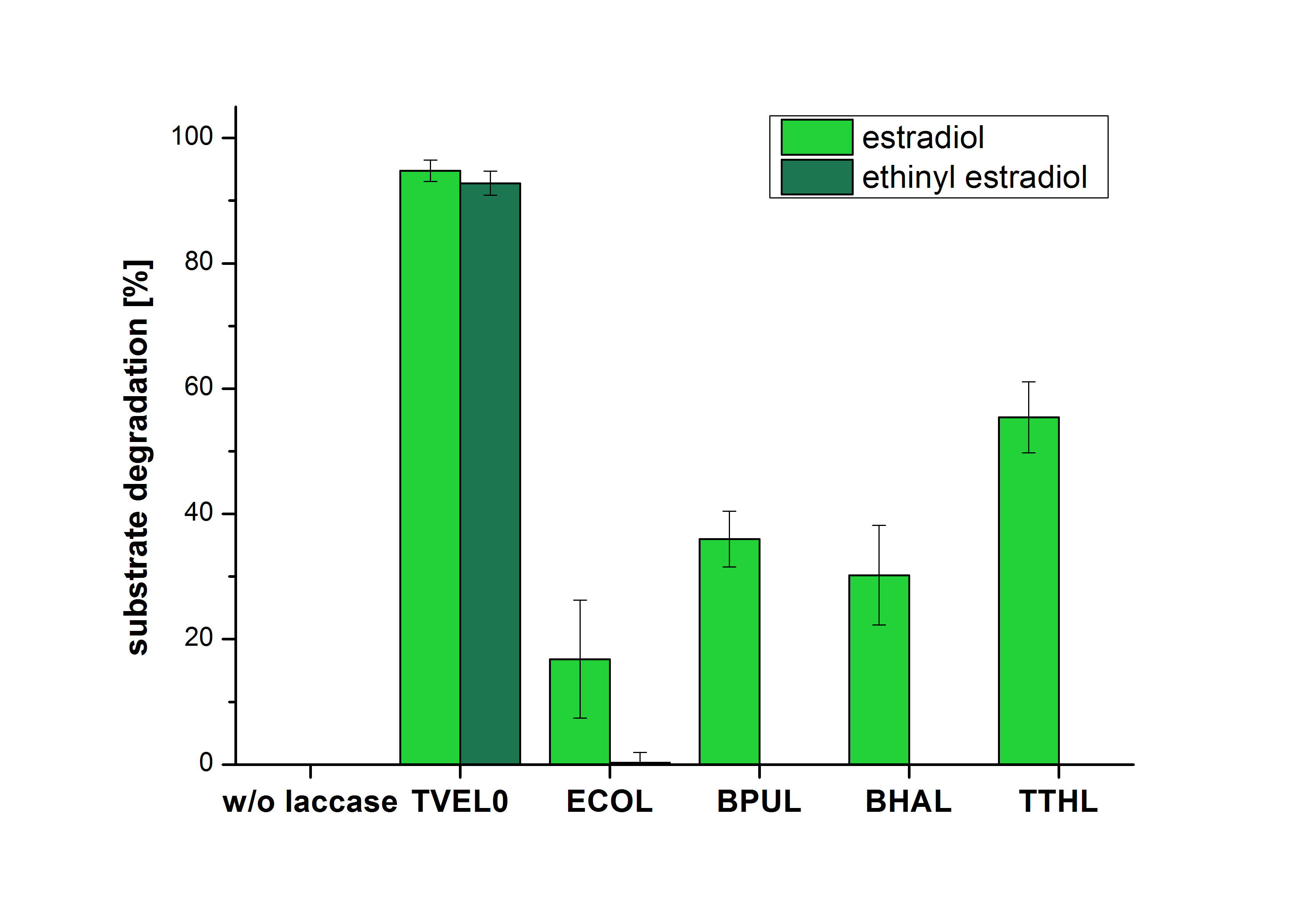
The measurements were made to test if the produced laccases were able to degrade different hormones. Therefore the produced laccases were inserted in the same concentrations (3 µg mL-1) to the different measurement approaches. To work with the correct pH value (which were measured by the Team Activity Test) Britton Robinson buffer at pH 5 was used for all measurements. The initial substrate concentration was 5 µg mL-1. The results of the reactions without ABTS are shown in Figure 25. On the Y-axis the percentages of degraded estradiol (blue) and ethinyl estradiol (red) are indicated. The X-axis displays the different tested laccases. The degradation was measured at t0 and after five hours of incubation at 30 °C. The negative control was the substrate in Britton Robinson buffer and showed no degradation of the substrates. The bought laccase TVEL0 which is used as positive control is able to degrade 94.7 % estradiol and 92.7 % ethinyl estradiol. The laccase BPUL (from Bacillus pumilus) degraded 35.9 % of used estradiol after five hours. ECOL was able to degrade 16.8 % estradiol. BHAL degraded 30.2 % estradiol. The best results were determined with TTHL (laccase from Thermus thermophilus). Here the percentage of degradation amounted 55.4 %.
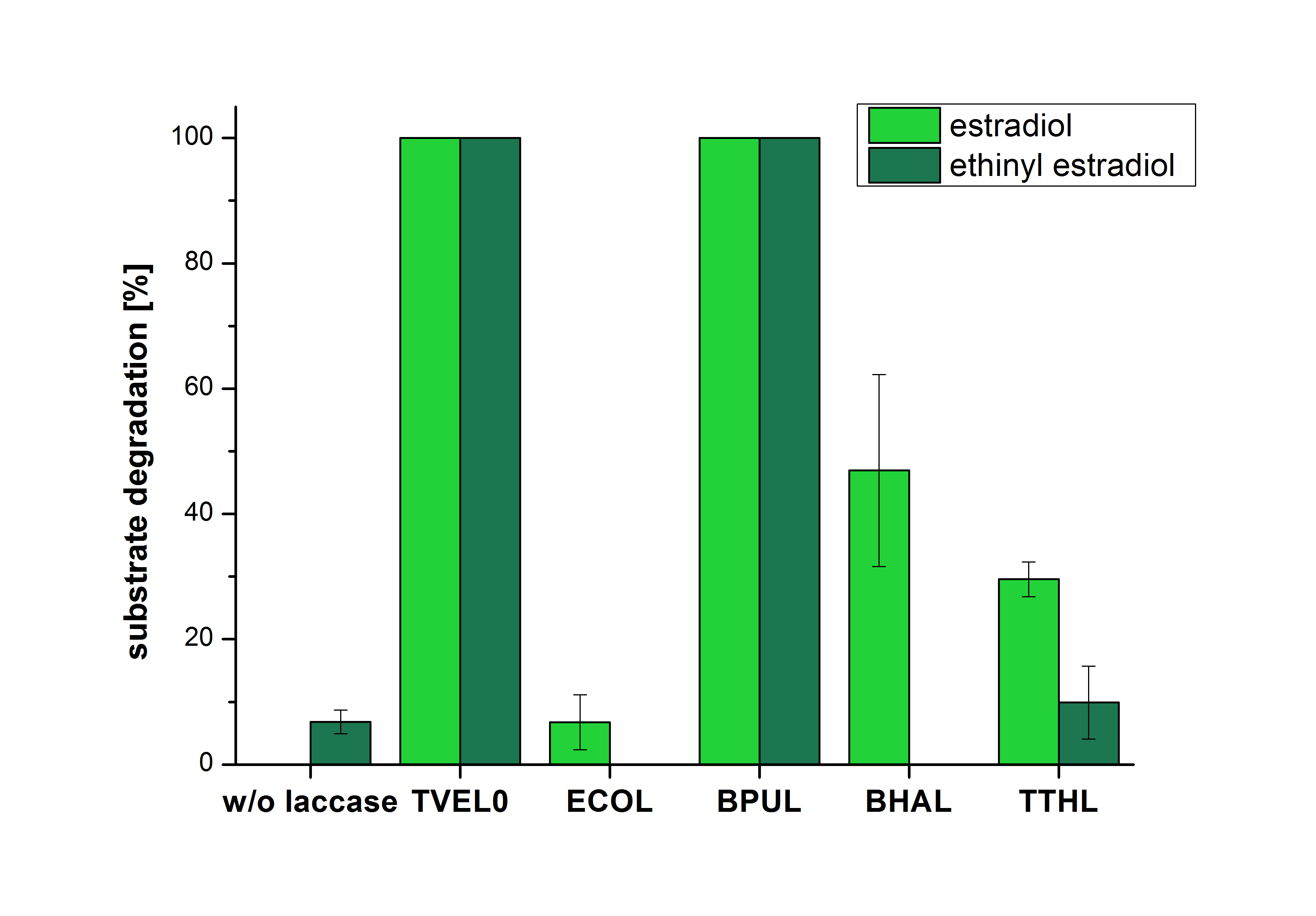
The results of the reactions of the laccases with addition of ABTS are shown in Figure 26. The experimental set ups were the same as the reaction approach without ABTS described above. The X-axis displays the different tested laccases. On the Y-axis the percentages of degraded estradiol (blue) and ethinyl estradiol (red) are shown. The degradation was measured at t0 and after five hours of incubation at 20 °C. The negative control showed no degradation of estradiol. 6.8 % of ethinyl estradiol was decayed. The positive control TVEL0 is able to degrade 100 % estradiol and ethinyl estradiol. The laccase BPUL (from Bacillus pumilus) degraded 46.9 % of used estradiol after ten minutes incubation. ECOL was able to degrade 6.7 % estradiol. BHAL degraded 46.9 % estradiol. With TTHL (laccase from Thermus thermophilus)a degradation 29.5 % were determined.
Immobilization
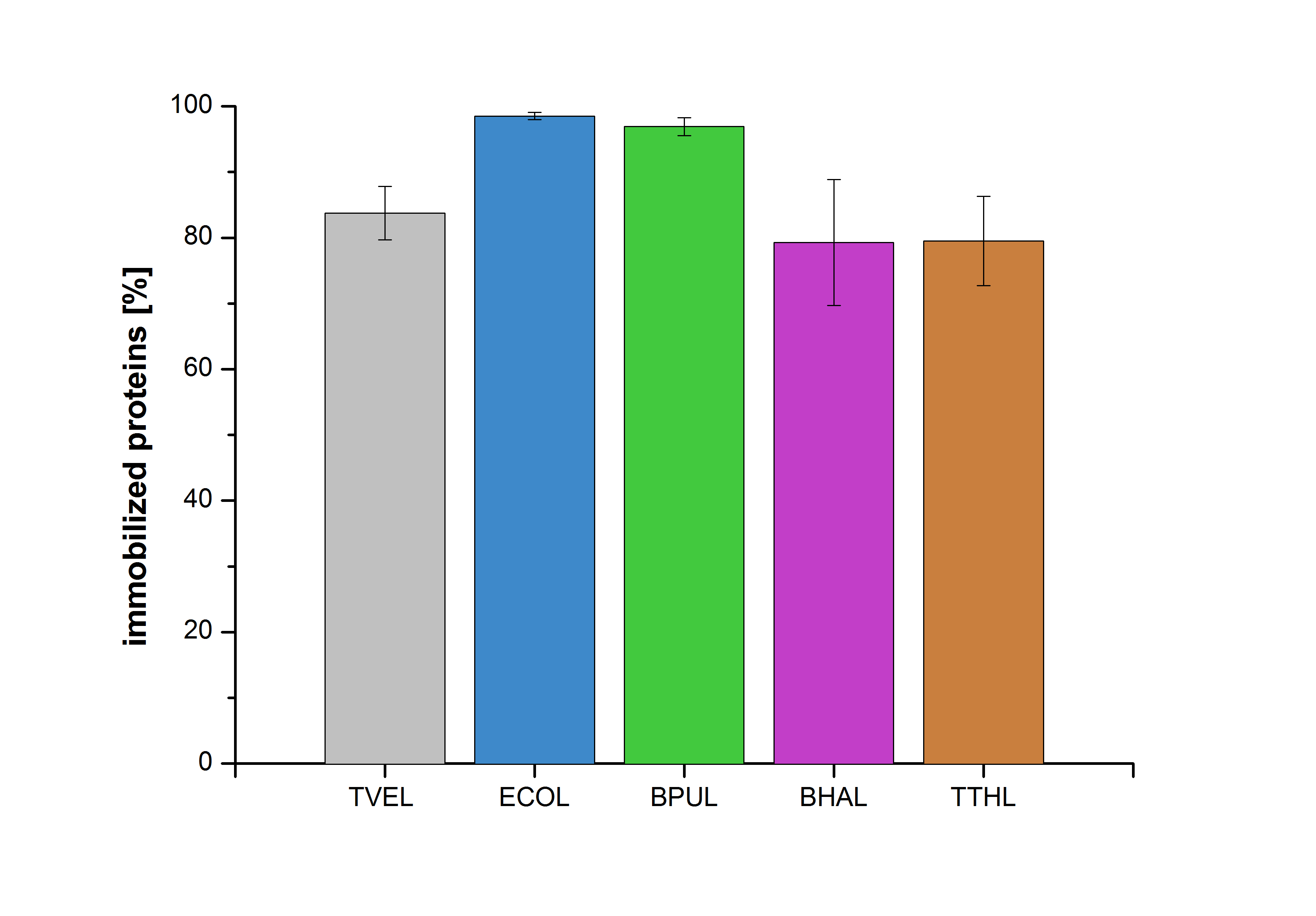
Figure 27 shows the percentage of laccases bound after incubation with CPC-beads, relative to the original concentration. The concentration of laccases in the supernatant after incubation was measured using Roti®-Nanoquant. The results showed that only 1% of ECOL laccases was still present in the supernatant. This illustrates that ECOL was successfully immobilized on the CPC-beads.
In figure 28, the enzymatic activity of ECOL in the supernatant is compared to the activity of nontreated ECOL. Although an activity can already be detected in the supernatant, this activity is low compared to the original.
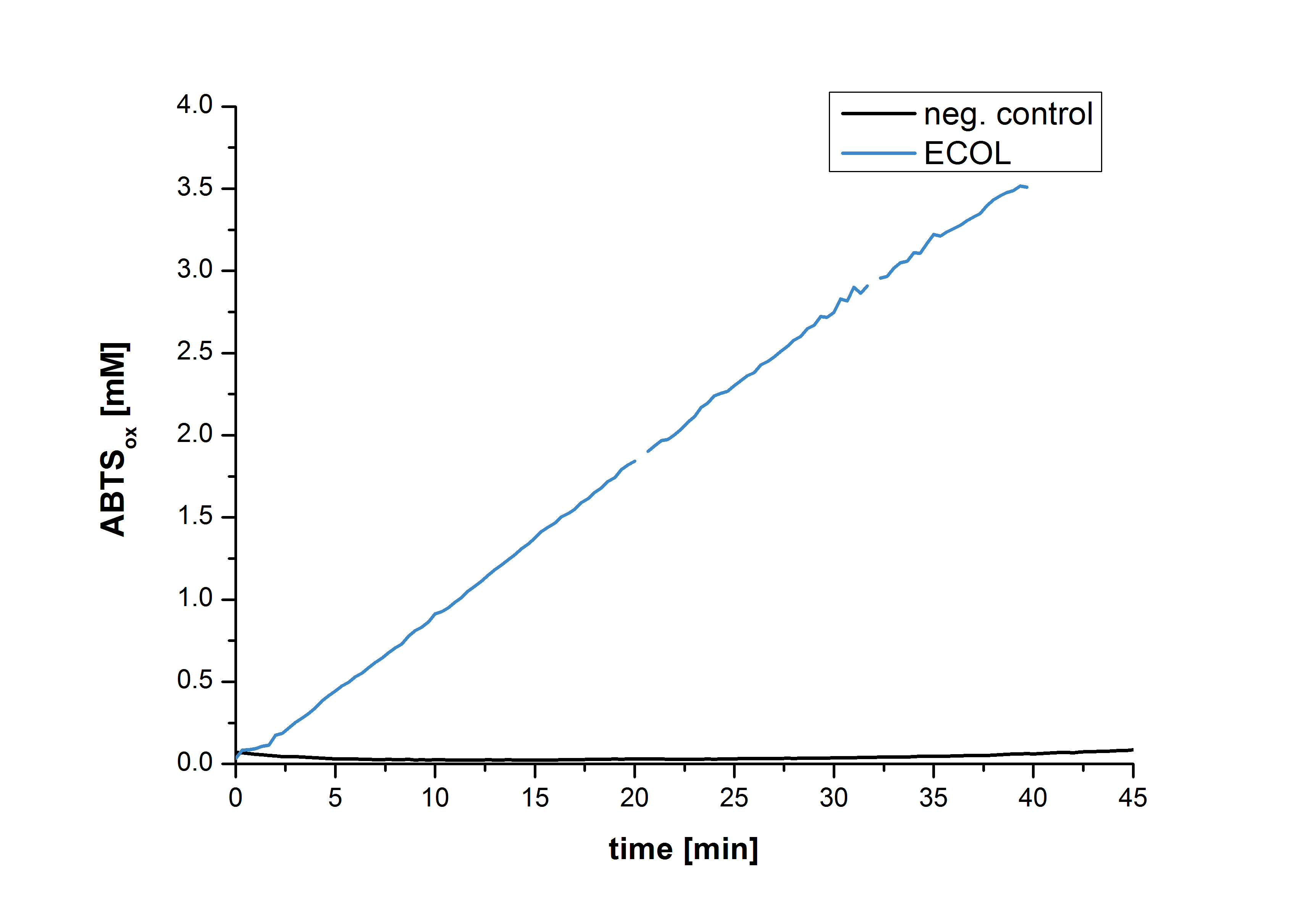
Figure 29 shows the illustration of ABTS oxidation by ECOL with time compared to the negative control. The increase in ABTS oxidized proves laccase activity even if a direct comparison with the original and not immobilized laccase solution was not possible due to the measuring methods.
Visulization

Figure 30: The color and the concentration of bacterium liquid. (A) The color degree among different bacterium liquid. The higher concentration of bacterium liquid showed redder. (B) The OD600 of different concentration of baterium liquid at different times using ultraviolet spectrophotometer.
We transferred our new part BBa_K1779204 (combined BBa_K863005 with BBa_E1010) into Escherichia coli BL21 (DE3). Figure 30 showed the bacterium liquid became red, which confirmed that we successfully made the laccase visible.