Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2660009"
| (6 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
- Light-activated protein | - Light-activated protein | ||
| − | This photoswitch made from a blue light photoreceptor VVD derived from the filamentous fungus <i>Neurospora crassa</i>. The VVD is currently one of the smallest photoreceptors among those tested as optogenetic tools.The positive Magnet (pMag) when | + | <br> |
| + | This photoswitch made from a blue light photoreceptor VVD derived from the filamentous fungus <i>Neurospora crassa</i>. The VVD is currently one of the smallest photoreceptors among those tested as optogenetic tools.<b>The positive Magnet (pMag)</b> when irradiated by a blue light change through electrostatic interactions. | ||
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| − | This part can be used with nMag (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2660008">BBa_K2660008</a></html>) to join different domains of a protein of interest when irradiated by blue light | + | This part was engineered to be a building block of the standard BioBrick framework, and can be used with nMag (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2660008">BBa_K2660008</a></html>) to join different domains of a protein of interest when irradiated by blue light like N-cas9 (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2660006">BBa_K2660006</a></html>) and C-cas9 (<html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K2660007">BBa_K2660007</a></html>) domains. |
<br><br> | <br><br> | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <h1>pMag- Light-activated protein </h1> | ||
| + | <h1>USTC </h1> | ||
| + | <p>This part is inserted into plasmid, and the correct construction of this recombinant plasmid was confirmed by PCR | ||
| + | identification and sequencing of the PCR products. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <div class="card" style="background-color: #fdfaf0; border: unset"> | ||
| + | <img class="card-img-top" src="https://2019.igem.org/wiki/images/f/f8/T--USTC--Cas9.png" alt="Card image"> | ||
| + | <div class="card-body"> | ||
| + | <p class="card-title" style=" text-align: center;">Figure1. Electrophoresis result PCR of C-Cas9+pMag and | ||
| + | N-Cas9+nMag. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <p>Besides, the E.coli was grown in LB liquid medium, and obtain protein by heating them. The sample was | ||
| + | electrophoresed on a sodium dodecyl sulfate(SDS)-polyacrylamide gel, followed by Coomassie blue staining.( The | ||
| + | pictures are blurred because of the poor photographic equipment) | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | <div class="card" style="background-color: #fdfaf0; border: unset"> | ||
| + | <img class="card-img-top" src="https://2019.igem.org/wiki/images/1/14/T--USTC--SDS_PAGE.png" alt="Card image"> | ||
| + | <div class="card-body"> | ||
| + | <p class="card-title" style=" text-align: center;">Figure2. SDS-PAGE for strain expressing aNAT, C-Cas9+pMag | ||
| + | and N-Cas9+nMag. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
<b>References</b><br> | <b>References</b><br> | ||
Latest revision as of 23:06, 21 October 2019
pMag
- Light-activated protein
This photoswitch made from a blue light photoreceptor VVD derived from the filamentous fungus Neurospora crassa. The VVD is currently one of the smallest photoreceptors among those tested as optogenetic tools.The positive Magnet (pMag) when irradiated by a blue light change through electrostatic interactions.
This part was engineered to be a building block of the standard BioBrick framework, and can be used with nMag (BBa_K2660008) to join different domains of a protein of interest when irradiated by blue light like N-cas9 (BBa_K2660006) and C-cas9 (BBa_K2660007) domains.
pMag- Light-activated protein
USTC
This part is inserted into plasmid, and the correct construction of this recombinant plasmid was confirmed by PCR identification and sequencing of the PCR products.
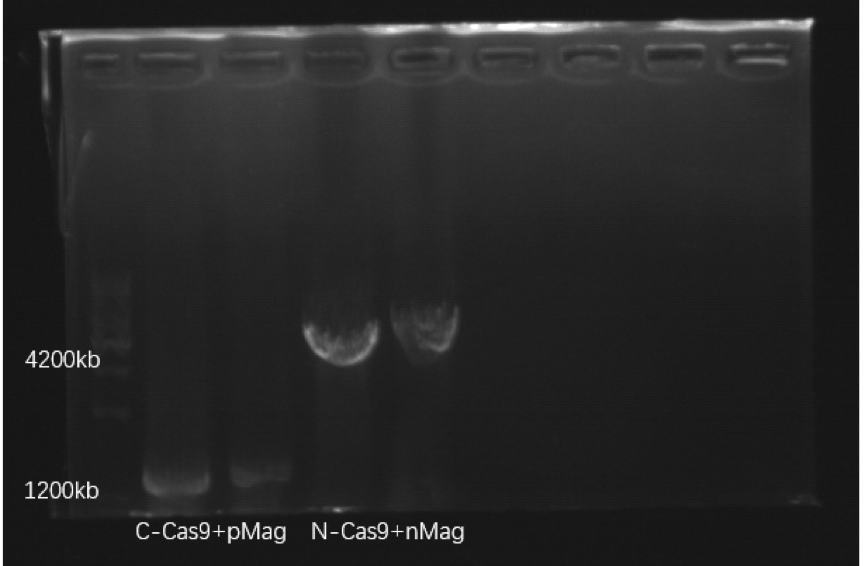
Figure1. Electrophoresis result PCR of C-Cas9+pMag and N-Cas9+nMag.
Besides, the E.coli was grown in LB liquid medium, and obtain protein by heating them. The sample was electrophoresed on a sodium dodecyl sulfate(SDS)-polyacrylamide gel, followed by Coomassie blue staining.( The pictures are blurred because of the poor photographic equipment)
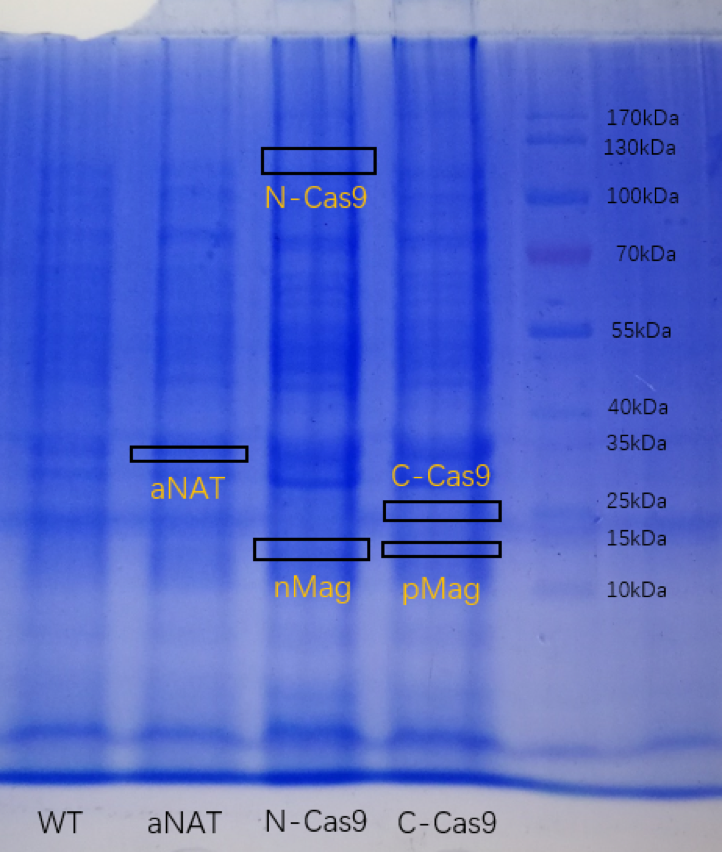
Figure2. SDS-PAGE for strain expressing aNAT, C-Cas9+pMag and N-Cas9+nMag.
References
Kawano, F. et al. Engineered pairs of distinct photoswitches for optogenetic control of cellular proteins. Nat. Commun. 6:6256 doi: 10.1038/ncomms7256 (2015)
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 87
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
