Part:BBa_K1933201
constitutive expression of anti-Norovirus GII.4 scFv fused to BclA with 6xHis tag
anti-Norovirus GII.4 scFv fused to BclA with 6xHis tag is one of a series of surface expressing fusion proteins that make up biodevice that aims to be the therapeutic solution against norovirus infections. This protein in particular is a single chained variable fragment(scFv) of a norovirus GII.4 strain fused to surface expression anchoring domain(BclA), connected by a 6xHis tag to be easily identified by Western blotting.
For more information, please visit [http://2016.igem.org/Team:Kyoto our wiki].
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal XhoI site found at 531
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Usage and Biology
NoV binding to Histo-blood group antigen (HBGA), expressed in red blood cells and duodenum cells, is suggested to be an important part of NoV invasion. Also, NoV binding to 12A2 antibody in its HBGA binding site has been demonstrated previously. [1] The scFv coded in our part derives from antibody 12A2, so it also sterically block the binding of NoV to HBGA in theory, which might neutralize NoV using the same mechanism.
Characterization
Sequence confirmed!
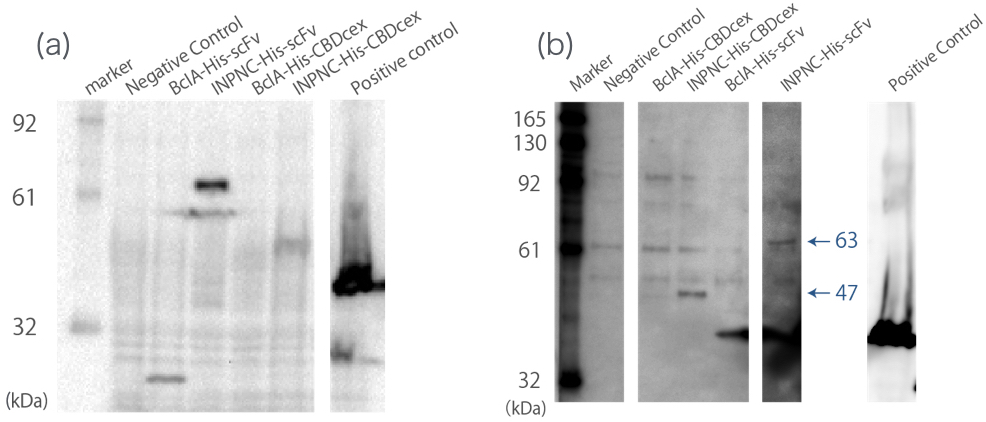
Western blotting
We used whole-cell Westernlotting with anti-His tag antibody(Fig.1(a)). Then, we prepared the membrane fraction from the E. coli lysate. Membrane fraction was solubilized and used for Nickel Sepharose purification and precipitates were examined by Western blotting against His tag(Fig.1(b)).
A band corresponding to BclA-His-scFv (33 kDa) was observed only in membrane fraction Western blotting, not in whole cell Western blotting (Fig.1(a),(b)), which indicates fusion protein was expressed and purified using Nickel Sepharose.
Scanning Electron Microscopy
First, we constructed INPNC-His-scFv and BclA-His-scFv (BclA:another surface display module) encoding plasmids. Then we transformed E. coli (strain:DH5α)with these plasmids, and observed its interaction with NoV-like particles (NoVLP, the capsid proteins of NoV) of NoV GII.4 strain. (Fig.2) We observed NoVLP only on the surface of INPNC-His-scFv expressing E. coli , as NoVLP could not be observed in E.coli expressing BclA-His-scFv, (Which may be due to low expression levels, seen in Fig.2), this NoVLP is not unspecifically mixed with the sample. Thus we concluded that we observed the binding of our INPNC-His-scFv expressing E. coli to NoVLP.
Thus, we conclude that this part did not work as expected.
- NoVLP was kindly given to us by Dr. Daisuke Sano in Hokkaido University.
For more information, please visit [http://2016.igem.org/Team:Kyoto our wiki].
Reference
[1]Shanker, Sreejesh, et al. "Structural basis for norovirus neutralization by an HBGA blocking human IgA antibody." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2016): 201609990.
| None |