Part:BBa_K1913002
chiA device regulated by pBAD
This part uses a pBAD promoter (BBa_I0500), weak RBS (BBa_B0032), chiA protein coding sequence (BBa_K1913000) and a double terminator (BBa_B0015). When induced with arabinose, it will produce chiA. A weak promoter was chosen to prevent formation of inclusion bodies during expression.
Usage and Biology
Introduction
Chitinases from Serratia marcescens are very well characterized, as Serratia marcescens is considered a model organism for chitin degradation. This chiA BioBrick is based on the chitinases produced by Serratia marcescens strain GEI, a strain which causes high mortality in the parasitic honeybee mite Varroa destructor. Tu et al1 cloned the chitinases into Escherichia coli, purified them and showed that ChiA and ChiB acted synergistically to increase mite mortality.
Structure and function
ChiA and ChiB are modular enzymes with both a carbohydrate binding domain and a distinct catalytic domain. They can display both endochitinase and exochitinase activity. Endochitinase activity means that the enzymes cleave randomly inside the long chitin polymers, while exochitinase activity only targets the polymer's ends. ChiA and ChiB are both processive enzymes with exochitinase activity, but they can also show endochitinase activity if the substrate is accessible enough. Their carbohydrate binding domains are oriented in opposite directions and they each attack the chitin polymers from opposite ends, which seems to explain their synergistic action. However, most studies on chitinase function have been done on synthetic substrates rather than natural substrates such as shrimp chitin. It is therefore not clear how the specificity of strain GEI's chitinases is related to substrate structure2.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 1205
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 1144
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 979
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI site found at 961
Characterization of chitinases
ChiA and ChiB were cloned into Escherichia coli BL21 and expressed using BioBrick devices BBa_K1913002 and BBa_K1913003 respectively. SDS-PAGE was performed to analyse the constructs for expression of the chitinases, but no significant expression could be observed (Figure 1). Expression was also tested with colloidal chitin plates, but this assay failed to yield results.

Figure 1. Photo of a 10% BioRad MiniProtean gel loaded with protein extracts from BL21 constructs with chitinase devices. Device BBa_K1913002 is supposed to express a 81.5 kDa protein, while BBa_K1913003 should express a 76 kDa protein and BBa_K1913004 should express both. They were induced with 0%, 0.2% or 1% arabinose. The gel was run for 38 minutes at 50 mA together with a gel for the cellular debris (not shown).
[1] Tu, S., Qiu, X., Cao, L., Han, R., Zhang, Y., & Liu, X. (2010). Expression and characterization of the chitinases from Serratia marcescens GEI strain for the control of Varroa destructor, a honey bee parasite. Journal of invertebrate pathology, 104(2), 75-82.
[2] VaajeâKolstad, G., Horn, S. J., Sørlie, M., & Eijsink, V. G. (2013). The chitinolytic machinery of Serratia marcescensâa model system for enzymatic degradation of recalcitrant polysaccharides. FEBS Journal, 280(13), 3028-3049.
Added by Thinker-Shenzhen
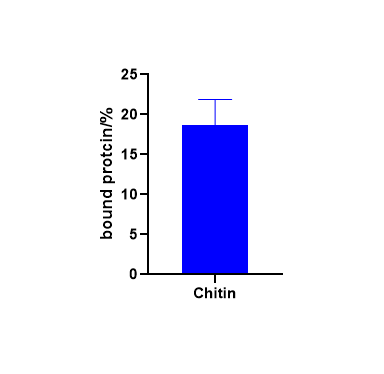
For the measurement of binding capacity
we took 2 Οmol/L of chitinase in 50 mmol/L phosphate buffer (pH=8) and mixed thoroughly at 4°C (assuming no degradation), reacted for 1 h on a rotary mixer, 10,000 r/min for 5 min and collected the supernatant, which was the unbound protein, by Protein concentration was measured by the BCA method.
For the measurement of chitinase activity, chitinase is able to hydrolyse chitin to produce N-acetylglucosamine, which further reacts with 35-dinitrosalicylic acid to produce a brownish-red compound with a characteristic absorption peak at 540 nm, and the activity of chitinase can be characterised by the change in absorbance value.
| None |