Part:BBa_K2985002
yerP->express self-resistence of surfactin
YerP gene plays an important role in surfactin production in bacterial cells. According to the information of many literatures, although the specific working principle of yerP gene has not been found yet, the current statement is that gene yerP encodes a specific resistance protein, so that bacterial cells can still grow at a higher surfactin concentration. At the same time, in the presence of yerP, the production of surfactin has been greatly improved, but for cell growth and Producing surfactin is not a necessary gene.
According to the research of Japanese scholars [1], although there is no direct evidence that the yerP gene is involved in the synthesis of surfactin, the resistance of bacterial cells containing yerP to surfactin, including the tolerance to intracellular surfactin, is still worth studying.
We analyzed the genome of Bacillus subtilis 168, but we did not find the existence of yerP in the large gene cluster of yerP. We designed primers to enter the cell genome by transferring the yerP gene. (Fig. 1)

Figure 1: the red gene is the yerP gene, which we inserted. Its location is between yerO and yerQ
We found our target gene fragment in Bacillus amylolyticus. By designing primers and PCR experiments, we obtained our target gene fragment. The following pictures of gel running were obtained, with a total length of 3198bp of yerP gene.
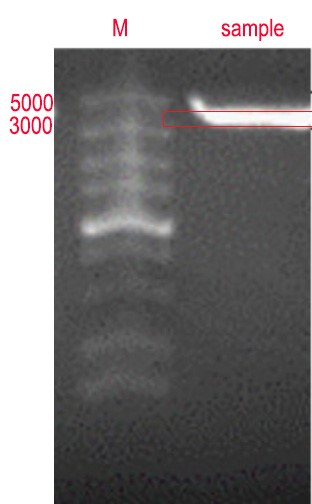
Figure 2: 0.8% agarose gel electrophoresis and PCR validation. The product has a signal band at 3198 bp, which is consistent with the target length.
However, due to the specific production of resistance protein has not found the relevant basis, did not carry out further research on its coding protein.
In order to confirm that yerP gene can improve the tolerance of the strain, the morphology of the strain was observed by electron microscopy.
File:Jiangnan-China yerP-figure 3.jpeg
Figure 1: Morphology of wild-type Bacillus subtilis 168 at higher surfactin concentration
File:Jiangnan-China yerP-figure 4.jpeg
Figure 1: The morphology of Bacillus subtilis after transformation at higher surfactin concentration
We can clearly compare the difference between before and after through the electron micrograph. Because of the unique negative effect of lipopeptide on the cell membrane, the cell membrane shows the damaged shape and the cell dies. However, after modification, the tolerance expressed by the yerP gene is reflected in its ability to protect the cell membrane, which also confirms the powerful role of the parts of the yerP gene.
At the same time, our research on this part is based on the previous transformation. We only get the great help of yerP gene to the strains producing surfactin through the fermentation experiment after that.
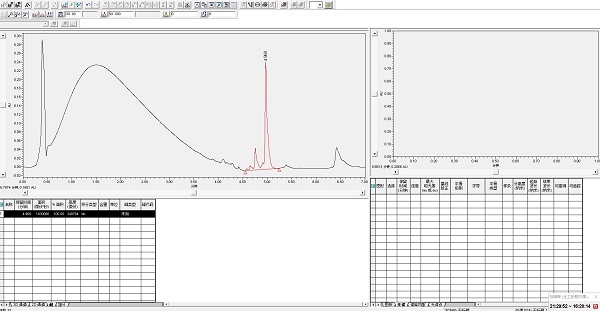
The value of surfactin was increased compared to the liquid phase diagram of the fermentation broth in the previous step, and there was also a difference due to the effect of fermentation batch on yield.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 408
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 112
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 2965
Illegal AgeI site found at 237
Illegal AgeI site found at 1627 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI site found at 2093
| None |
