Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3781207"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3781207 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3781207 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | + | [[File:T--TU Kaiserslautern--Projektlogo.png|100px|right|MocloMania]] | |
| − | < | + | This composite part contains the <html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3781005">sAP secretion signal</a>, a coding sequence for the <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3781001">SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain</a> as well as a C-terminal <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3781016">mCerulean</a> fluorescent tag. The invidual basic parts are joined together by the MoClo connectors for <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3781301">B2/B3</a> and <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3781304">B4/B5</a>.</html> |
| − | + | <p><b>L1_sAP_RBD_mCerulean</b> allows for <b>transgenic expression</b> of the SARS-CoV2 receptor binding domain in <b><i>Leishmania tarentolae</i></b> and <b>secretion</b> of the fusion protein into the <b>culture medium</b>. The fused <b>mCerulean</b> should allow for <b>visualisation</b> of the recombinant fusion protein in the cell culture supernatant with the help of <b>fluorescence spectroscopy</b>, giving insight into the achieved <b>expression levels</b>. Furthermore, this L1 part was assembled to <b>verify</b> the correct design and construction of its <b>underlying L0 basic parts.</b></p> | |
| − | <!-- --> | + | |
| − | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | + | <b>level</b> 1 |
| + | |||
| + | <b>size</b> 1470 bp | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b>antibiotic resistance in <i>E. Coli</i></b> ampicillin | ||
| + | |||
| + | <b>plasmid backbone</b> <html><a href"https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3781105">weird_plex</a></html> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <h1>Data</h1> | ||
| + | |||
| + | We were able to <b>successfully assemble</b> this composite part into our L1 expression vector <html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3781105">weird_plex</a></html> and <b>confirm</b> the integrity of the resulting <b>L1 construct</b> via <b>restriction digest</b> and gel electrophoresis, see <i>Figure 1</i>. Along with subsequent <b>sequencing</b>, this <b>verified</b> the correct adaptation of the <b>underlying basic parts</b> to the MoClo <b>cloning standard</b>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div><ul> | ||
| + | <li style="display: inline-block;"> [[File:T--TU Kaiserslautern--Gelbild L1 Fluorophore B5.png|thumb|none|500px|<b>Figure 1</b> | <b>Test digest of L1 constructs</b> using <i>SacI</i><br> | ||
| + | <b>1</b> | <html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3781201">L1_3xHA_RBD_mVenus</a></html> | 6098 + 2515 bp<br> | ||
| + | <b>2</b> | <html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3781200">L1_3xHA_RBD_mCerulean</a></html>| 6098 + 2515 bp<br> | ||
| + | <b>3</b> | <html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3781210">L1_sAP_RBD_mVenus</a></html> | 6071 + 2515 bp<br> | ||
| + | <b>4</b> | <b>L1_sAP_RBD_mCerulean</b> | 6071 + 2515 bp<br> | ||
| + | <b>L</b> | Thermofischer GeneRuler Plus Ladder [bp]]] </li> | ||
| + | </ul></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | This L1 composite part has been <b>successfully transfected</b> into <i>Leishmania</i> and recombinant protein expression could be observed via <b>immunostaining</b> on <b>western blot</b>, see <i>Figure 2</i>. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <div><ul> | ||
| + | <li style="display: inline-block;"> [[File:T--TU Kaiserslautern--Blot L1 sAP RBD mCerulean RBD 02.10.png|thumb|none|600px|<b>Figure 2</b> | <b>Immunoblot</b> of L1 transfected Leishmania | stained against <b>RBD</b><br> | ||
| + | <b>1</b> | <b>L1_sAP_RBD_mCerulean</b> | 51.9 kDa<br> | ||
| + | <b>2</b> | <html><a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K378123">L1_sAP_RBD_Strep8His</a></html> | 27.7 kDa<br> | ||
| + | <b>n.c.</b> | negative control | untransfected <i>Leishmania</i> culture<br> | ||
| + | <b>p.c.</b> | RBD-GFP | 54 kDa<br> | ||
| + | <b>L</b> | Thermofischer PageRuler Protein Ladder [kDa]<br> | ||
| + | 1. AB | ms <b>anti-RBD</b> | 1:2,000<br> | ||
| + | 2. AB | rb <b>anti-ms HRP</b> | 1:10,000<br> ]] </li> | ||
| + | </ul></div> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <h1>The MocloMania collection</h1> | ||
| + | <p>This L1 construct was assembled using basic parts from the <b>MocloMania collection</b>, the very first collection of genetic parts specifically designed and optimized for Modular Cloning assembly and recombinant protein expression in the protozoan parasite <i>Leishmania tarentolae</i>.</p> | ||
| + | <p>Are you trying to express <b>complexly glycosylated proteins</b>? Large antibody side chains? Human proteins that require <b>accurate post-translational modification</b>? Then Leishmania might be just the right organism for you! <i>Leishmania tarentolae</i>’s glycosylation patterns resemble those of human cells more closely than any other microbial expression host, while still delivering all the benefits of microbial production systems like <b>easy transfection</b> and <b>cultivation</b>.</html><ref><b>Langer T</b>, Corvey C, Kroll K, Boscheinen O, Wendrich T, Dittrich W. Expression and purification of the extracellular domains of human glycoprotein VI (GPVI) and the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) from Rattus norvegicus in Leishmania tarentolae. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2017 Nov 26;47(10):1008-1015. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2017.1365252. Epub 2017 Aug 31. PMID: 28857681.</ref><html> So instead of relying on mammalian cell lines, try considering Leishmania as your new expression host of choice!</p> | ||
| + | <p>Our MocloMania collection will allow you to easily modify your protein of choice and make it suitable for downstream <b>detection</b> and <b>purification procedures</b> - all thanks to the help of <b>Modular Cloning</b>. This cloning system was first established by <b>Weber et al.</b> in <b>2011</b> and relies on the ability of <b>type IIS restriction enzymes</b> to cut DNA outside of their recognition sequence, hereby generating four nucleotide overhangs.</html><ref><b>Weber E</b>, Engler C, Gruetzner R, Werner S, Marillonnet S (2011) A Modular Cloning System for Standardized Assembly of Multigene Constructs. PLoS ONE 6(2): e16765. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0016765</ref><html> Every basic part in our collection is equipped with a <b>specified set of overhangs</b> that assign it to its designated position within the reading frame. These so-called <b>cloning positions</b> are labelled <b>B2-B5</b> from upstream to downstream. By filling all positions with the basic parts of your choice, you can easily generate variable genetic constructs that code for the <b>fusion protein</b> of your desire.</p> | ||
| + | <p>We furthermore provide a specifically domesticated <b>Leishmania expression vector</b>, named <a href="https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3781105"><b>weird_plex</b></a>, which will package your fusion construct into a functional <b>transcriptional unit</b> that is optimized for high expression in Leishmania. | ||
| + | <p>The best part? Because of the type IIS restriction properties and the specifity of the generated overhangs, restriction and ligation of your construct can all happen <b>simultaneously</b> in a simple <b>one-step</b>, <b>one-pot reaction</b>. This will safe you a lot of time and frustration in your cloning endeavours!</p> | ||
| + | <p>Do we have your attention? In the <b>table below</b> you can find some basic information on how our cloning system, along with most other MoClo systems, is set up. Please feel free to check out our wiki to find more information on <a href="https://2021.igem.org/Team:TU_Kaiserslautern/Description">Leishmania and Modular Cloning</a> as well as to understand how the part that you are looking at integrates into our <a href="https://2021.igem.org/Team:TU_Kaiserslautern/Part_Collection"><b>part collection</b></a>. See you there!</p> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" | ||
| + | |+ style="text-align: left;" | <b>MOCLO</b> | Important nomenclature and parameters | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <b>Level</b> || <b>What does this level contain?</b> || <b>antibiotic resistance</b> || <b>Enzyme used for ligation</b> | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <b>L0</b> || The foundation to every MoClo construct which are basic <b>genetic units</b>, such as coding sequences, promoters, terminators || spectinomycin || BbsI | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <b>L1</b> || Several L0 parts assembled into a functional <b>transcriptional unit</b>, e.g. consisting of promoter, coding region and terminator || ampicillin || BsaI | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | <b>L2</b> || Multiple transcriptional units added into one <b>multi-gene construct</b>, e.g. a protein of interest fused to a selection marker || kanamycin || BbsI | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <span class='h3bb'><h1>Sequence and Features</h1></span> | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3781207 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3781207 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
Latest revision as of 03:39, 22 October 2021
L1_sAP_RBD_mCerulean, MocloMania Composite
This composite part contains the sAP secretion signal, a coding sequence for the SARS-CoV-2 receptor binding domain as well as a C-terminal mCerulean fluorescent tag. The invidual basic parts are joined together by the MoClo connectors for B2/B3 and B4/B5.
L1_sAP_RBD_mCerulean allows for transgenic expression of the SARS-CoV2 receptor binding domain in Leishmania tarentolae and secretion of the fusion protein into the culture medium. The fused mCerulean should allow for visualisation of the recombinant fusion protein in the cell culture supernatant with the help of fluorescence spectroscopy, giving insight into the achieved expression levels. Furthermore, this L1 part was assembled to verify the correct design and construction of its underlying L0 basic parts.
level 1
size 1470 bp
antibiotic resistance in E. Coli ampicillin
plasmid backbone weird_plex
Data
We were able to successfully assemble this composite part into our L1 expression vector weird_plex and confirm the integrity of the resulting L1 construct via restriction digest and gel electrophoresis, see Figure 1. Along with subsequent sequencing, this verified the correct adaptation of the underlying basic parts to the MoClo cloning standard.
-
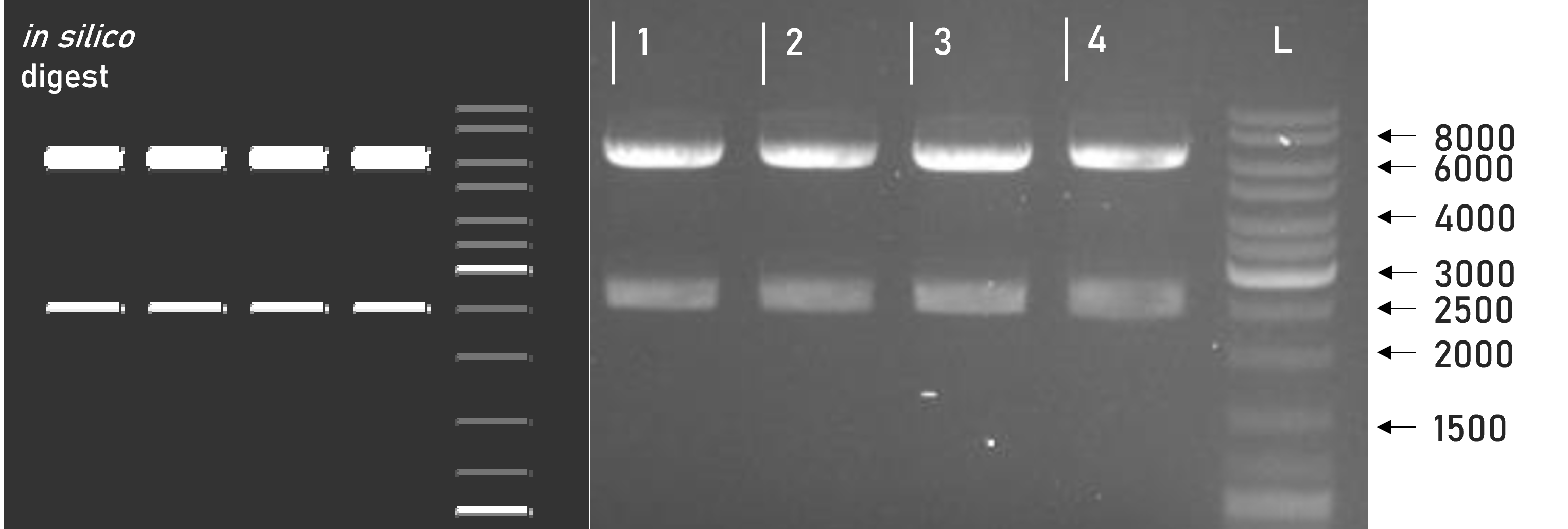 Figure 1 | Test digest of L1 constructs using SacI
Figure 1 | Test digest of L1 constructs using SacI
1 | L1_3xHA_RBD_mVenus | 6098 + 2515 bp
2 | L1_3xHA_RBD_mCerulean| 6098 + 2515 bp
3 | L1_sAP_RBD_mVenus | 6071 + 2515 bp
4 | L1_sAP_RBD_mCerulean | 6071 + 2515 bp
L | Thermofischer GeneRuler Plus Ladder [bp]
This L1 composite part has been successfully transfected into Leishmania and recombinant protein expression could be observed via immunostaining on western blot, see Figure 2.
-
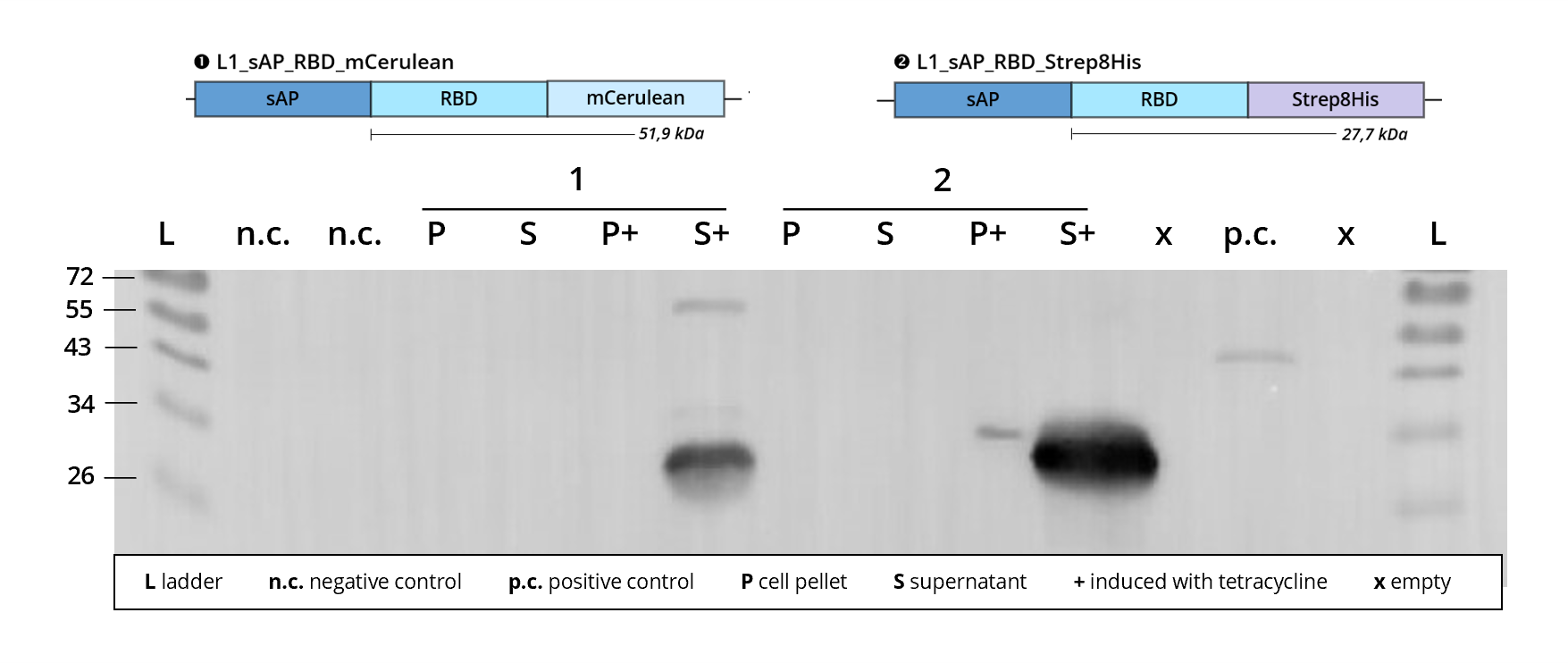 Figure 2 | Immunoblot of L1 transfected Leishmania | stained against RBD
Figure 2 | Immunoblot of L1 transfected Leishmania | stained against RBD
1 | L1_sAP_RBD_mCerulean | 51.9 kDa
2 | L1_sAP_RBD_Strep8His | 27.7 kDa
n.c. | negative control | untransfected Leishmania culture
p.c. | RBD-GFP | 54 kDa
L | Thermofischer PageRuler Protein Ladder [kDa]
1. AB | ms anti-RBD | 1:2,000
2. AB | rb anti-ms HRP | 1:10,000
The MocloMania collection
This L1 construct was assembled using basic parts from the MocloMania collection, the very first collection of genetic parts specifically designed and optimized for Modular Cloning assembly and recombinant protein expression in the protozoan parasite Leishmania tarentolae.
Are you trying to express complexly glycosylated proteins? Large antibody side chains? Human proteins that require accurate post-translational modification? Then Leishmania might be just the right organism for you! Leishmania tarentolae’s glycosylation patterns resemble those of human cells more closely than any other microbial expression host, while still delivering all the benefits of microbial production systems like easy transfection and cultivation.[1] So instead of relying on mammalian cell lines, try considering Leishmania as your new expression host of choice!
Our MocloMania collection will allow you to easily modify your protein of choice and make it suitable for downstream detection and purification procedures - all thanks to the help of Modular Cloning. This cloning system was first established by Weber et al. in 2011 and relies on the ability of type IIS restriction enzymes to cut DNA outside of their recognition sequence, hereby generating four nucleotide overhangs.[2] Every basic part in our collection is equipped with a specified set of overhangs that assign it to its designated position within the reading frame. These so-called cloning positions are labelled B2-B5 from upstream to downstream. By filling all positions with the basic parts of your choice, you can easily generate variable genetic constructs that code for the fusion protein of your desire.
We furthermore provide a specifically domesticated Leishmania expression vector, named weird_plex, which will package your fusion construct into a functional transcriptional unit that is optimized for high expression in Leishmania.
The best part? Because of the type IIS restriction properties and the specifity of the generated overhangs, restriction and ligation of your construct can all happen simultaneously in a simple one-step, one-pot reaction. This will safe you a lot of time and frustration in your cloning endeavours!
Do we have your attention? In the table below you can find some basic information on how our cloning system, along with most other MoClo systems, is set up. Please feel free to check out our wiki to find more information on Leishmania and Modular Cloning as well as to understand how the part that you are looking at integrates into our part collection. See you there!
| Level | What does this level contain? | antibiotic resistance | Enzyme used for ligation |
| L0 | The foundation to every MoClo construct which are basic genetic units, such as coding sequences, promoters, terminators | spectinomycin | BbsI |
| L1 | Several L0 parts assembled into a functional transcriptional unit, e.g. consisting of promoter, coding region and terminator | ampicillin | BsaI |
| L2 | Multiple transcriptional units added into one multi-gene construct, e.g. a protein of interest fused to a selection marker | kanamycin | BbsI |
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal PstI site found at 598
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal PstI site found at 598
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 536
Illegal XhoI site found at 6 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal PstI site found at 598
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal PstI site found at 598
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 684
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1432 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI.rc site found at 708
- ↑ Langer T, Corvey C, Kroll K, Boscheinen O, Wendrich T, Dittrich W. Expression and purification of the extracellular domains of human glycoprotein VI (GPVI) and the receptor for advanced glycation end products (RAGE) from Rattus norvegicus in Leishmania tarentolae. Prep Biochem Biotechnol. 2017 Nov 26;47(10):1008-1015. doi: 10.1080/10826068.2017.1365252. Epub 2017 Aug 31. PMID: 28857681.
- ↑ Weber E, Engler C, Gruetzner R, Werner S, Marillonnet S (2011) A Modular Cloning System for Standardized Assembly of Multigene Constructs. PLoS ONE 6(2): e16765. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0016765