Part:BBa_K3743006
L7Ae
Part Description
L7Ae is a member of a protein's family that binds K-turns in RNA to stabilize the tightly kinked conformation. They are very popular and are important in the assembly of RNA–protein complexes central to translation, splicing and site-specific RNA modification. The interaction is used to control the synthesis of L7Ae proteins, and it is also influenced by N6 methylation of a key adenine in the k-turn during box C/D snoRNP assembly. Finally, the L7Ae–k-turn interaction can be used to form nanoscale assemblies.
Usage
L7Ae protein inhibits transcription by binding to its kink-turn (riboswitch) and it’s linked to dCas13 with a Gly Ser linker. The method simply recognises and attaches to mRNA in the cancerous environment, resulting in the consumption of the L7Ae protein. The inhibitory impact on transcription is decreased as a result of not binding to kink-turn, resulting in transcription activation and a rise in vaccine production.
Literature Characterization by AFCM-Egypt 2022 team
In order for our regulatory CRISPR-based system, which L7Ae attaches to, to operate as a regulator, domain the RNA of k-turn should be unstructured in the absence of L7Ae. In this figure, we examine how L7Ae affects both the native sequence and the mutant version of the k-turn. and in-line probing for both original and mutant RNA at concentrations of 0, 2.5, 5, and 10 M AfL7Ae, respectively. Positions of reactivity in the native 5′-UTR RNA in the presence of L7Ae are shown by the black circles drawn on the fluorogram as shown in figure 3
Characterization by mathematical modeling by AFCM-Egypt 2022 team
This model is to simulate the kinetics of the riboswitch (L7Ae with kink turns) that is used in our circuit. The designed circuit is to detect if the increasing substance is either phenylalanine or tyrosine via TyrR. So if phenylalanine level is elevated, L7Ae is formed as it is downstream TyrR that forms a complex via binding with its kink-turn on another circuit; that complex inhibits expression of cas12g, so the circuit will be able to express lacZ alpha (beta-galactosidase) in diagnostic circuit or PAH in the therapeutic circuit. If tyrosine level is elevated with a decreased level of phenylalanine, it activates tyrR inhibitory promoter so no L7Ae would be expressed resulting in cas12g expression to control the circuit as shown figure (4) and graph (1).

Figure (4) illustrates the kinetics of all reactions in riboswitch model

Graph (1) illustrates riboswitch kinetics in which Q represents the condition where L7Ae is expressed and bound to its kink-turns ,therefore inhibiting the expression of cas12g. However, M represents no expression of L7Ae in which cas12g would be expressed to control the circuit if the phenylalanine is absent.
Experimental Characterization by AFCM-Egypt 2022
This figure shows an experimental characterization of this part as it's validated through gel electrophoresis as it is in lane 5. The runnning part (ordered from IDT) included ParoF promoter - P2A - L7Ae.
Literature Characterization
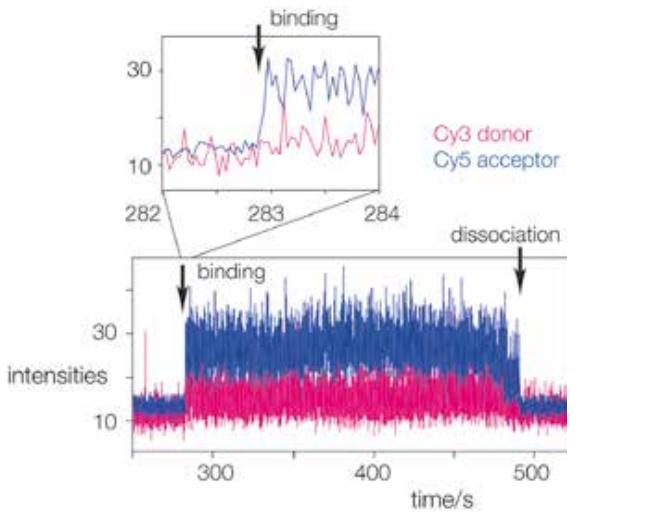
Real time single-molecule FRET observation of RNA folding when bound to the L7Ae protein is performed. The binding of terminally donor-acceptor fluorescently labelled RNA to the immobilised L7Ae protein can be seen. When the RNA binds to the L7Ae, it folds, increasing FRET efficiency and increasing the intensity of the Cy5 acceptor (blue trace) as shown in figure(1). The inset illustrates an extension of the region where the RNA binds to the protein, resulting in an immediate rise in FRET efficiency, indicating a conformational capture mechanism.(1)
Characterization Of Mutational Landscape
After performing mutagenesis prediction of mutational landscape of L7Ae and tested the effect of these mutations on the evolutionary fitness of the protein after generating multiple sequence alignment of the protein sequence and predict mutational landscapes. As shown in the chart, the (G108S) mutation showed the highest score compared to other mutations. On the contrary, we can see that the (G108K) contributed to the lowest evolutionary fitness to L7Ae. As shown in Figure (2)
References
1.Lilley, D. M. (2019). The L7Ae proteins mediate a widespread and highly functional protein–RNA interaction. The Biochemist, 41(2), 40-44.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
| None |