Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa B0033"
(→Contribution of SCAU-China) |
|||
| (15 intermediate revisions by 5 users not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
Weaker RBS based on Ron Weiss thesis. Strengths relative to <bbpart>BBa_B0030</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_B0031</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_B0032</bbpart>. | Weaker RBS based on Ron Weiss thesis. Strengths relative to <bbpart>BBa_B0030</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_B0031</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_B0032</bbpart>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Improvement=== | ||
| + | <b>Group:iGEM2019_JiangnanU_China</b> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
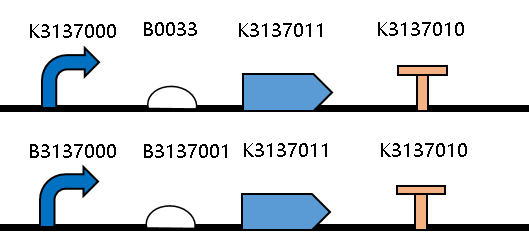
| + | This year, we improved the sequence of the RBS <bbpart>BBa_B0033</bbpart>, and got the RBS <bbpart>BBa_K3137001</bbpart>. | ||
| + | [[Image:JiangnanUchina improve 1.png|400px|thumb|center|Figure1. Maps of the constructed plasmids]] | ||
| + | As we all know, RBS refers to a sputum-rich untranslated region upstream of the initiation codon AUG. <bbpart>BBa_B0033</bbpart> is a weaker RBS based on Ron Weiss thesis. Compared with <bbpart>BBa_B0030</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_B0031</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_B0032</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_B0034</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_B0033</bbpart> is the weakest, and whose RBS strength is 0.35% of <bbpart>BBa_B0034</bbpart>. By analyzing their sequence, we found that <bbpart>BBa_B0033</bbpart> has fewer purines and no not have AAA sequence. SO we designed the RBS by adjusting the proportion of bases. | ||
| + | [[Image:JiangnanUchina improve 2.png|400px|thumb|center|Figure2. Sequences of the original RBS and improved RBS]] | ||
| + | Then we ligated the two RBS with promotor <i>rsmH</i> (<bbpart>BBa_K3137000</bbpart>) and gene <i>gfp</i> (<bbpart>BBa_K3137011</bbpart>) and transform into <i>E. coli</i> BL21 to compare their green fluorescence. And take <I>E. coli</i> BL21 as a control. | ||
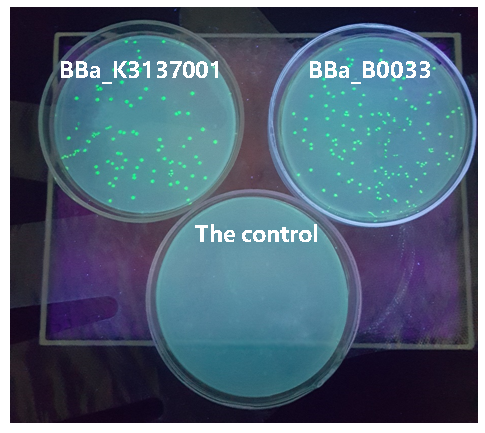
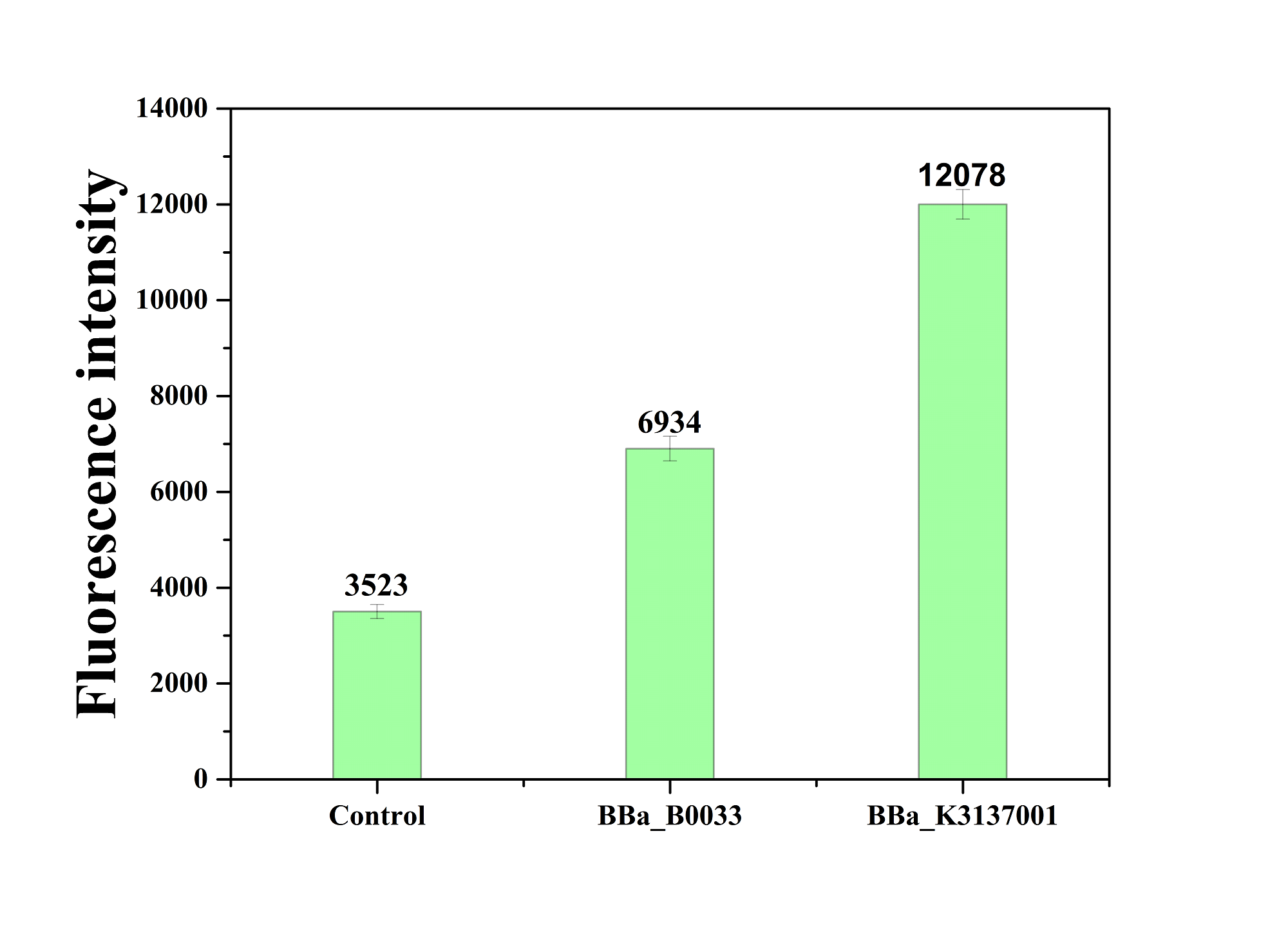
| + | The figure below shows that BBa_K3137001 has the stronger fluorescently protein expression than <bbpart>BBa_B0033</bbpart>, that means it’s efficient to increase the protein expression by increasing the number of purines in the RBS sequence, which is beneficial to the binding of ribosomes. | ||
| + | [[Image:JiangnanUchina improve 3.png|400px|thumb|left|Figure3. Expression of <I>gfp</i> driven by <bbpart>BBa_K3137001</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_B0033</bbpart> and control]] | ||
| + | [[Image:JiangnanUchina improve 4.png|400px|thumb|right|Figure4. Fluorescence intensity of <i>gfp</i> driven by <bbpart>BBa_K3137001</bbpart>, <bbpart>BBa_B0033</bbpart> and control]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
| Line 11: | Line 26: | ||
<span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
<partinfo>BBa_B0033 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_B0033 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
===Functional Parameters=== | ===Functional Parameters=== | ||
<partinfo>BBa_B0033 parameters</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_B0033 parameters</partinfo> | ||
(Relative to <partinfo>B0034</partinfo>) | (Relative to <partinfo>B0034</partinfo>) | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html><hr><h3 style="color:ltblue;"><a href="http://2010.igem.org/Team:Warsaw/Stage1/RBSMeas">Team Warsaw 2010's measurement</a></h3> | ||
| + | RBS strength (relative to <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0034">B0034</a>): 0,35% | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Functional Parameters: Austin_UTexas== | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <body> | ||
| + | <partinfo>BBa_B0033 parameters</partinfo> | ||
| + | (Relative to <partinfo>B0034</partinfo>) | ||
| + | <h3><center>Burden Imposed by this Part:</center></h3> | ||
| + | <figure> | ||
| + | <div class = "center"> | ||
| + | <center><img src = "https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/f/fa/T--Austin_Utexas--no_burden_icon.png" style = "width:160px;height:120px"></center> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <figcaption><center><b>Burden Value: 4.6 ± 4.2% </b></center></figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | <p> Burden is the percent reduction in the growth rate of <i>E. coli</i> cells transformed with a plasmid containing this BioBrick (± values are 95% confidence limits). This BioBrick did not exhibit a burden that was significantly greater than zero (i.e., it appears to have little to no impact on growth). Therefore, users can depend on this part to remain stable for many bacterial cell divisions and in large culture volumes. Refer to any one of the | ||
| + | <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3174002">BBa_K3174002</a> - <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3174007">BBa_K3174007</a> pages for more information on the methods, an explanation of the sources of burden, and other conclusions from a large-scale measurement project conducted by the <a href="http://2019.igem.org/Team:Austin_UTexas">2019 Austin_UTexas team</a>.</p> | ||
| + | <p>This functional parameter was added by the <a href="https://2020.igem.org/Team:Austin_UTexas/Contribution">2020 Austin_UTexas team.</a></p> | ||
| + | </body> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Contribution of SCAU-China=== | ||
| + | ---- | ||
| + | <p>In order to regulate our lysis time and thereby control product concentration in our quorum-sensing-based T4 lysis device, we used this element in front of our T4 endolysin and regulated it.</p> See more detail in '''BBa_K4632024'''[https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K4632024] | ||
Latest revision as of 00:26, 11 October 2023
RBS.4 (weaker) -- derivative of BBa_0030
Weaker RBS based on Ron Weiss thesis. Strengths relative to BBa_B0030, BBa_B0031, BBa_B0032.
Improvement
Group:iGEM2019_JiangnanU_China
This year, we improved the sequence of the RBS BBa_B0033, and got the RBS BBa_K3137001.
As we all know, RBS refers to a sputum-rich untranslated region upstream of the initiation codon AUG. BBa_B0033 is a weaker RBS based on Ron Weiss thesis. Compared with BBa_B0030, BBa_B0031, BBa_B0032, BBa_B0034, BBa_B0033 is the weakest, and whose RBS strength is 0.35% of BBa_B0034. By analyzing their sequence, we found that BBa_B0033 has fewer purines and no not have AAA sequence. SO we designed the RBS by adjusting the proportion of bases.
Then we ligated the two RBS with promotor rsmH (BBa_K3137000) and gene gfp (BBa_K3137011) and transform into E. coli BL21 to compare their green fluorescence. And take E. coli BL21 as a control. The figure below shows that BBa_K3137001 has the stronger fluorescently protein expression than BBa_B0033, that means it’s efficient to increase the protein expression by increasing the number of purines in the RBS sequence, which is beneficial to the binding of ribosomes.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Functional Parameters
| biology | -NA- |
| efficiency | 0.01 |
(Relative to BBa_B0034)
Team Warsaw 2010's measurement
RBS strength (relative to B0034): 0,35%
Functional Parameters: Austin_UTexas
Burden Imposed by this Part:

Burden is the percent reduction in the growth rate of E. coli cells transformed with a plasmid containing this BioBrick (± values are 95% confidence limits). This BioBrick did not exhibit a burden that was significantly greater than zero (i.e., it appears to have little to no impact on growth). Therefore, users can depend on this part to remain stable for many bacterial cell divisions and in large culture volumes. Refer to any one of the BBa_K3174002 - BBa_K3174007 pages for more information on the methods, an explanation of the sources of burden, and other conclusions from a large-scale measurement project conducted by the 2019 Austin_UTexas team.
This functional parameter was added by the 2020 Austin_UTexas team.
Contribution of SCAU-China
In order to regulate our lysis time and thereby control product concentration in our quorum-sensing-based T4 lysis device, we used this element in front of our T4 endolysin and regulated it.
See more detail in BBa_K4632024[1]