Part:BBa_K1021003
bar (bialaphos resistance)
The bialaphos resistance (bar) gene confers resistance to bialaphos and phosphinothricin.
Usage and Biology
The common fungus transformation system of entomopathogen Metarhizium anisopliae was based on resistance to the herbicide glufosinate ammonium (phosphinothricin), conferred by the bar gene.
Team NYMU 2016 characterized the bar marker gene, a twin of this part, using the bar expression cassette on vector pBARGPE1 with our chassis organism M.anisopliae.
The transformants carrying the bar gene can grow on the PDA containing glufosinate ammonium.
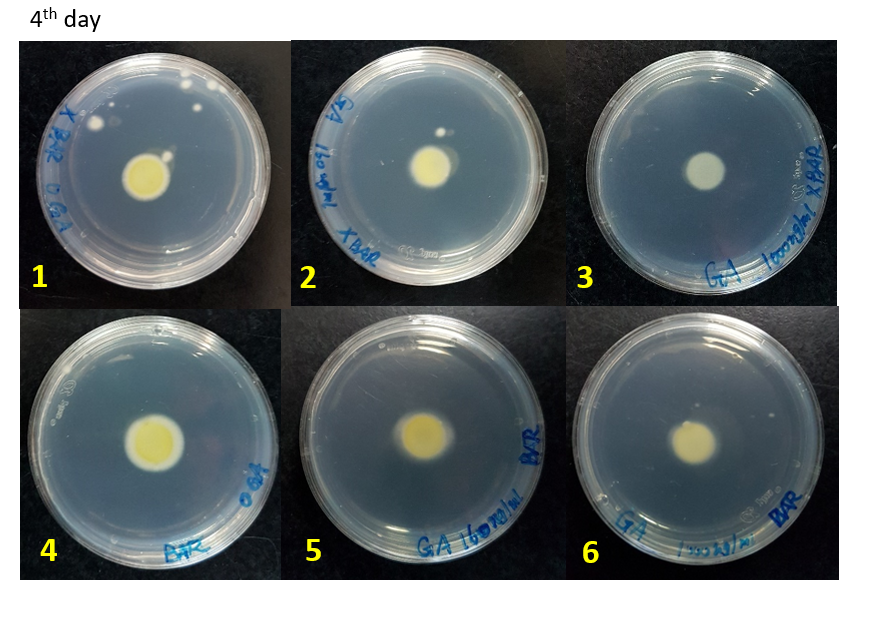
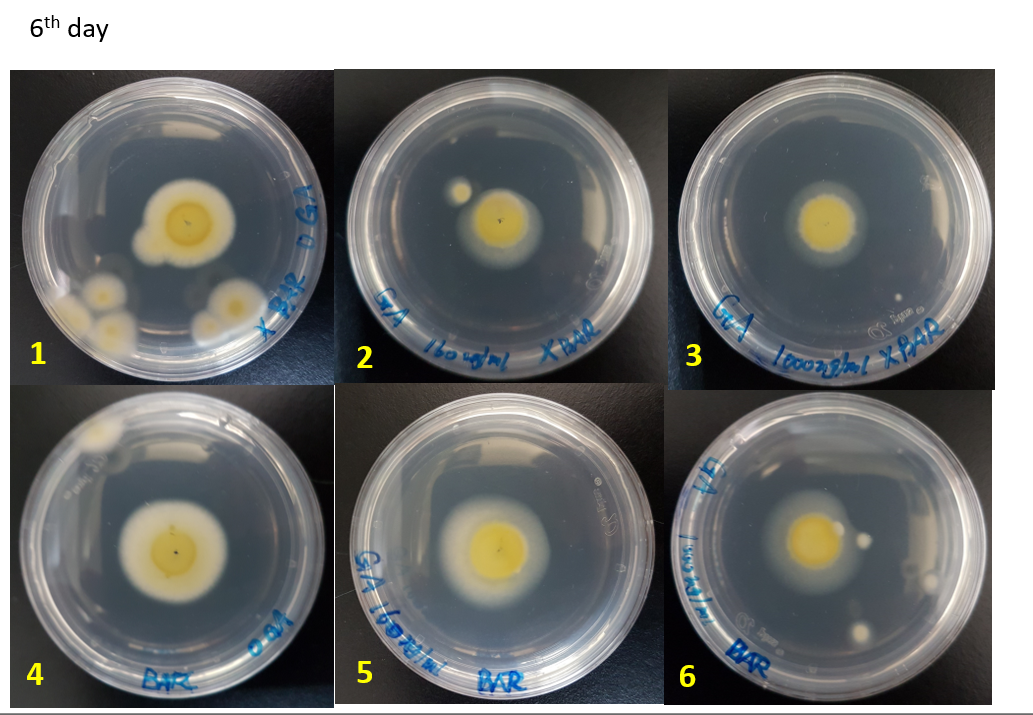
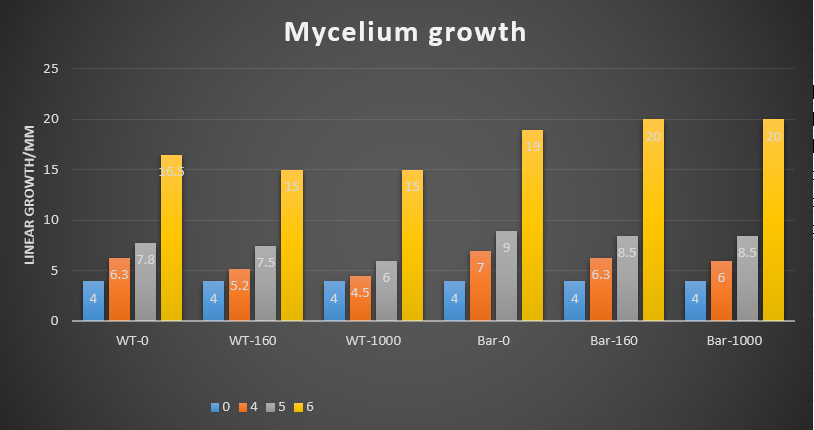
We did the glufosinate ammonium inhibition test using three different concentrations (0, 160, 1000 ug/mL) with bar transformants and wildtype as a control, the result is showed below.
The initial radius were all 4mm. The mycelium length was measured on day 4, 5 and 6 after starting M.anisopliae conidia cultivation on solid media. The mycelium length was measured on the same line on each plate.
- The higher glufosinate ammonium concentration, the more sparse the mycelium grows outward.
Data:
WT-0, 160, 1000 ug/mL: Wild type strains grew on the media contained 0, 160, 1000 ug/mL.
Bar-0, 160, 1000 ug/mL: Bar transformants grew on the media contained 0, 160, 1000 ug/mL.
[[Image:Bar2.png|center|600px]
These results showed that glufosinate ammonium affect the growth of the mycelium, but not as effectively as expected. It may be caused by the degradation of this herbicide due to the long store.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 545
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 54
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 205
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 451 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
| None |