Part:BBa_K2549017
LaG17-mN1ce-tTAA
This part is the one original published[1], and we test but not used for further experiments. LaG17 (Part:BBa_K2549004) is used as the extracellular sensor module to receive the signal input from GFP. mN1ce (Part:BBa_K2549007), which has 3 more EGF repeats than mN1c, is served as the transmembrane core domain of SynNotch. tTAA (Part:BBa_K2446057) is an improved tetracycline-controlled transactivator[2], which is cleaved after SynNotch activation and drives the expression of the amplifier. Besides, a CD8α signal peptide (Part:BBa_K2549044) and a Myc-tag (Part:BBa_K823036) are added to the N terminal of LaG17 (Part:BBa_K2549004) for membrane targeting and easy determination of surface expression.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 87
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 2265
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 127
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 1180
Biology
Our characterization

Please note that LaG17-mN1ce-tTAA was not test in the experiment above.
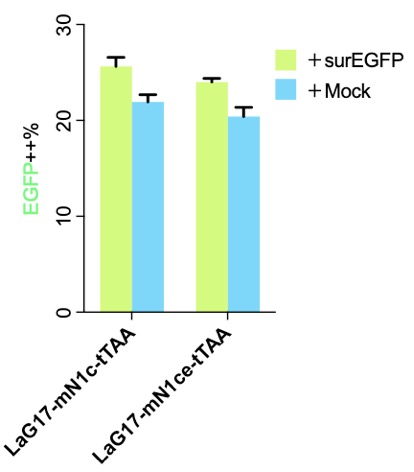
Part:BBa_K2549006 used in the experiments above is exactly as the published version, and the only difference was we transiently transfected the cells while the authors created stable cells and picked a cell clone for further experiments. Our results show three things: (1) SynNotch background activation is very high, which is why we put a lot effect in http://2018.igem.org/Team:Fudan/Optimization ; (2) mN1c might be better than mN1ce, not only shorter but a little higher signal-noise-ratio; (3) LaG17 is NOT a good extracellular antibody for SynNotch.
SynNotch receptors function well in Morsut L et al 2016

Please refer to the original article for more details.
References
- ↑ Engineering Customized Cell Sensing and Response Behaviors Using Synthetic Notch Receptors. Morsut L, Roybal KT, Xiong X, ..., Thomson M, Lim WA. Cell, 2016 Feb;164(4):780-91 PMID: 26830878; DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2016.01.012
- ↑ Exploring the sequence space for tetracycline-dependent transcriptional activators: novel mutations yield expanded range and sensitivity. Urlinger S, Baron U, Thellmann M, ..., Bujard H, Hillen W. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2000 Jul;97(14):7963-8 PMID: 10859354
//cds/receptor
| None |

