Part:BBa_K3111503
TmEncH_DARPin929_StrepII + TmEncH_StrepII + miniSOG_TP
T. maritima encapsulin (6-His) and DARPin929 fusion protein co-expressed with miniSOG in order to report targeting of HER2+ cells and cause a cytotoxic effect in them upon illumination. In addition, T. maritima encapsulin monomer by itself is added to the composite part, hoping to reduce steric hindrance on the outer side of an assembled encapsulin.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 171
Illegal BglII site found at 586
Illegal BglII site found at 1837
Illegal BglII site found at 2252
Illegal BamHI site found at 950
Illegal BamHI site found at 3296 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 2667
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 2872
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 3516
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 520
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 551
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 2186
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 2217
Composite Part Design
Surface display of large peptides on encapsulin C-terminus has not been previously described. Our major concern was that the fusion of DARPins on the T. maritima encapsulin monomer would hinder the assembly of 60-mer encapsulin. Our first design, shown in Figure 1 (top), involved C-terminal fusion of the DARPin on the encapsulin coding sequence. However, after discussions with Prof. Steve Brocchini we considered a second cloning strategy observed in Figure 1 (bottom). This involved the downstream cloning of an additional T. maritima encapsulin monomer under its own T7 promoter and ribosome binding site. The rationale was that simultaneous expression of fused and non-fused encapsulin monomers would allow the assembly of an encapsulin with a mixture of the 2 monomers. This would consequently reduce the DARPin load and potentially facilitate the assembly compared to original case where each monomer would have a fused DARPin.
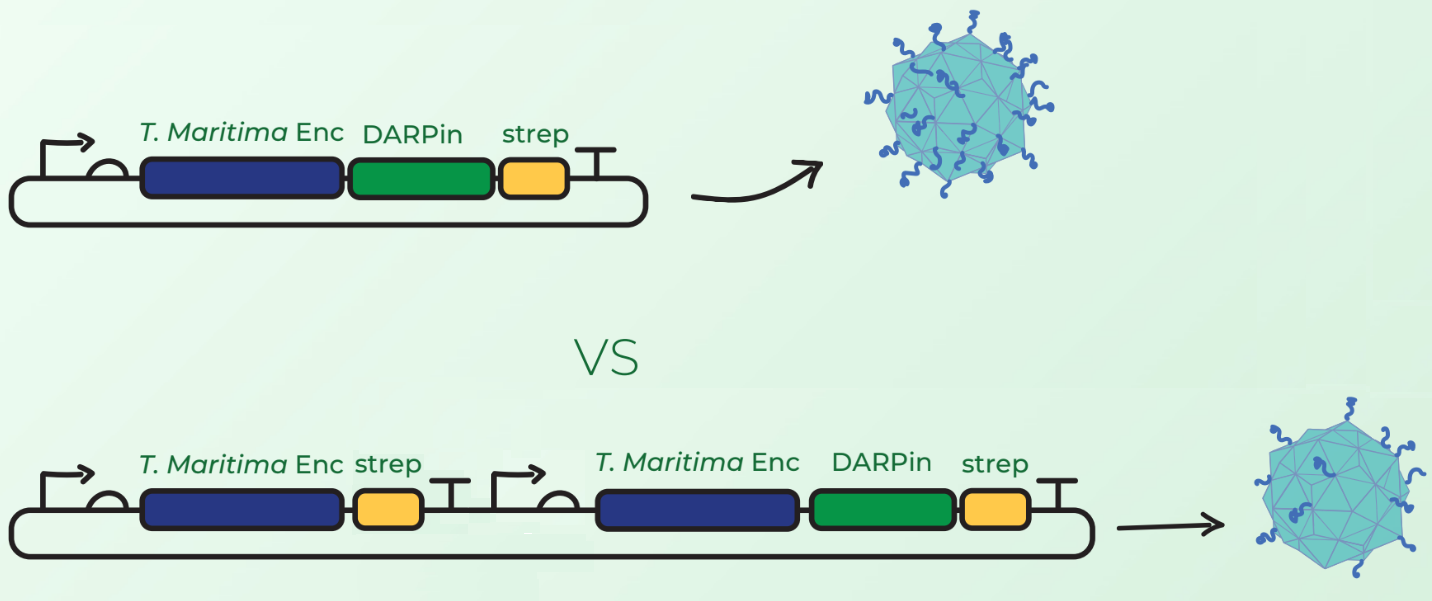
Experimental Results
Loading cytotoxic cargo
From Figure 1 we could clearly observe that T. maritima encapsulin monomer with C-terminally fused DARPin929 and T. maritima(6-His) encapsulin monomer by itself were both expressed. Since miniSOG does not possess a StrepII tag, thus the presence of the band at 15 kDa indicated its expression and that it was bound on some of the T. maritima encapsulin shells prior heat treatment for SDS analysis, thus confirming loading.
From gel analysis shown in Figure 3 we estimated that only about 4% of purified encapsulins had a DARPin joined to them. To quantify loading, fluorescence spectrophotometric analysis was conducted. Loading capacity was estimated to be 8.19+-0.21 molecules of miniSOG. On the other hand, BBa_K3111502 showed a much higher loading of 13.61+-0.34 miniSOG molecules per encapsulin. We theorise that this difference is caused by the surface display of DARPins slowing down the assembly of encapsulins and giving the targeting peptide present on miniSOG more time to form hydrophobic interactions to the inner shell of encapsulin monomers.
Cytotoxicity assay
Preliminary cytotoxicity tests using cell proliferation reagent WST-1 revealed that BBa_K3111502 outperformed BBa_K3111503, with 30% and 21% of reduction in cell viability after 30 minutes of illumination respectively. Therefore, additional experiments were only performed on BBa_K3111502.
| None |



