Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K731710"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K731710 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K731710 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | This is a platform for the characterization of terminator efficiency by fluorimetric measurements and ratiometric analysis under IPTG inducible tac promoter’s control ([[Part:BBa_|BBa_]]). It was built starting from | + | This is a platform for the characterization of terminator efficiency by fluorimetric measurements and ratiometric analysis under IPTG inducible ''tac'' promoter’s control ([[Part:BBa_|BBa_]]). It was built starting from [[Part:BBa_K731700|BBa_K731700]], where the T7 promoter was replaced with the ''tac'' promoter by insertion/deletion mutagenesis. The platform has been used for the analysis of T7 wild type terminator's ([[Part:BBa_K731721|BBa_K731721]])and an ''E. coli'' terminator's ([[Part:BBa_K731722|BBa_K731722]]) effects on protein synthesis. |
| − | The combined use of BBa_K731710 and [[Part:BBa_K731700|BBa_K731700]] | + | The combined use of BBa_K731710 and [[Part:BBa_K731700|BBa_K731700]] allows to analyze also any potential difference in terminators' activity due to different RNA polymerases. |
<div style="text-align:center">[[Image:K731710image.jpg]]</div> | <div style="text-align:center">[[Image:K731710image.jpg]]</div> | ||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| − | Our experiments exploited an E. coli lysogen strain carrying T7 RNA polymerase and lacIq. Additionally, the cells, i.e. E. coli BL21(DE3) pLysS, also contained a plasmid encoding T7 lysozyme and chloramphenicol resistance. T7 lysozyme is a natural inhibitor of T7 RNA polymerase activity, thus reducing background expression of the target genes. The T7 RNA polymerase is behind a lacUV5 promoter. | + | Our experiments exploited an ''E. coli'' lysogen strain carrying T7 RNA polymerase and lacIq. Additionally, the cells, i.e. ''E. coli'' BL21(DE3) pLysS, also contained a plasmid encoding T7 lysozyme and chloramphenicol resistance. T7 lysozyme is a natural inhibitor of T7 RNA polymerase activity, thus reducing background expression of the target genes. The T7 RNA polymerase is behind a lacUV5 promoter. |
| Line 60: | Line 60: | ||
To identify optimal conditions, we screened samples that were and were not sonicated, sample dilutions to decrease the scattering of light, IPTG concentration, time of induction and time after induction. We found that the best results were obtained with induction with 0.5 mM IPTG for 3 h, followed by sonication and centrifugation. The cleared supernatant was then diluted 3-fold with phosphate buffer saline (PBS, composition) and stored overnight at 4 °C. Finally, fluorescence was measured with a Varian Cary Eclipse spectrofluorimeter as described above. The samples were left overnight at 4 °C to allow for sufficient time for the fluorescent proteins to properly mature (i.e. protein folding and chromophore formation). Each measurement was made in quadruplicate from different colonies from different transformations and from different plates. | To identify optimal conditions, we screened samples that were and were not sonicated, sample dilutions to decrease the scattering of light, IPTG concentration, time of induction and time after induction. We found that the best results were obtained with induction with 0.5 mM IPTG for 3 h, followed by sonication and centrifugation. The cleared supernatant was then diluted 3-fold with phosphate buffer saline (PBS, composition) and stored overnight at 4 °C. Finally, fluorescence was measured with a Varian Cary Eclipse spectrofluorimeter as described above. The samples were left overnight at 4 °C to allow for sufficient time for the fluorescent proteins to properly mature (i.e. protein folding and chromophore formation). Each measurement was made in quadruplicate from different colonies from different transformations and from different plates. | ||
| − | This protocol was used to characterize a T7 wild type terminator ([[Part:BBa_K731721|BBa_K731721]])and an E. coli terminator ([[Part:BBa_K731722|BBa_K731722]]). | + | This protocol was used to characterize a T7 wild type terminator ([[Part:BBa_K731721|BBa_K731721]])and an ''E. coli'' terminator ([[Part:BBa_K731722|BBa_K731722]]). |
These terminators's activity was measured as the ratio between the two proteins' levels using the equation found in literature for termination efficiency. | These terminators's activity was measured as the ratio between the two proteins' levels using the equation found in literature for termination efficiency. | ||
Doing this measurements, however, we realized that terminators can have an effect also on mCherry expression, enhancing it. (We further investigated this effect operating an in vitro transcription-translation reaction. This was done using the twin backbone of BBa_K731710, with T7 promoter instead of Ptac. For the results, see [[Part:BBa_K731700]].) As a consequence of this unexpected outcome, we defined other two parameters that are here summarized in addition to the literature definition of termination efficiency: | Doing this measurements, however, we realized that terminators can have an effect also on mCherry expression, enhancing it. (We further investigated this effect operating an in vitro transcription-translation reaction. This was done using the twin backbone of BBa_K731710, with T7 promoter instead of Ptac. For the results, see [[Part:BBa_K731700]].) As a consequence of this unexpected outcome, we defined other two parameters that are here summarized in addition to the literature definition of termination efficiency: | ||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
| − | We submitted also this backbone with each terminator used in this study inserted in the cloning region as measurement plasmids; we hope that this could be helpful for anyone who want to verify and further delve into our results. They are [[Part:BBa_K731711|BBa_K731711]] for the T7 terminator and [[Part:BBa_K731712|BBa_K731712]] for the E. coli terminator. | + | We submitted also this backbone with each terminator used in this study inserted in the cloning region as measurement plasmids; we hope that this could be helpful for anyone who want to verify and further delve into our results. They are [[Part:BBa_K731711|BBa_K731711]] for the T7 terminator and [[Part:BBa_K731712|BBa_K731712]] for the ''E. coli'' terminator. |
More information about the procedure used, the results obtained and our considerations can be found in the Trento iGEM 2012 web page. | More information about the procedure used, the results obtained and our considerations can be found in the Trento iGEM 2012 web page. | ||
Revision as of 09:46, 19 September 2012
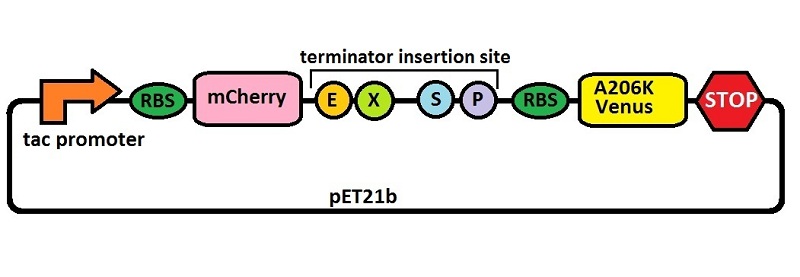
Platform for terminators analysis under the control of tac promoter
This is a platform for the characterization of terminator efficiency by fluorimetric measurements and ratiometric analysis under IPTG inducible tac promoter’s control (BBa_). It was built starting from BBa_K731700, where the T7 promoter was replaced with the tac promoter by insertion/deletion mutagenesis. The platform has been used for the analysis of T7 wild type terminator's (BBa_K731721)and an E. coli terminator's (BBa_K731722) effects on protein synthesis.
The combined use of BBa_K731710 and BBa_K731700 allows to analyze also any potential difference in terminators' activity due to different RNA polymerases.
Usage and Biology
Our experiments exploited an E. coli lysogen strain carrying T7 RNA polymerase and lacIq. Additionally, the cells, i.e. E. coli BL21(DE3) pLysS, also contained a plasmid encoding T7 lysozyme and chloramphenicol resistance. T7 lysozyme is a natural inhibitor of T7 RNA polymerase activity, thus reducing background expression of the target genes. The T7 RNA polymerase is behind a lacUV5 promoter.
Experimental set up:
We made some preliminary analyses to define the best procedure to use this platform. We found that the emission from mVenus was much stronger than the mCherry emission, resulting in some spectral overlap. To improve the quality of the data, off-peak excitation and emission wavelengths were identified that minimized the effect. Therefore, mVenus was excitated at 485 nm (excitation peak is at 515 nm), and the emission of mVenus was collected at its maximum position, i.e. 528 nm. The maximum mCherry excitation wavelength was used (587 nm), but the emission of mCherry was read at 615 nm, as opposed to the maximum at 609 nm. Here is a summary these wavelengths:
| Excitation (nm) | Emission(nm) | |
| mCherry | 587 | 609 |
| Venus | 515 | 528 |
TABLE 1. Excitation and emission wavelengths from literature
| Excitation (nm) | Emission(nm) | |
| mCherry | 587 | 615 |
| Venus | 485 | 528 |
TABLE 2. Excitation and emission wavelengths adapted for the characterizations with this part
The data were collected from cells that were expressed for 4 h with 0.1 mM isopropyl β-D-1-thiogalactopyranoside (IPTG). To identify optimal conditions, we screened samples that were and were not sonicated, sample dilutions to decrease the scattering of light, IPTG concentration, time of induction and time after induction. We found that the best results were obtained with induction with 0.5 mM IPTG for 3 h, followed by sonication and centrifugation. The cleared supernatant was then diluted 3-fold with phosphate buffer saline (PBS, composition) and stored overnight at 4 °C. Finally, fluorescence was measured with a Varian Cary Eclipse spectrofluorimeter as described above. The samples were left overnight at 4 °C to allow for sufficient time for the fluorescent proteins to properly mature (i.e. protein folding and chromophore formation). Each measurement was made in quadruplicate from different colonies from different transformations and from different plates.
This protocol was used to characterize a T7 wild type terminator (BBa_K731721)and an E. coli terminator (BBa_K731722). These terminators's activity was measured as the ratio between the two proteins' levels using the equation found in literature for termination efficiency. Doing this measurements, however, we realized that terminators can have an effect also on mCherry expression, enhancing it. (We further investigated this effect operating an in vitro transcription-translation reaction. This was done using the twin backbone of BBa_K731710, with T7 promoter instead of Ptac. For the results, see Part:BBa_K731700.) As a consequence of this unexpected outcome, we defined other two parameters that are here summarized in addition to the literature definition of termination efficiency:
The parameters used to analyze the data are:
apparent termination efficiency as defined in literature, 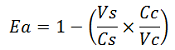
raw termination efficiency, that not consider the mCherry contribution, 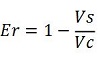
time-folds rise in mCherry expression caused by the terminator relatively to the control construct without intervening terminator, ![]()
where
-Vs is the A206K Venus peak’s intensity of the construct with the terminator of interest inserted in the prefix-suffix linker
-Vc is the A206K Venus peak’s intensity of the control construct with no terminator
-Cs is the mCherry peak’s intensity of the construct with the terminator inserted
-Cc is the mCherry peak’s intensity of the control construct
The results we obtained follow:
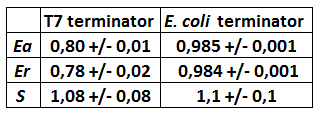
TABLE 1. BBa_K731721 T7 terminator's and BBa_K731722 E. coli terminator's effects on protein expression under tac promoter control.
The table outlines the results we obtained: while the apparent termination efficiency is calculated considering the ratio of A206K Venus's emission peak over mCherry's one, the raw termination efficiency considers just the effect of the terminator on A206K Venus expression. The "S" parameter, eventually, represents the increase in mCherry expression caused by the terminator's presence.
FIGURE 1. BBa_K731721 T7 terminator's and BBa_K731722 E. coli terminator's transcriptional termination efficiencies under tac promoter control.
The chart evdences the comparison between apparent and raw termination efficiency found for the two terminators used for the analysis.
We submitted also this backbone with each terminator used in this study inserted in the cloning region as measurement plasmids; we hope that this could be helpful for anyone who want to verify and further delve into our results. They are BBa_K731711 for the T7 terminator and BBa_K731712 for the E. coli terminator.
More information about the procedure used, the results obtained and our considerations can be found in the Trento iGEM 2012 web page.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal EcoRI site found at 6865
Illegal SpeI site found at 2
Illegal PstI site found at 16
Illegal NotI site found at 9
Illegal NotI site found at 6871 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal EcoRI site found at 6865
Illegal BglII site found at 6011
Illegal BamHI site found at 6847
Illegal XhoI site found at 753 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal prefix found at 6865
Illegal suffix found at 2 - 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal prefix found at 6865
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal XbaI site found at 6880
Illegal SpeI site found at 2
Illegal PstI site found at 16
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 714
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1051
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 4231
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 4391
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 5979
Illegal AgeI site found at 6815 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal BsaI site found at 2228
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 3310