Part:BBa_K1991009
Pcons-RBS-LO-AOX2-His
DISPLAYING AOX ENZYME ON THE CELL SURFACE OF E. COLI
A protein can be displayed on the cell surface of E. coli by fusing to Lpp-OmpA. Lipoprotein ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P69776 Lpp]) is a major outer membrane of E. coli which interacts with the peptidoglycan to maintain the structure and function of cell membrane. Another transmembrane protein called outer membrane protein A ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/P0A910 OmpA]) is involved in bacterial conjugation and phage infection. A study showed that Lpp-OmpA hybrid can direct the heterologous protein GFP to the external surface of E. coli (Enzyme Microb Technol. 2001). Bacillus lipase (J Microbiol. 2014) and Fungi xylanase (Curr Microbiol. 2015) were demonstrated to be displayed on the cell surface of E. coli and maintained the functional enzyme activities. In iGEM 2016 MINGDAO's project, AOX (alcohol oxidase) was displayed on bacterial surface by fusing with Lpp-OmpA, which was proved by protein analysis, enzyme activity assay and TMB assay
PROTEIN EXPRESSION ANALYSIS
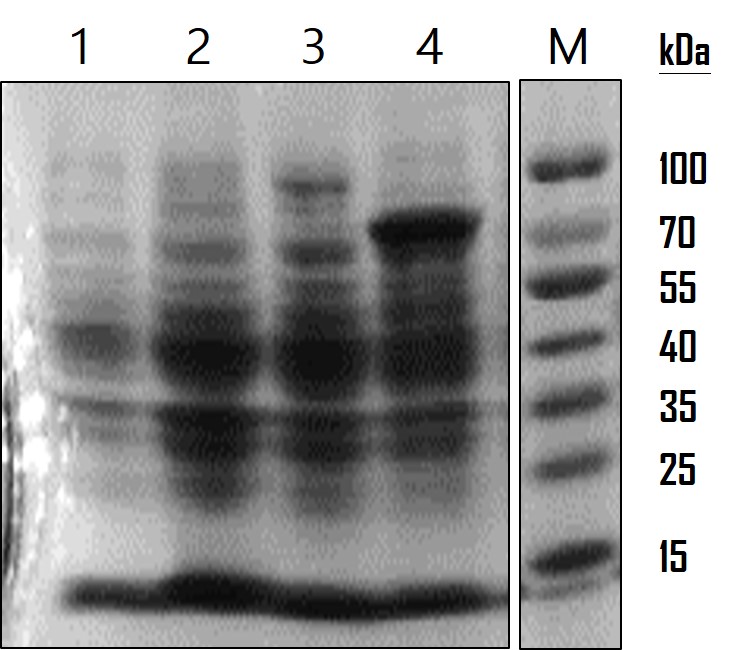
To analyze the AOX gene expression, we run on a SDS-PAGE gel and observed by Coomassie Blue staining. The overnight-cultured E. coli were centrifuged and lysed with Lysis Buffer (12.5 mM Tris pH 6.8, 4% SDS). The resulting lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE with a 10% polyacrylamide gel. The gel was stained with 0.25% Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 for 2 hours and destained until the protein bands were clear. As the data showed in Figure 1, LO protein was expressed at around the estimated molecular weight of 17 kDa, LO-AOX fusion protein at 91 kDa and AOX protein at 79 kDa. The protein expression level was low compared to AOX expression but significant compared to WT and LO. However, so far we cannot confirm whether LO fusion protein is able to direct AOX or GFP proteins displayed on the cell surface of E. coli. We’re planning to do a subcellular fractionation to separate the outer membrane proteins for analysis in the future.
Figure 1: AOX protein analysis. SDS-PAG and Coomassie Blue staining were used to observe protein expression level. Lane 1: wild-type E. coli as a mock control; Lane 2: LO outer membrane protein (BBa_K1991007) (17 kDa) expression in E. coli; Lane 3: LO-AOX fusion protein BBa_K1991009) (91 kDa) expression in E. coli.; Lane 4: AOX protein BBa_K1991003) (79 kDa) expression in E. coli.
ENZYME ACTIVITY ASSAY
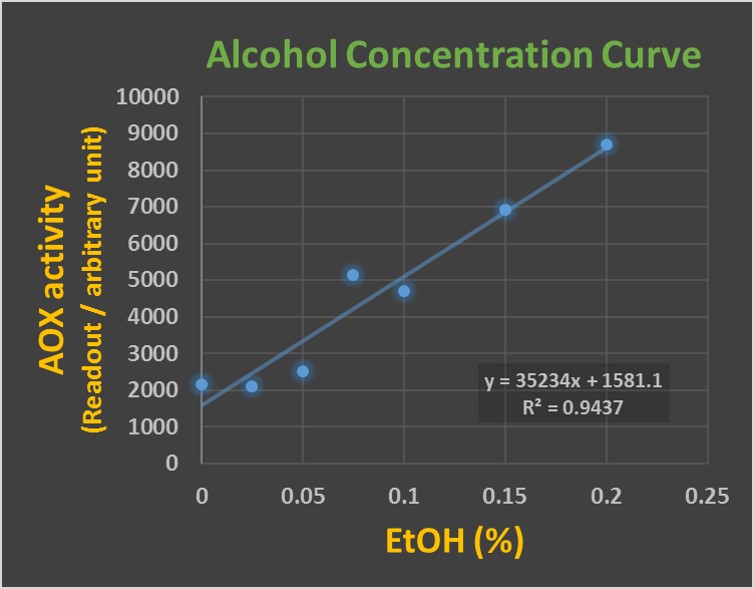
After AOX gene expression was confirmed, we want to know its enzyme activity. AOX catalyzes the oxidation of alcohol in the following chemical reaction C2H5OH + O2 → CH3CHO + H2O2 and generates hydrogen peroxide. We examined the activity of AOX enzyme by measuring H2O2 production from the oxidation of ethanol. Fluorimetric Hydrogen Peroxide Assay Kit of Sigma-Aldrich was used for the study. In the kit, the red peroxidase substrate is designed to react with hydrogen peroxide to generate red fluorescence signal that can be detected at Ex/Em = 540/590 nm in the microplate reader. We prepared 1ml of overnight cultured E. coli displaying LO-AOX enzyme. The bacteria were centrifuged and resolved in Assay Buffer provided by the Sigma-Aldrich kit. Then, the resulting lysates were mixed with the increasing concentrations of ethanol from 0%, 0.025%, 0.05%, 0.075%, 0.10%, 0.15% to 0.2% for 3 minutes at room temperature. The tested alcohol concentrations were at the range from 0.03% (the alcohol law limit for safety driving) to 0.2% (people may lose consciousness at this level). The following procedure was according to the manufacture’s instruction. The data were read out at Ex/Em = 540/590 nm in the microplate reader (BioTek Microplate Spectrophotometer). As Figure 2 showed, the intensities of AOX activity were significantly and linearly correlated to the concentration of ethanol in a dose-dependent manner. The results indicated that LO-AOX enzyme we produced has a functional enzyme activity and reacted with alcohol concentration dose-dependently, implying we can use this assay to measure the unknown sample of alcohol.
Figure 2: AOX protein analysis. SDS-PAG and Coomassie Blue staining were used to observe protein expression level. Lane 1: wild-type E. coli as a mock control; Lane 2: LO outer membrane protein (17 kDa) expression in E. coli; Lane 3: LO-AOX fusion protein (91 kDa) expression in E. coli.; Lane 4: AOX protein (79 kDa) expression in E. coli.
TMB ASSAY (PERFORMED BY NCTU-FORMOSA 2016)
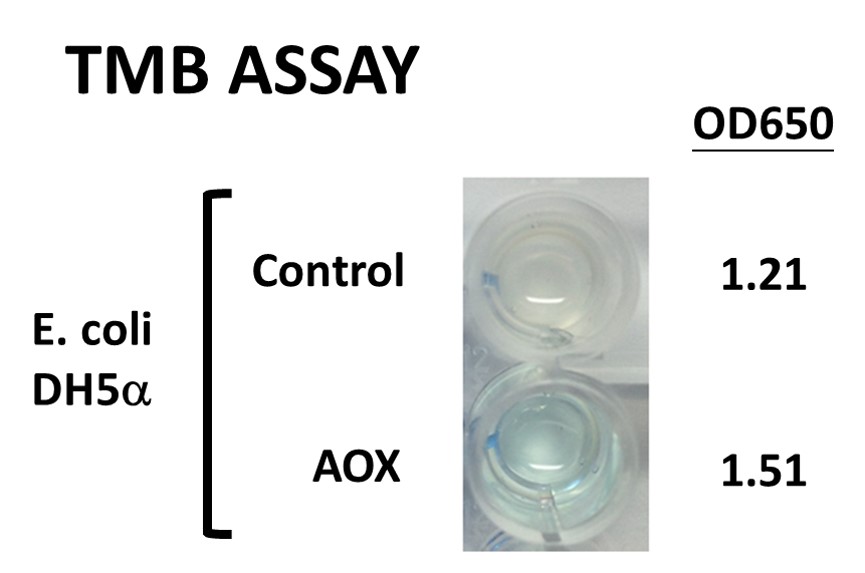
To test the enzyme activity of AOX protein, which catalyzes the oxidation of alcohol and generates H2O2 products, produced by iGEM Team Mingdao, NCTU-FORMOSA performed HRP-TMB assay. TMB (3,3',5,5'-Tetramethylbenzidine) is oxidized and changed to a deep blue color during the enzymatic degradation of H2O2 by horse radish peroxidase (HRP). The concentration of H2O2 can be determined by checking the color change, indicating TMB assay can be used to examine the enzyme activity of AOX with the substrate of alcohol. NCTU-FORMOSA cultivated 3ml of the E.coli DH5alpha carrying the Mingdao iGEM team’s biobrick (i.e., Pcons-RBS-LO-AOX/pSB1C3, BBa_K1991009) in the LB media supplemented with Chloramphenicol. And we prepared another one as the control which didn’t have any plasmid. The next day, NCTU-FORMOSA centrifuged 1mL of bacteria expressing LO-AOX enzyme followed by being suspended in PBS. The control group was adjusted to the OD values at the same level of the LO-AOX group. After mixing bacterial samples with ethanol, TMB was added as a substrate of HRP and incubated in the dark for 3 min. The color of solution was significantly changed to blue at an OD650 of 1.51 compared to 1.21 in the control group, clearly demonstrating the ethanol was oxidized by AOX. As a result, NCTU-FORMOSA proved the function of their BioBrick by testing the AOX enzyme activity.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30
Illegal NotI site found at 2498 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 497
Illegal XhoI site found at 2507 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 452
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
| None |