Part:BBa_K4437500
DeadRBS (non-coding)
Usage and Biology
This part, titled "DeadRBS", is an RBS derived from a study by Kosuri et al. (2013), which determined how translational efficiency changes depending on the strength of the RBS used in E. coli [1] The library from which the DeadRBS was sourced was synthesized using Agilent's oligo library synthesis [1]. Although the DeadRBS (BBa_K4437500) has experimentally demonstrated to have a low affinity for the ribosome, it is still capable of producing trace amounts of protein, which is a tool that can be leveraged by future teams aiming to produce trace amounts of certain genes in an operon [1]. For our experiments, the DeadRBS was an important component in our composite part collection, as it served as a negative control and a point of reference against which to assess and analyse other protein expression levels.
Design
This RBS is directly sourced from the library assembled and tested by Kosuri et al. (2013), and was selected by our team for its ability to result in trace protein expression levels. In order to insert this RBS upstream of the FLAG-phasin-HlyA sequence, it was designed into a forward primer with a unique BstAPI restriction enzyme cut site at its 5' end. This provided an efficient means to ensure the DeadRBS-FLAG-phasin-HlyA fragment was compatible for ligation into the BBa_K934001 plasmid, while also providing a facile way to discern whether or not addition and amplification of the part including the RBS was successful.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Characterization
The successful amplification of the FLAG-phasin-HlyA insert to produce the DeadRBS-FLAG-phasin-HlyA DNA fragment was determined by the into the successful insertion of this fragment into the BBa_K934001 plasmid. As the specific BstAPI and BstBI restriction enzyme pair included on the forward and reverse primer, respectively, the digestion --and subsequent ligation reactions -- involving these enzymes would otherwise have proven unsuccessful. Finally, SDS-PAGE assays confirmed low protein production levels characteristic of the DeadRBS.
Figure 1. Agarose electrophoresis of purified DNA. Lane 1 contains a 2log 1000bp ladder. Lanes 20-24 contain the DeadRBS-FLAG-phasin-HlyA insert in the BBa_K934001 plasmid, transformed in and purified from BL21 E. coli. Lane 20 indicates banding at the anticipated range of approximately 7100bp, indicating the successful insertion and transformation of the BBa_K4437502 insert.
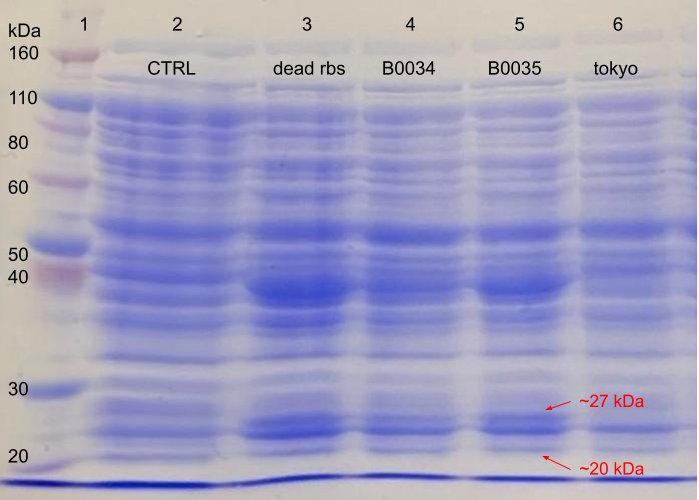
Figure 2.The expression of RBS-FLAG-phasin-hlyA with varying RBS strengths from the PHB construct (BBa_K934001) from BL21 (DE3) E.coli strain autoinduced for 24 hours. The process was visualised using 10% SDS-PAGE in 100V for 20 minutes and 180V for 40 minutes. The gel was stained with Coomassie blue. The gel was loaded as follows: (1) Ladder, (2) Lanmodulin positive control (BBa_K3945001), (3) Dead RBS upstream of phasin-Hlya in PHB construct (BBa_K4437501), (4) B0034 RBS upstream of phasin-Hlya in PHB construct (BBa_K226003), (5) B0035 upstream of phasin-Hlya in PHB construct (BBa_K4437502), (6) Tokyo 2012 PHB construct only (BBa_K934001).
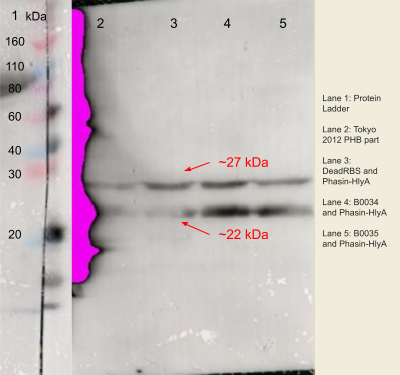
Figure 3.The expression of phasin-hlyA with varying RBS strengths from the PHB construct (BBa_K934001) from BL21 (DE3) E.coli strain autoinduced for 48 hours on an SDS page using Anti-FLAG antibodies and the complementary capture antibody. The process was visualised using 10% SDS-PAGE in 100V for 20 minutes and 180V for 40 minutes. The gel was loaded as follows: (1) Ladder; (2) Tokyo 2012 PHB construct only (BBa_K934001); (3) B0034 RBS upstream of phasin-HlyA in PHB plasmid (BBa_K4437500); (4)B0034 RBS upstream of phasin-HlyA in PHB construct (BBa_K226002); (5) B0035 upstream of phasin-Hlya in PHB construct (BBa_K4437504).
References
1. Kosuri S, Goodman DB, Cambray G, Mutalik VK, Gao Y, Arkin AP, et al. Composability of regulatory sequences controlling transcription and translation in Escherichia coli. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 2013 Aug 20;110(34):14024–9.
| None |