Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1041000"
(→Sequencing) |
(→Sequencing) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
The biobrick was sent off to a company for sequencing. | The biobrick was sent off to a company for sequencing. | ||
<gallery> | <gallery> | ||
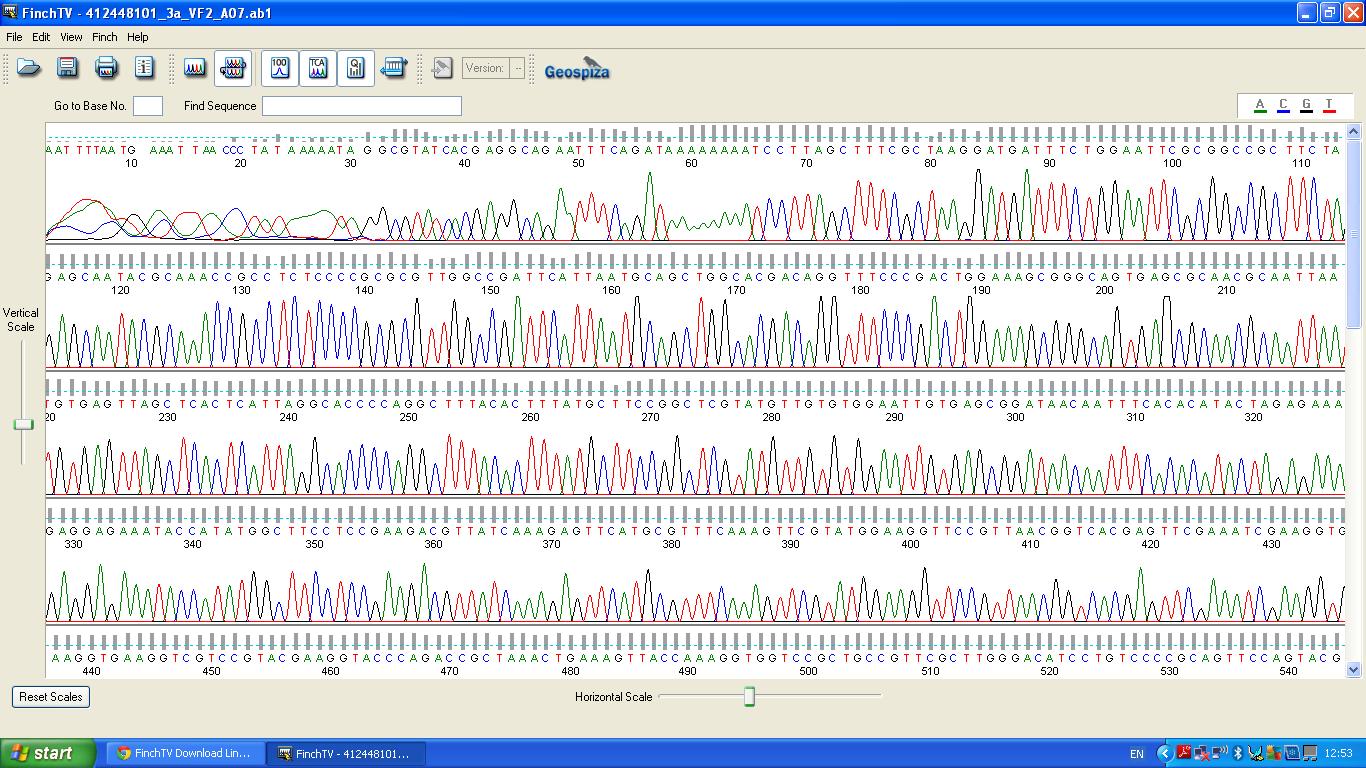
| − | image:3a vf2 0-540.JPG | + | image:3a vf2 0-540.JPG|K1041000 sequencing |
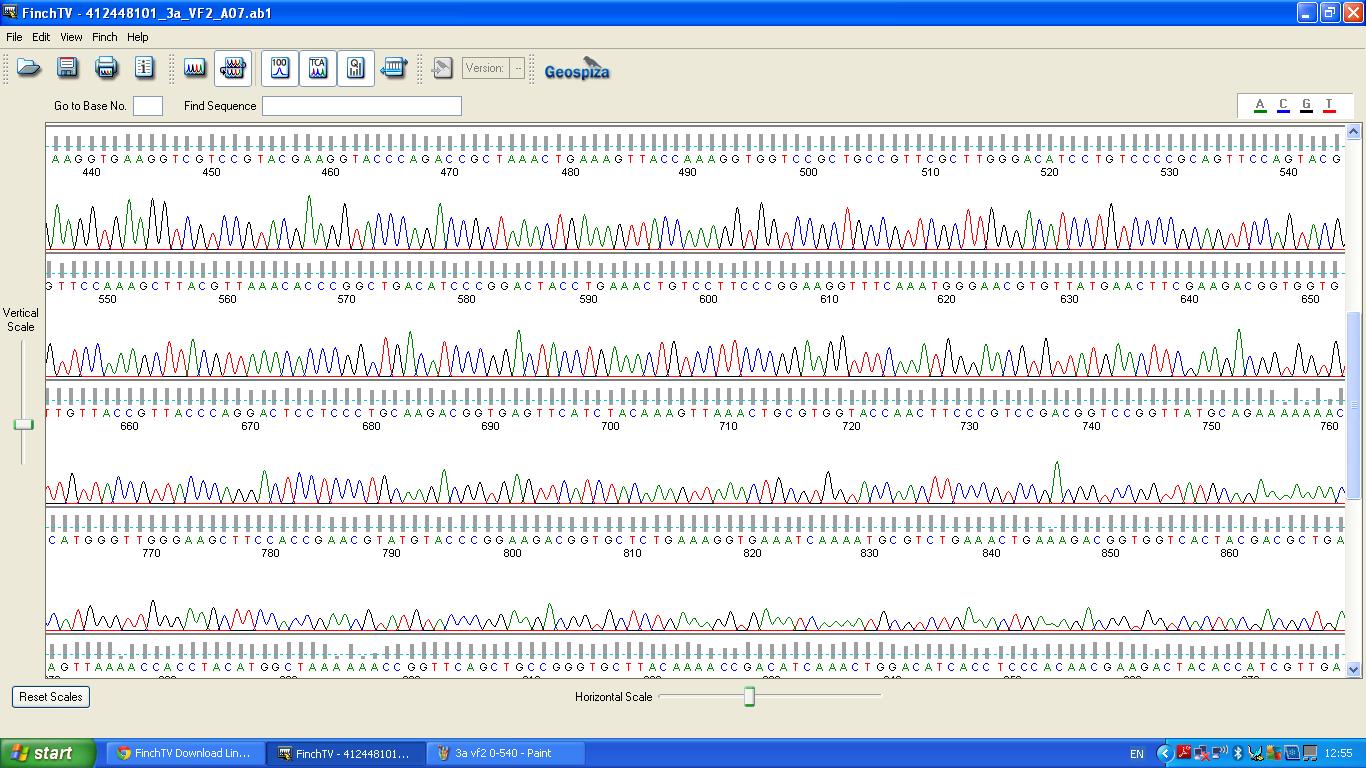
| − | image:3a vf2 440-860.JPG | + | image:3a vf2 440-860.JPG|K1041000 sequencing |
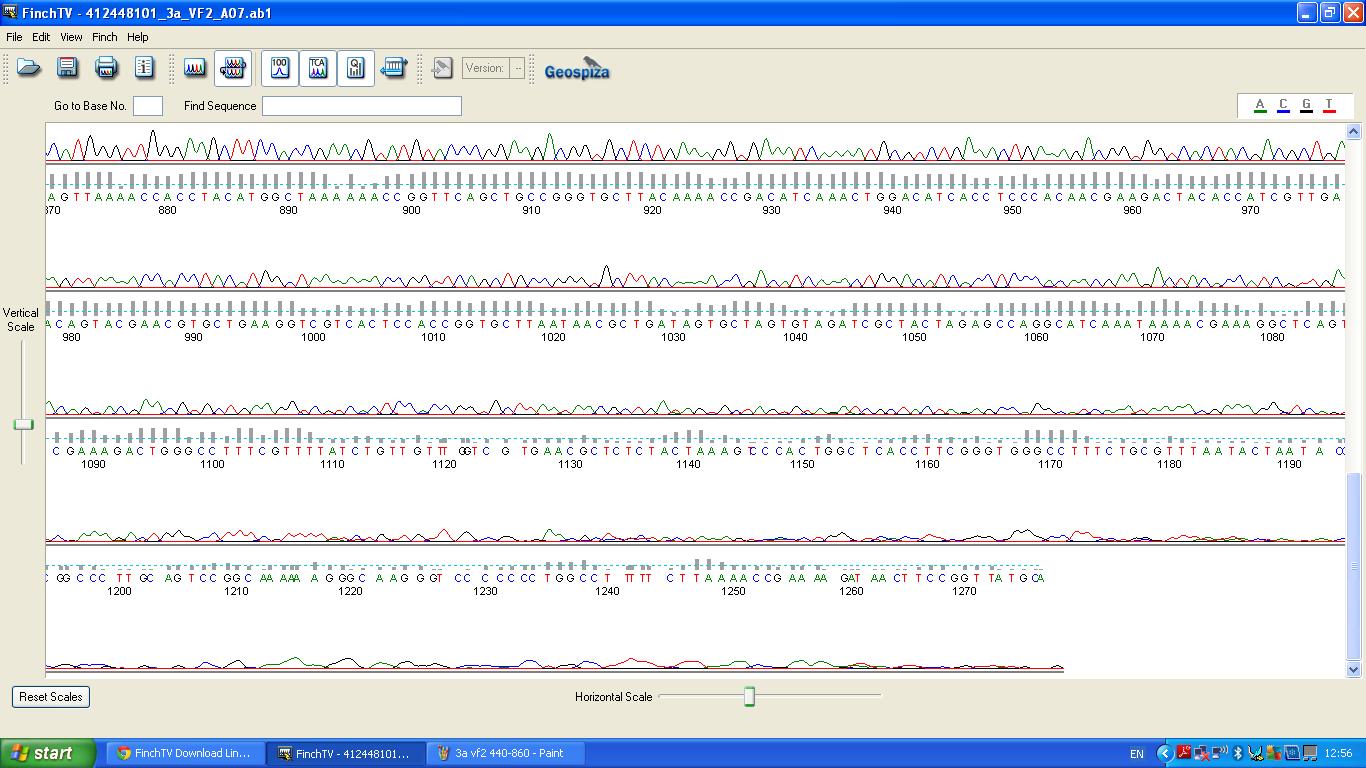
| − | + | image:3a vf2 860-.JPG|K1041000 sequencing | |
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
Revision as of 12:24, 13 September 2013
RFP Coding Device
Team NRP-UEA (2013) used mutagenesis to add a Nde1 site at the start of the RFP coding region of the biobrick BBa_J04450. This enables a restriction digest with Nde1 to be performed allowing the RFP coding region to be excised from the plasmid.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 781
Illegal AgeI site found at 893 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Composite part of the following BioBricks:
- BBa_R0010: Promoter (lacI regulated)
- BBa_B0034: RBS (Elowitz 1999)
- BBa_E1010: Red Fluorescent Protein from Discosoma striata
- BBa_B0015: Double Terminator
Characterisation
Characterisation of this biobrick involved comparisons with the original Bba_J04450 biobrick by performing transformations, restriction digests and BLAST analysis. We also had our biobrick sequenced.
Transformation
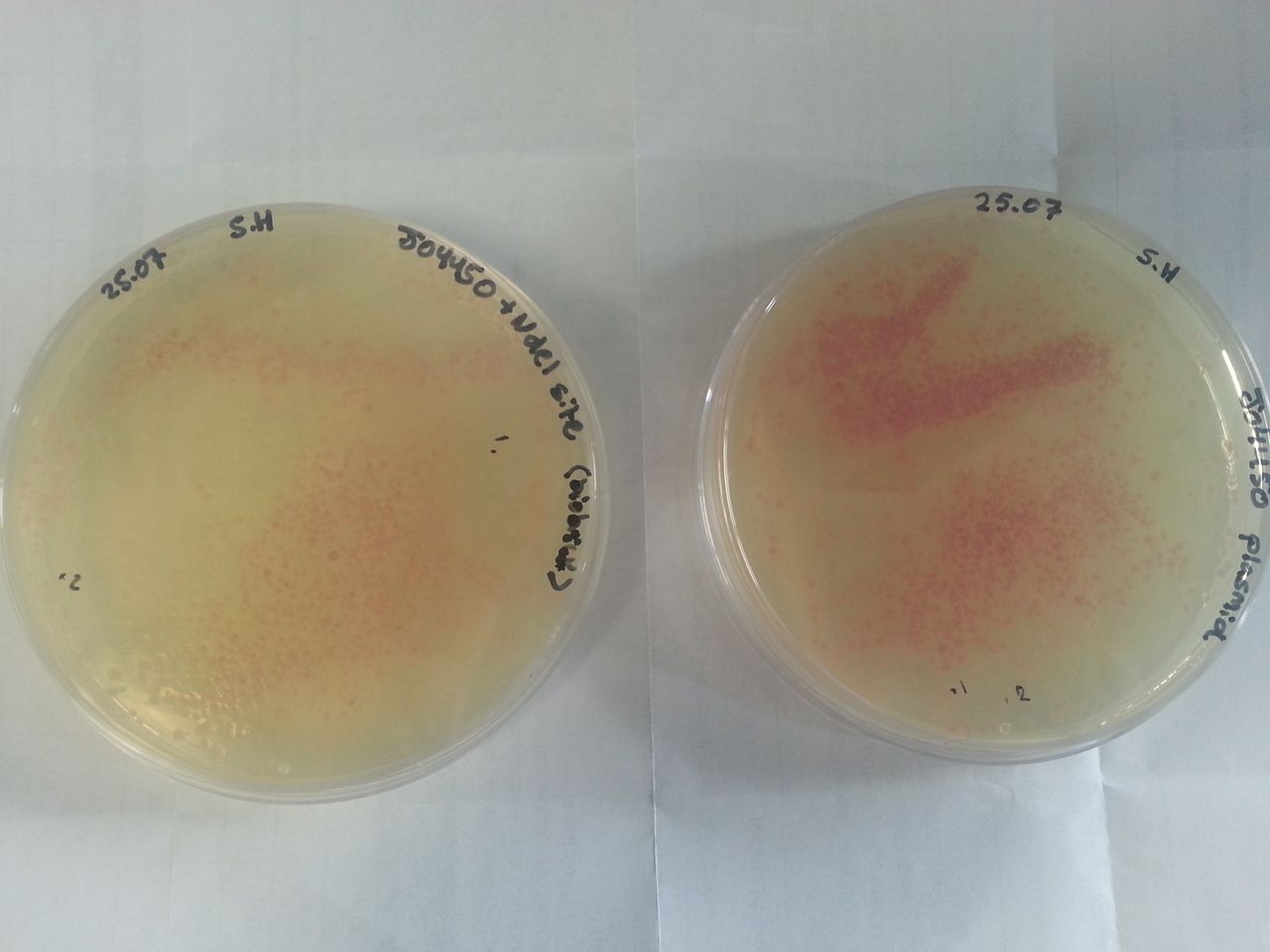
Parts BBa_K1041000 and BBa_J04450 were transformed into Alpha-Select competent E.Coli cells and plated onto LB Agar plates which contained the antibiotic ampicillin. Both plates have colonies that appear red under natural light fig.1. Therefore the addition of a NdeI site has not effected the ability for the RFP gene to be transcribed.
Sequencing
The biobrick was sent off to a company for sequencing.