Difference between revisions of "User:VolkerMorath"
VolkerMorath (Talk | contribs) |
VolkerMorath (Talk | contribs) |
||
| (6 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| + | [[test]]<br> | ||
| + | [[test2]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ==Extension of the standard compability to RFC10 and RFC25== | ||
| + | [http://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Munich Team TU_Munich 2012] extended the standard compability to RFC10 and RFC25 by adding the | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | Editing Part:BBa J04450 (section) | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
[https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=User:VolkerMorath/Pictures => Pictures] | [https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=User:VolkerMorath/Pictures => Pictures] | ||
| − | <groupparts> | + | <groupparts>iGEM012 TU_Munich</groupparts> |
| + | <groupparts>iGEM08 Freiburg</groupparts> | ||
'''Adeno-associated Virus''' | '''Adeno-associated Virus''' | ||
| Line 86: | Line 99: | ||
'''The Simian virus 40''' | '''The Simian virus 40''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | The SV40 is a non-enveloped polyomavirus virus, containing a double stranded DNA genome of 5.2 kb. In comparism to other gene transfer vectors the genome of the virus is circular. Thus it lacks the terminal repeat regions characterizing many other viral vectors with linear genomes. The icosahedral capsid of the virus is formed by three virus-encoded proteins (VP1, VP2, and VP3), transcribed by the SV40 late promoters (LP). On the opposite strand the early (EP) promoters are located, driving the expression of the large T antigen (Tag) and a small t antigen (tag). Near a unique BglI site, there are the regulatory sequences, the origin of replication, and packaging signals. According to that the early and late polyadenylation signals are close to each other as well. | ||
| + | |||
| + | SV40 derived vectors have repeatedly proven to be effective, for example in gene delivery to the liver or hematopoietic progenitor cells. The vectors can be stable produced at a very high titer, lacking in immunogenicity and providing high levels of transgene expression in both resting and dividing cells. The principle limitation is the size of insert (≤5 kb) which can be packaged by SV40-derived vectors. | ||
| + | |||
{| style="color:black" cellpadding="6" cellspacing="1" border="2" align="right" | {| style="color:black" cellpadding="6" cellspacing="1" border="2" align="right" | ||
! colspan="2" style="background:#66bbff;"|[] | ! colspan="2" style="background:#66bbff;"|[] | ||
| Line 95: | Line 113: | ||
|- | |- | ||
|'''Family:''' | |'''Family:''' | ||
| − | | | + | |Polyomaviridae |
|- | |- | ||
|'''Genus:''' | |'''Genus:''' | ||
| − | | | + | |Polyomavirus |
|- | |- | ||
|'''Host range''' | |'''Host range''' | ||
| − | | | + | |Human, monkeys |
|- | |- | ||
|'''Capacity:''' | |'''Capacity:''' | ||
| − | | | + | |5200bp |
|- | |- | ||
|} | |} | ||
| Line 111: | Line 129: | ||
<br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br> | ||
<br><br><br><br> | <br><br><br><br> | ||
| + | |||
===Single stranded DNA Viruses=== | ===Single stranded DNA Viruses=== | ||
Latest revision as of 17:02, 19 May 2016
Extension of the standard compability to RFC10 and RFC25
[http://2012.igem.org/Team:TU_Munich Team TU_Munich 2012] extended the standard compability to RFC10 and RFC25 by adding the
Editing Part:BBa J04450 (section)
Adeno-associated Virus
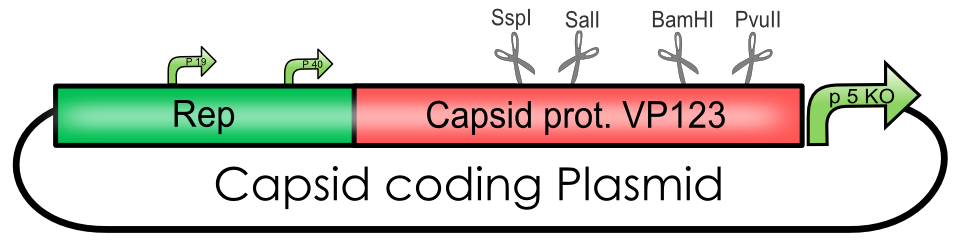
Explanation of the Capsid coding plasmid
The Adeno-associated Virus - Capsid coding BioBricks
| Name | Description | Author | Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_K404001 | [AAV2]-Rep-VP123 | Team Freiburg 2010 | 4214 |
| BBa_K404002 | [AAV2]-Rep-VP123_p5-TATAless | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 4386 |
| BBa_K404003 | [AAV2]-Rep-VP123(ViralBrick-587KO-empty)_p5-TATAless | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 4386 |
| BBa_K404004 | [AAV2]-Rep-VP13(ViralBrick-587KO-empty)_p5-TATAless | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 4402 |
| BBa_K404005 | [AAV2]-Rep-VP23(ViralBrick-587KO-empty)_p5-TATAless | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 4402 |
| BBa_K404006 | [AAV2]-VP123 | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2208 |
| BBa_K404007 | pCMV_[AAV2]-VP123 | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2998 |
| BBa_K404008 | [AAV2]-VP1 | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2202 |
| BBa_K404009 | pCMV_[AAV2]-VP1 | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2910 |
| BBa_K404010 | [AAV2]-VP2 | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 1830 |
| BBa_K404011 | pCMV_[AAV2]-VP2 | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2500 |
| BBa_K404012 | [AAV2]-VP3 | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 1635 |
| BBa_K404013 | pCMV_[AAV2]-VP3 | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2305 |
| BBa_K404150 | [AAV2]-VP23 | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 1917 |
| BBa_K404151 | [AAV2]-VP23 (ViralBrick-587KO-Empty) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 1917 |
| BBa_K404152 | [AAV2]-VP1up | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 411 |
| BBa_K404153 | [AAV2]-NLS | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 21 |
| BBa_K404154 | pCMV_Z-EGFR-1907_[AAV2]-VP23 (ViralBrick-587KO-Empty) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2767 |
| BBa_K404155 | pCMV_Z-EGFR-1907_Short-Linker_[AAV2]-VP23 (ViralBrick-587KO-Empty) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2785 |
| BBa_K404156 | pCMV_Z-EGFR-1907_Middle-Linker_[AAV2]-VP23 (ViralBrick-587KO-Empty) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2797 |
| BBa_K404157 | pCMV_Z-EGFR-1907_Long-Linker_[AAV2]-VP23 (ViralBrick-587KO-Empty) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2809 |
| BBa_K404158 | pCMV_Z-EGFR-1907_SEG-Linker_[AAV2]-VP23 (ViralBrick-587KO-Empty) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2881 |
| BBa_K404159 | pCMV_CFP_Middle-Linker_[AAV2]-VP23 (ViralBrick-587KO-Empty) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3337 |
| BBa_K404160 | pCMV_His-Tag_Middle-Linker_[AAV2]-VP23 (ViralBrick-587KO-Empty) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2641 |
| BBa_K404161 | pCMV_DARPin-E01_Middle-Linker_[AAV2]-VP23 (ViralBrick-587KO-Empty) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3082 |
| BBa_K404162 | pCMV_Z-EGFR-1907_Middle-Linker_[AAV2]-VP23 (ViralBrick-587KO-BAP) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2857 |
| BBa_K404163 | pCMV_Z-EGFR-1907_Middle-Linker_[AAV2]-VP23 (ViralBrick-587KO-His-Tag) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2830 |
| BBa_K404164 | pCMV_VP1up_NLS_Z-EGFR-1907_[AAV2]-VP23 (ViralBrick-587KO-Empty) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3211 |
| BBa_K404165 | pCMV_VP1up_NLS_mVenus_[AAV2]-VP23 (ViralBrick-587KO-Empty) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3751 |
| BBa_K404166 | pCMV_VP1up_NLS_His-Tag_[AAV2]-VP23 (ViralBrick-587KO-Empty) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3056 |
| BBa_K404167 | pCMV_VP1up_NLS_mVenus_VP23(ViralBrick-587-KO-BAP) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3811 |
| BBa_K404168 | pCMV_VP1up_NLS_mVenus_VP2/3(ViralBrick-587-KO-His) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3784 |
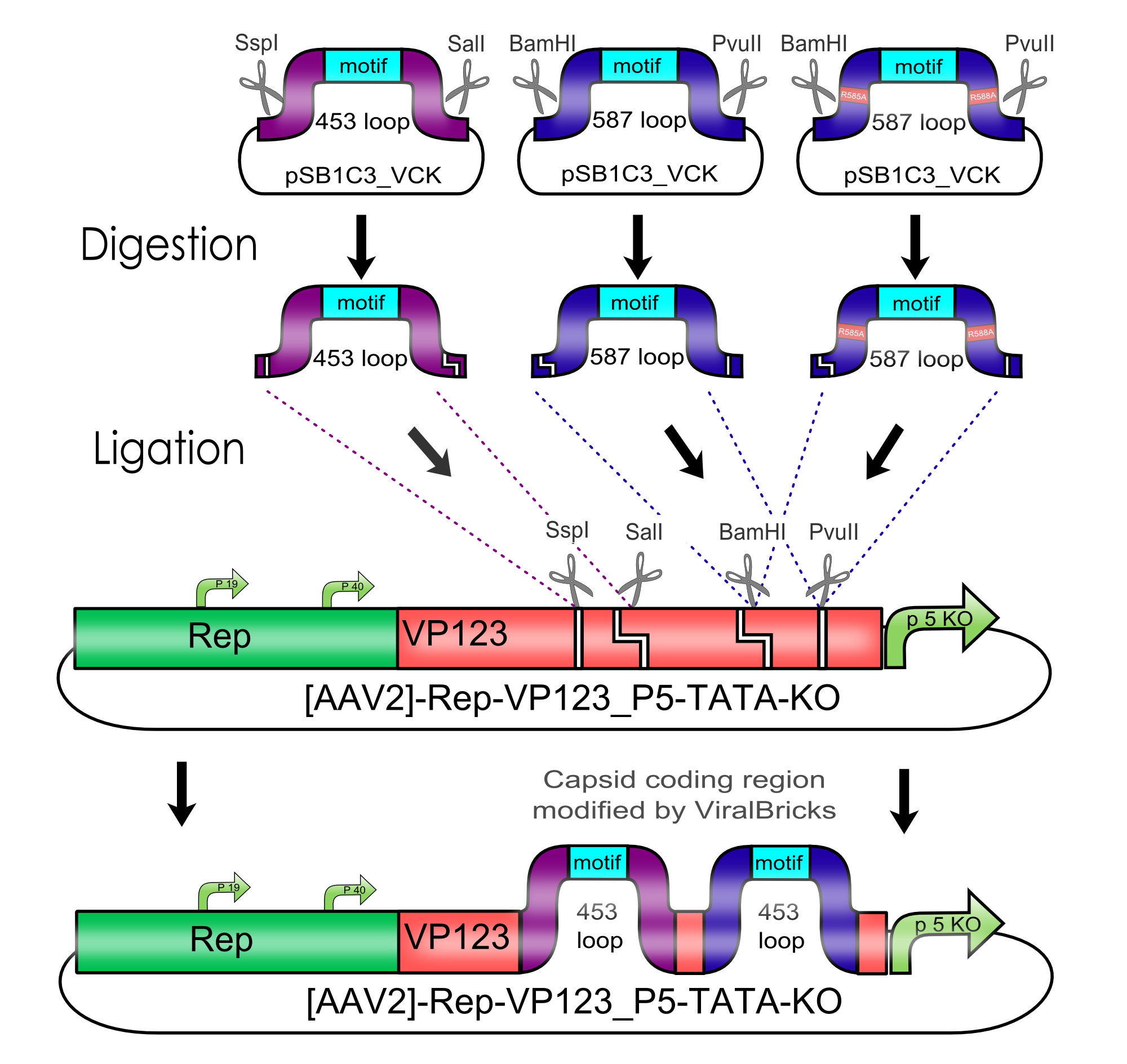
| BBa_K404204 | ViralBrick-453-Z34C | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 165 |
| BBa_K404206 | ViralBrick-587-His-Tag | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 105 |
| BBa_K404210 | ViralBrick-587KO-Empty | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 72 |
| BBa_K404222 | [AAV2]-Rep-VP123_P5-TATAless (ViralBrick-453-His-Tag) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 4410 |
| BBa_K404223 | [AAV2]-Rep-VP123_p5-TATAless (ViralBrick-453-RGD) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 4419 |
| BBa_K404224 | [AAV2]-Rep-VP123_P5-TATAless (ViralBrick-453-Z34C) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 4488 |
| BBa_K404225 | [AAV2]-Rep-VP123_P5-TATAless (ViralBrick-587-BAP) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 4446 |
| BBa_K404227 | [AAV2]-Rep-VP123_P5-TATAless (ViralBrick-587-RGD) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 4428 |
| BBa_K404229 | [AAV2]-Rep-VP123_P5-TATAless (ViralBrick-587KO-BAP) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 4446 |
| BBa_K404232 | [AAV2]-Rep-VP123_P5-TATAless (ViralBrick-587KO-RGD) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 4428 |
| BBa_K404234 | [AAV2]-Rep-VP123_P5-TATAless (ViralBrick-587KO-Z34C-Spacer) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 4503 |
| BBa_K404235 | [AAV2]Rep-VP123_p5TATAless (ViralBrick 453 Z34C-587 HSPG-KO) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 4488 |
| BBa_K404236 | [AAV2]Rep-VP123_p5TATAless (ViralBrick 453 RGD-587 HSPG-KO) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 4419 |
| BBa_K404241 | pCMV_[AAV2]VP123 (ViralBrick-453-BAP) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3049 |
| BBa_K404242 | pCMV_[AAV2]VP123 (ViralBrick-453-His-Tag) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3022 |
| BBa_K404243 | pCMV_[AAV2]VP123 (ViralBrick-453-RGD) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3031 |
| BBa_K404244 | pCMV_[AAV2]VP123 (ViralBrick-453-Z34C) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3100 |
| BBa_K404246 | pCMV_[AAV2]-VP123ex (ViralBrick-587-BAP) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3058 |
| BBa_K404247 | pCMV_[AAV2]-VP123ex (ViralBrick-587-His-Tag) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3031 |
| BBa_K404248 | pCMV_[AAV2]-VP123ex (ViralBrick-587-RGD) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3040 |
| BBa_K404250 | pCMV_[AAV2]-VP123ex (ViralBrick-587-Beta-lactamase) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3787 |
| BBa_K404251 | pCMV_[AAV2]-VP123ex (ViralBrick-587KO-BAP) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3058 |
| BBa_K404252 | pCMV_[AAV2]-VP123ex (ViralBrick-587KO-Empty) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2998 |
| BBa_K404253 | pCMV_[AAV2]-VP123ex (ViralBrick-587KO-His-Tag) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3031 |
| BBa_K404254 | pCMV_[AAV2]-VP123ex (ViralBrick-587KO-RGD) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3040 |
| BBa_K404255 | pCMV_[AAV2]-VP123ex (ViralBrick-587KO-Z34C) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3100 |
| BBa_K404256 | pCMV_[AAV2]-VP123ex (ViralBrick-587KO-Z34C-Spacer) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3115 |
| BBa_K404314 | DARPin-E01 | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 459 |
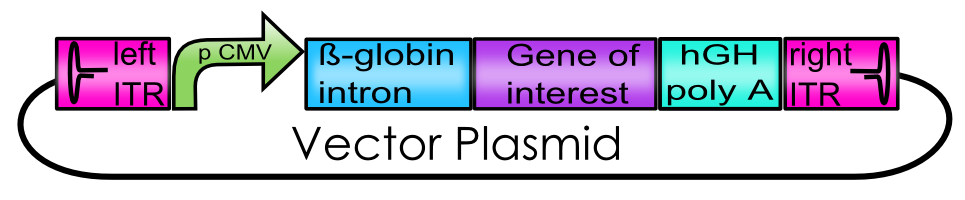
Explanation of the Vector Plasmid
The Adeno-associated Virus - Vector plasmid BioBricks
| Name | Description | Author | Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_K404100 | [AAV2]-left-ITR | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 147 |
| BBa_K404101 | [AAV2]-right-ITR | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 138 |
| BBa_K404108 | hGH terminator | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 481 |
| BBa_K404114 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_pCMV | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 809 |
| BBa_K404115 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_phTERT | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 612 |
| BBa_K404116 | hGH_[AAV2]-right-ITR | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 632 |
| BBa_K404117 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_pCMV_betaglobin | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 1310 |
| BBa_K404118 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_phTERT_betaglobin | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 1113 |
| BBa_K404119 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_pCMV_betaglobin_mVenus_hGH_[AAV2]-right-ITR | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2687 |
| BBa_K404120 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_pCMV_betaglobin_CFP_hGH_[AAV2]-right-ITR | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2687 |
| BBa_K404121 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_pCMV_betaglobin_mCherry_hGH_[AAV2]-right-ITR | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2826 |
| BBa_K404122 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_pCMV_betaglobin_mGMK_TK30_hGH_[AAV2]-right-ITR | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3659 |
| BBa_K404123 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_phTERT_betaglobin_mVenus_hGH_[AAV2]-right-ITR | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2490 |
| BBa_K404124 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_phTERT_betaglobin_mGMK_TK30_hGH_[AAV2]-right-ITR | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3462 |
| BBa_K404125 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_phTERT_betaglobin_CD_hGH_[AAV2]-right-ITR | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3057 |
| BBa_K404126 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_pCMV_betaglobin_CD_hGH_[AAV2]-right-ITR | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 3254 |
| BBa_K404127 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_pCMV_betaglobin_mVenus_[AAV2]-right-ITR | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2200 |
| BBa_K404128 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_pCMV_mVenus_hGH_[AAV2]-right-ITR | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2190 |
| BBa_K404129 | [AAV2]-left-ITR_phTERT_betaglobin_mCherry_hGH_[AAV2]-right-ITR | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 2629 |
The Adeno-associated Virus - Other system parts
| Name | Description | Author | Length |
|---|---|---|---|
| BBa_K404090 | [AAV2]-Rep40ex | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 940 |
| BBa_K404092 | [AAV2]-Rep68ex | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 1612 |
| BBa_K404094 | [AAV2]-AAPex | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 616 |
| BBa_K404103 | p5 promoter | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 166 |
| BBa_K404104 | p5-TATAless promoter | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 164 |
| BBa_K404105 | p40 promoter | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 182 |
| BBa_K404107 | Beta-Globin-Intron | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 495 |
| BBa_K404201 | ViralBrick-453-BAP | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 114 |
| BBa_K404202 | ViralBrick-453-His-Tag | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 87 |
| BBa_K404203 | ViralBrick-453-RGD | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 96 |
| BBa_K404205 | ViralBrick-587-BAP | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 132 |
| BBa_K404207 | ViralBrick-587-RGD | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 114 |
| BBa_K404208 | ViralBrick-587-Beta Lactamase (BLA) | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 174 |
| BBa_K404209 | ViralBrick-587KO-BAP | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 132 |
| BBa_K404211 | ViralBrick-587KO-His-Tag | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 105 |
| BBa_K404212 | ViralBrick-587KO-RGD | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 114 |
| BBa_K404213 | ViralBrick-587KO-Z34C | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 174 |
| BBa_K404214 | ViralBrick-587KO-Z34C-Spacer | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 189 |
| BBa_K404302 | Z-EGFR-1907 | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 174 |
| BBa_K404303 | Z-EGFR-1907_Short-Linker | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 192 |
| BBa_K404304 | Z-EGFR-1907_Middle-Linker | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 204 |
| BBa_K404305 | Z-EGFR-1907_Long-Linker | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 216 |
| BBa_K404306 | Z-EGFR-1907_SEG-Linker | Freiburg Bioware 2010 | 288 |
Virus Construction Kit
info AT biobricks DOT org
Viral Vectors are modified viruses that are used in molecular biology to transfer genetic material into desired cells. The adventage of viral vectors is that the different viral mechanismns can be employed to transduce the target cell in an specific and efficient manner. This process is called transduction when eucaryotic cells are the target of the gene transfer.
Key properties of a viral vector
- Safety: Viral vectors are often engineered on the basis of an human infectious virus. To reduce the risks for people that handle the virus and patient of an viral vector base therapy the genetic material of the viurs is manipulated in a way to knock-out the ability of the viral vector to reproduce. To reach this requirement the genes coding for the production of the viral capsid are often provided in trans to ensure that the viral vector does not contain the information for
- Low toxicity: For any use the effect the viral vector has on the transduced cells is important to consider. The [http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cytopathic_effect cytopathic effect] describes the effect of the physiology and morphology the infection with a viral particle has. For the use in vivo the immune response that is triggered by the viral vector has to be considered.
- Stability: Some viruses evolved a genome organisation that makes it possible to rearrage its genome easily. This feature has been used in the evolution to outflank the immune system of host organisms successfully but is absolute not desired in gene transfer with viral vectors and has to be reduced therefor.
- Cell type specificity: Many viruses evolved in a way that they are able to transduce many different cell types giving them a wide host cell range. For experimental and therapeutical applications a more narrow cell specificity can be desired. There viral vector systems should provide the possibility to modify the viral tropism in order to target specific cell types.
- Identification: ????
Main applications of viral vectors:
Double stranded DNA Viruses
The Adenovirus
| [http://expasy.org/viralzone/all_by_species/183.html Adenovirus] | |
|---|---|
| 200px | |
| Group: | ds DNA Virus |
| Family: | Adenoviridae |
| Genus: | Mastadenovirus |
| Host range | Human, mammals |
| Capacity: | 35000bp |
The Simian virus 40
The SV40 is a non-enveloped polyomavirus virus, containing a double stranded DNA genome of 5.2 kb. In comparism to other gene transfer vectors the genome of the virus is circular. Thus it lacks the terminal repeat regions characterizing many other viral vectors with linear genomes. The icosahedral capsid of the virus is formed by three virus-encoded proteins (VP1, VP2, and VP3), transcribed by the SV40 late promoters (LP). On the opposite strand the early (EP) promoters are located, driving the expression of the large T antigen (Tag) and a small t antigen (tag). Near a unique BglI site, there are the regulatory sequences, the origin of replication, and packaging signals. According to that the early and late polyadenylation signals are close to each other as well.
SV40 derived vectors have repeatedly proven to be effective, for example in gene delivery to the liver or hematopoietic progenitor cells. The vectors can be stable produced at a very high titer, lacking in immunogenicity and providing high levels of transgene expression in both resting and dividing cells. The principle limitation is the size of insert (≤5 kb) which can be packaged by SV40-derived vectors.
| [] | |
|---|---|
| 200px | |
| Group: | ds DNA Virus |
| Family: | Polyomaviridae |
| Genus: | Polyomavirus |
| Host range | Human, monkeys |
| Capacity: | 5200bp |
Single stranded DNA Viruses
The Adeno-associated Virus
| [http://expasy.org/viralzone/all_by_species/226.html Adeno-associated Virus] | |
|---|---|
| 200px | |
| Group: | ss DNA Virus |
| Family: | Parvoviridae |
| Genus: | Dependovirus |
| Host range | Human, vertebrates |
| Capacity: | 4700bp |
In the iGEM competition 2010 the Team Freiburg bioware constructed a Virus Construction Kit that makes the Adeno-associated virus (AAV2) available for all users of the parts registry.
The Adeno-associated virus is a well studied vector for eukaryotic gene transfer.
Double stranded RNA Viruses
Single stranded RNA (+) Viruses
Single stranded RNA (-) Viruses
Double stranded RNA retro-transcribing Viruses
Single stranded RNA retro-transcribing Viruses
The Lentivirus
| [http://expasy.org/viralzone/all_by_species/264.html Lentivirus] | |
|---|---|
| 200px | |
| Group: | ds DNA Virus |
| Family: | Retroviridae |
| Genus: | Lentivirus |
| Host range | Vertebrate |
| Capacity: | 9750bp |
References: 1)http://expasy.org/viralzone/