Part:BBa_K1080005
CTH1
Usage and Biology
Chlorophyll is a light harvesting pigment that has an isocyclic ring formation, as it is part of the tetrapyrrol family. CTH1 protein is a functional protein that is developed in the presence of oxygen or copper. This isocyclic formation is formed by the action of the protein Mg-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl ester oxidative cyclase 2 in the gene CTH1. This protein catalyzes the Mg-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl, which converts to divinyl protochlorophyllide in the presence of NADPH and O2. [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Regulation+and+Localization+of+Isoforms+of+the+Aerobic+Oxidative+Cyclase+in+Chlamydomonas+reinhardtii+%E2%80%A0] [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=PMID%3A+1905926]
Copper target 1 protein - functional variant produced under copper and/or oxygen sufficient conditions [GI:15650866; PMID: 11910013; 14673103]; CTH1; Mg-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl ester (oxidative) cyclase, aerobic oxidative cyclase; orthologous to Rubrivaxgelatinosus aerobic oxidative cyclase [PMID: 11790744; 14617630]; predicted chloroplast transit peptide 1-35; Orthologous to CRD1; CHL27B [PMID: 15849308]
Operon Usage
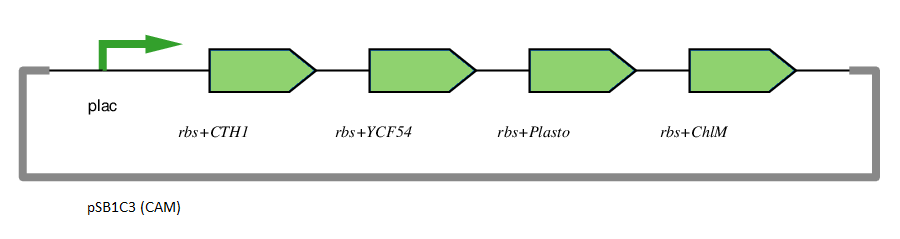
Figure 1: This gene has been used in an operon with other genes responsible for catalysing the biosynthesis pathway from Mg-protoporphyrin IX to Protochlorophyllide. CTH1, Plastocyanin, and YCF54 are involved in the oxidative cyclase pathway. ChlM methylates Mg-protoporphyrin IX, facilitating the highly-regulated catalysis of Mg-chelatase. CTH1 catalyses the conversion of Mg-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl into divinyl protochlorophyllide, interacting with YCF54 and Plastocyanin.
The insertion of magnesium is the key component of the chlorophyll biosynthesis pathway.
The plasmid is under the control of the lac promoter.
Biobrick Design:
Source Genbank accession: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/AF337037.3 AF337037.3]
Source Uniprot reference: [http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q9AR22 Q9AR22]
cDNA gene sequence from Chlamydomonas reinhardtii was sourced from NCBI database, chloroplast targeting sequence was removed. EcoRI/XbaI/SpeI/PstI restriction sites were removed via codon adjustment, biobrick prefix and RBS were added to start of gene, biobrick suffix added to end of gene.
Biobrick construction: Gibson assembly of 3 synthesised DNA fragments into BB vector.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 305
Illegal BglII site found at 413 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 103
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 259
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 880
Amino acid sequence
MVAATAAPQE VEGFKVMRDG IKVASDETLL TPRFYTTDFD EMERLFSLEL NKNMDMEEFE
AMLNEFKLDY NQRHFVRNET FKEAAEKIQG PTRKIFIEFL ERSCTAEFSG FLLYKELGRR
LKATNPVVAE IFTLMSRDEA RHAGFLNKAM SDFNLALDLG FLTKNRKYTF FKPKFIFYAT
YLSEKIGYWR YISIYRHLQR NPDNQLYPLF EYFENWCQDE NRHGDFFTAV LKARPEMVND
WAAKLWSRFF CLSVYITMYL NDHQRDAFYS SLGLNTTQFN QHVIIETNKS TERIFPAVPD
VENPEFFRRM DLLVKYNAQL VNIGSMNLPS PIKAIMKAPI LERMVAEVFQ VFIMTPKESG
SYDLDANKTA LVY
References and documentation are available. Please note the modified algorithm for extinction coefficient.
Number of amino acids: 373
Molecular weight: 43873.3
Theoretical pI: 5.98
Amino acid composition:
Ala (A) 28 7.5%
Arg (R) 23 6.2%
Asn (N) 23 6.2%
Asp (D) 19 5.1%
Cys (C) 3 0.8%
Gln (Q) 11 2.9%
Glu (E) 31 8.3%
Gly (G) 12 3.2%
His (H) 6 1.6%
Ile (I) 18 4.8%
Leu (L) 35 9.4%
Lys (K) 23 6.2%
Met (M) 15 4.0%
Phe (F) 33 8.8%
Pro (P) 15 4.0%
Ser (S) 17 4.6%
Thr (T) 21 5.6%
Trp (W) 4 1.1%
Tyr (Y) 17 4.6%
Val (V) 19 5.1%
Pyl (O) 0 0.0%
Sec (U) 0 0.0%
(B) 0 0.0% (Z) 0 0.0% (X) 0 0.0%
Total number of negatively charged residues (Asp + Glu): 50
Total number of positively charged residues (Arg + Lys): 46
Atomic composition:
Carbon C 1999 Hydrogen H 3041 Nitrogen N 515 Oxygen O 563 Sulfur S 18
Formula: C1999H3041N515O563S18 Total number of atoms: 6136
Extinction coefficients:
Extinction coefficients are in units of M-1 cm-1, at 280 nm measured in water.
Ext. coefficient 47455 Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 1.082, assuming all pairs of Cys residues form cystines
Ext. coefficient 47330
Abs 0.1% (=1 g/l) 1.079, assuming all Cys residues are reduced
Estimated half-life:
The N-terminal of the sequence considered is M (Met).
The estimated half-life is:
30 hours (mammalian reticulocytes, in vitro).
>20 hours (yeast, in vivo).
>10 hours (Escherichia coli, in vivo).
Instability index:
The instability index (II) is computed to be 36.26 This classifies the protein as stable.
Aliphatic index: 77.69
Grand average of hydropathicity (GRAVY): -0.313
Source
Chlamydomonas reinhardtii
References
Allen, M. D., et al. (2008). "Regulation and localization of isoforms of the aerobic oxidative cyclase in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii." Photochem Photobiol 84(6): 1336-1342.
Walker, C. J., et al. (1991). "Synthesis of divinyl protochlorophyllide. Enzymological properties of the Mg-protoporphyrin IX monomethyl ester oxidative cyclase system." Biochem J 276 ( Pt 3): 691-697.
| None |
