Part:BBa_K1218026:Experience
This experience page is provided so that any user may enter their experience using this part.
Please enter
how you used this part and how it worked out.
Experimental data (provided by the 2013 Stanford-Brown iGEM Team)
Thermal denaturation: thermodynamic evidence of silver binding
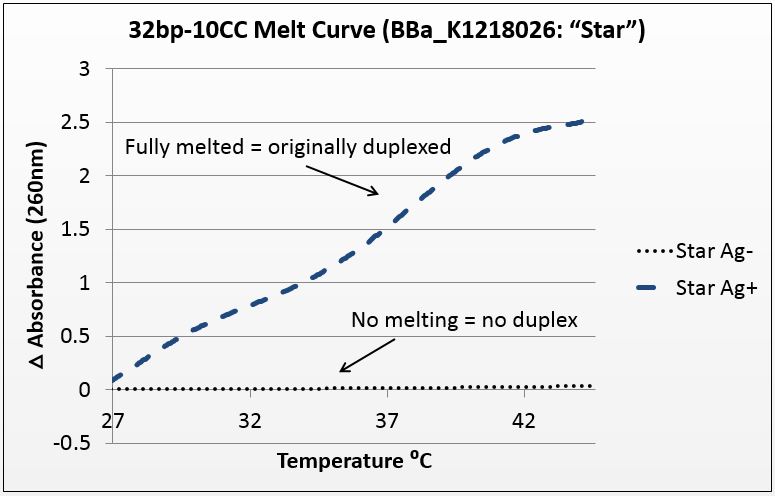
For this experiment, we sought to unequivocally prove that there was silver uptake by the excised duplex. To do this, we annealed the strands in two conditions: Ag+ (silver present) and Ag- (silver absent). The mismatch-complementary oligonucleotides in this sample were shown to only anneal in the presence of Ag+.
It is known that when double-stranded DNA is heated, it “melts,” or experiences a breakdown of its secondary structure. Beer’s law states that for a fixed volume and molecule, absorbance is proportional to concentration. As DNA melts, the concentration of nucleotides doubles, and the absorbance will increase similarly.
To show intercalation, we hypothesized that in this highly-mismatched strand, annealing will only occur in the presence of silver. Consequently, those strands should only show an absorbance increase with temperature if they were annealed with silver. That which does not anneal will not melt.
The graph below is the average of four trials, plotted for unit-less change in absorbance at 260nm (absorbance of dsDNA) over increasing temperature. The spectrophotometer we had access to restricted temperature to a maximum of 45°C, which we factored into the sequence design. 535 data points for each trial were taken across a 20°C temperature difference, rendering the ensuing data quite statistically significant.
Figure 1: average of four trials on 32bp10CC Star sequence, P value of 10^-272 in paired T-Test.
Applications of BBa_K1218026
User Reviews
UNIQ7ca4237cff17507c-partinfo-00000000-QINU UNIQ7ca4237cff17507c-partinfo-00000001-QINU