Part:BBa_K3385034
CRISPR_aplD_KO
Theoretical expectation: aplD encodes a gamma-adaptin involved in endosomal cargo transport and affects filamentous growth and pellet formation. Deletion of the gene was expected to result in a hyperbranched morphology.
Full guide construct for knockout of the transport involved protein aplD in A. niger. This BioBlock has to be cloned into the PacI/Nt.BbvCI digested pFC330 backbone.

Functionality: The sgRNA efficiency has been accessed through the technique to assess protospacer efficiency (TAPE) [2]. A repair oligo is used to mediate homologous recombination, where a highly efficient sgRNA will show no colonies without the repair oligo, while less efficient sgRNA will show a reduced number of colonies.
Results: Below is a picture showing A. niger transformed with CRISPR_aplD_KO and the repair oligo for aplD. It shows efficient gene deletion when it's transformed with a repair oligo.

To see if the K/O’s were successful, other than looking at macromorphology, tissue PCRs were performed. By the amplification of specific primers, upstream and downstream of the gene, it can be verified if the gene has successfully been knocked out. If it has been knocked out the primers are gonna be closer to each other resulting in a smaller band in the Tissue PCR. However if the gene is still present in the genome, the band size will be the same as the target gene as seen in the table below.
| Targeted gene | Expected gene length after K/O | Control lenght |
|---|---|---|
| ΔchsC | 704 bp | 1867 bp |
| ΔaplD | 590 bp | 3807 bp |
| ΔracA | 709 bp | 1920 bp |

Summary: From the different experiments it can be assumed that ΔaplD plays an important role in proper growth. Therefore, the ΔaplD mutant is not viable.
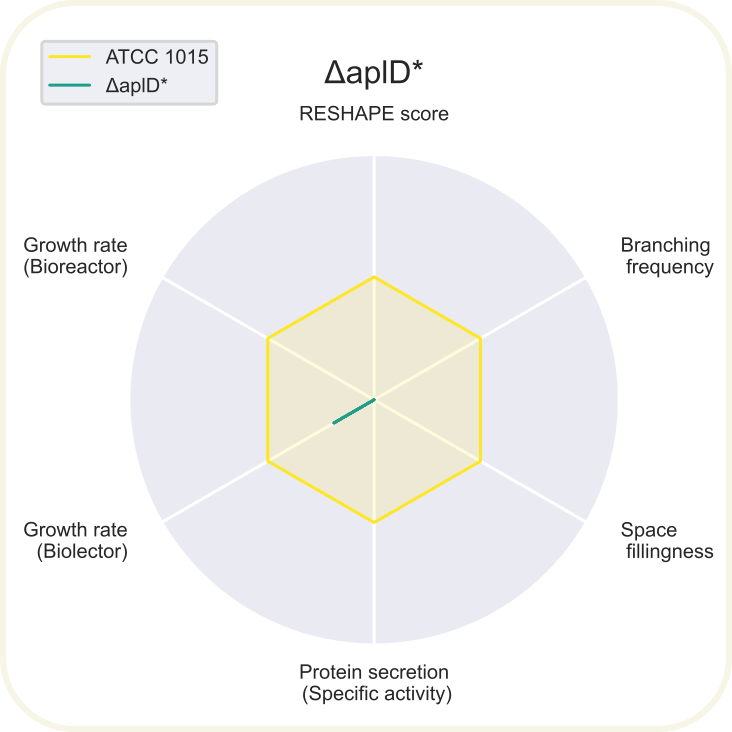
Radar chart showing 6 different parameters of ΔaplD normalized to the reference values from ATCC 1015 (shown in yellow). Read about the axis in the summary section on the result page.
*Indicates that not all data was obtained to fill out the chart.
Plates
The strain was grown on Yeast Extract Peptone Dextrose (YPD), Transformation Media (TM), Creatine Sucrose Agar (CREA) and Czepek Yeast Extract Agar (CYA).
Microscope pictures and Simulation model
Unfortunately, we did not get a microscopy picture of ΔaplD where it was possible to see branching angles, curvature of mycelia, etc. Thus we could not analyze the images properly and simulate the growth.BioLector
Comparing the growth kinetics of the ΔaplD mutant with the reference strain ATCC 1015 in the BioLector, the mutant exhibits a much longer lag phase followed by a three times longer exponential growth phase. The growth rate for the mutant is also much lower than for the reference strain, at μMax0.10h-1 versus &muMax0.28h-1. Additionally, only one out of the three replicates showed any growth at all.
Growth profile of ΔaplD over 72 hours, measuring absorbance at 620 nm. Plotted against the reference strain (ATCC 1015) shown in yellow.
Bioreactor and Protein secretion
ΔaplD was not run in the bioreactor due to time limitations. Data for growth in bioreactor and protein secretion for this strain were therefore not obtained.Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal EcoRI site found at 489
Illegal EcoRI site found at 660
Illegal EcoRI site found at 831
Illegal SpeI site found at 978 - 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal EcoRI site found at 489
Illegal EcoRI site found at 660
Illegal EcoRI site found at 831
Illegal NheI site found at 333
Illegal SpeI site found at 978 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal EcoRI site found at 489
Illegal EcoRI site found at 660
Illegal EcoRI site found at 831 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal EcoRI site found at 489
Illegal EcoRI site found at 660
Illegal EcoRI site found at 831
Illegal SpeI site found at 978 - 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal EcoRI site found at 489
Illegal EcoRI site found at 660
Illegal EcoRI site found at 831
Illegal SpeI site found at 978
Illegal AgeI site found at 204 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 162
References:
[1] A CRISPR-Cas9 System for Genetic Engineering of Filamentous Fungi. Nodvig CS, Nielsen JB, Kogle ME, Mortensen UH. PLoS One. 2015 Jul 15;10(7):e0133085. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0133085. eCollection 2015. PONE-D-15-11561 [pii] PubMed 26177455
[2] Efficient Oligo nucleotide mediated CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing in Aspergilli. Nodvig CS, Hoof JB, Kogle ME, Jarczynska ZD, Lehmbeck J, Klitgaard DK, Mortensen UH. Fungal Genet Biol. 2018 Jan 8. pii: S1087-1845(18)30004-5. doi: 10.1016/j.fgb.2018.01.004. 10.1016/j.fgb.2018.01.004 PubMed 29325827
