Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3114015"
(→Characterization) |
|||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
We determined the percent successful assembly using this part as well as the original BBa_K1467400 by counting the total number of red and white colonies 24 hours after transformation of our Golden Gate reactions. Each of the Golden Gate assembly reactions contained the same amount of destination vector and DNA inserts in the form of PCR products. They were conducted as per our Golden Gate assembly [https://2019.igem.org/Team:Calgary/Experiments protocol.] | We determined the percent successful assembly using this part as well as the original BBa_K1467400 by counting the total number of red and white colonies 24 hours after transformation of our Golden Gate reactions. Each of the Golden Gate assembly reactions contained the same amount of destination vector and DNA inserts in the form of PCR products. They were conducted as per our Golden Gate assembly [https://2019.igem.org/Team:Calgary/Experiments protocol.] | ||
| − | [[Image:T--Calgary--FlipperColonyData.png| | + | [[Image:T--Calgary--FlipperColonyData.png|600px|thumb|center|Figure 1. Percent of colonies that are white in appearance 24 hours after transformation for Golden Gate assembly reactions using pSB1A3-BBa_K1467400, pSB1A3-BBa_K3114015, and pSB1A3-BBa_K1467200 as destination vectors. Control reactions were conducted by adding all reagents to the Golden Gate reaction except the DNA inserts. Values represent the mean for three replicates. Error bars indicate standard error of the mean (SEM).]] |
| − | The results suggest that using the improved RFP flipper [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3114015 BBa_K3114015] resulted in a greater percentage of successful assembly reactions compared to the original RFP flipper [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1467400 BBa_K1467400]. However, the reason for this is unclear. | + | The results suggest that using the improved RFP flipper [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3114015 BBa_K3114015] resulted in a greater percentage of successful assembly reactions compared to the original RFP flipper [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1467400 BBa_K1467400]. However, the reason for this is unclear. |
===Sequences and Features=== | ===Sequences and Features=== | ||
Revision as of 03:54, 20 October 2019
Improved RFP coding device - Golden Gate Module Flipper
This is an improvement of part (BBa_K1467400)
Usage and Biology
This part is a Golden Gate flipper with an RFP device, flanking inverted BsaI sites, and fusion sites compatible with the MoClo assembly standard. This part can be used to convert entire transcriptional units from the Golden Gate MoClo assembly standard into standard BioBricks. It can also be used to convert any BioBrick RFC[10]-compatible vector to a Golden Gate destination vector.
This part has been improved from BBa_K1467400 by substituting the LacI-regulated promoter (BBa_R0010) with a strong constitutive promoter (BBa_J23100). We also exchanged the RBS for a stronger one.
This part allows for colony screening following Golden Gate reactions. Colonies containing the correct assembly should be white in appearance, as the Golden Gate modules will have replaced the RFP device in the vector. Unsuccessful colonies should be red under UV and natural light.
[FLIPPER image]
Design
The substitutions that we made in the RFP device were intended to maximize RFP expression and decrease the amount of time required to observe if the colonies are red. The strong constitutive promoter BBa_J23100 and strong RBS BBa_B0030 were chosen because they are very well-characterized.
We also codon optimized this part for high expression in E. coli.
Characterization
iGEM Calgary used this part to convert pSB1A3 to our Golden Gate destination vector. The synthesized sequence was first cloned into linearized pSB1A3 using an EcoRI + PstI digestion and ligation. The product was sequence confirmed. Following this, we successfully used the part as our destination vector to create six genetic constructs via Golden Gate assembly.
We determined the percent successful assembly using this part as well as the original BBa_K1467400 by counting the total number of red and white colonies 24 hours after transformation of our Golden Gate reactions. Each of the Golden Gate assembly reactions contained the same amount of destination vector and DNA inserts in the form of PCR products. They were conducted as per our Golden Gate assembly protocol.
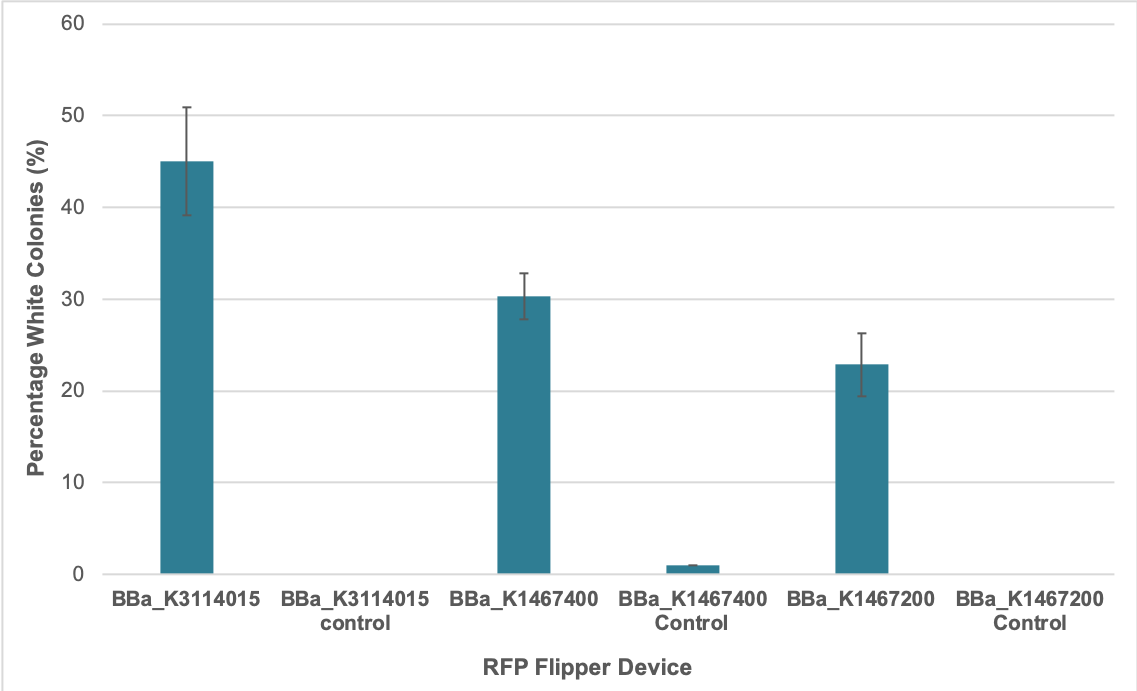
The results suggest that using the improved RFP flipper BBa_K3114015 resulted in a greater percentage of successful assembly reactions compared to the original RFP flipper BBa_K1467400. However, the reason for this is unclear.
Sequences and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 18
Illegal NheI site found at 41 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 629
Illegal AgeI site found at 741 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 882
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 6
