Help:Proteins
(Redirected from Help:Protein coding sequences and domains)
There are several different types of parts in the Registry associated with proteins.
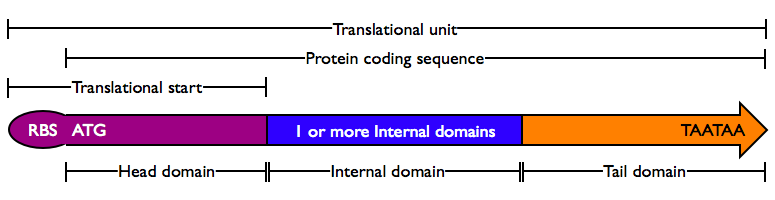
- Translational units begin with the RBS, the site of ribosome binding and translational initiation, and end with a stop codon, the site of translational termination.
- Protein coding sequences are DNA sequences that encode mRNAs that can be translated into a polypeptide chain which then folds into a 3 dimensional structure called a protein. Protein coding sequences begin with a start codon and end with stop codon.
- Protein domains encode portions of proteins and can be assembled together to form protein coding sequences. There are three types of protein domains, including Head domains, Internal domains and Tail domains.
- Translational start is a DNA sequence that encodes an ribosome binding site and Head domain.
For answers to common questions on these part types, see the FAQ.
Protein domains
- Glossary of terms relating to protein domain parts
- How to design protein domain parts
- How to enter protein domain parts in the Registry (coming soon!)
- How to construct protein domain parts
- How to assemble proteins domain parts
- Browse commonly used domains.
Protein coding sequences
- Glossary of terms relating to protein coding sequence parts
- How to design protein coding sequence parts
- Entering protein coding sequence parts in the Registry (coming soon!)
- How to construct protein coding sequence parts
- Browse commonly used protein coding sequence parts
Translational units
- Glossary of terms relating to translational units
- How to design translational unit parts
- Entering translational unit parts in the Registry (coming soon!)
- How to construct translational unit parts
Links
- [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/entrez/query.fcgi?db=Protein&itool=toolbar Entrez Protein] is a compilation of protein amino acid sequences
- [http://www.pir.uniprot.org/ UniProt] has both protein sequence and functional information
- [http://www.rcsb.org/pdb/Welcome.do Protein Data Bank (PDB)] has three dimensional structural information on proteins.