Part:BBa_K1658001
Cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase CAD1 - 2
Cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase (CAD, EC 1.1.1.195) is an NADP(H) specific oxidoreductase catalysing the reversible conversion of cinnamyl aldehydes to the corresponding alcohols or monolignols (Mansel et al., 1974; Wyrambik and Griesebach, 1975; Boudet et al., 1995). Polymerization of the three monolignols: /?-coumaryl, sinapyl and coniferyl alcohols lead to lignin. The enzyme is closely related to lignification, and chemical inhibition of its activity reduces the synthesis of lignins (Moesbacher et al., 1990; Mauch-Mani and Slusarenko, 1996).
Since the sequence obtained as mRNA of Ocimum Basilicum, we have obey the codon bias rule in order to express the enzyme in Escherichia Coli BL21(DE3) properly.
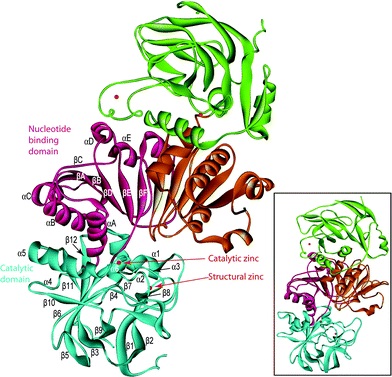
Figure1:The predicted three-dimensional structure of CAD1. Data were analysed by the SWISS-MODEL software, and the figure was prepared with the program MOLMOL. a-helices are indicated in red and yellow, b-sheets by arrows, and turns and coils by curled lines. The NADPH binding and substrate binding sites are also indicated.
Since the sequence obtained as mRNA of Ocimum Basilicum, we have obey the codon bias rule in order to express the enzyme in Escherichia Coli BL21(DE3) properly.
Design Notes
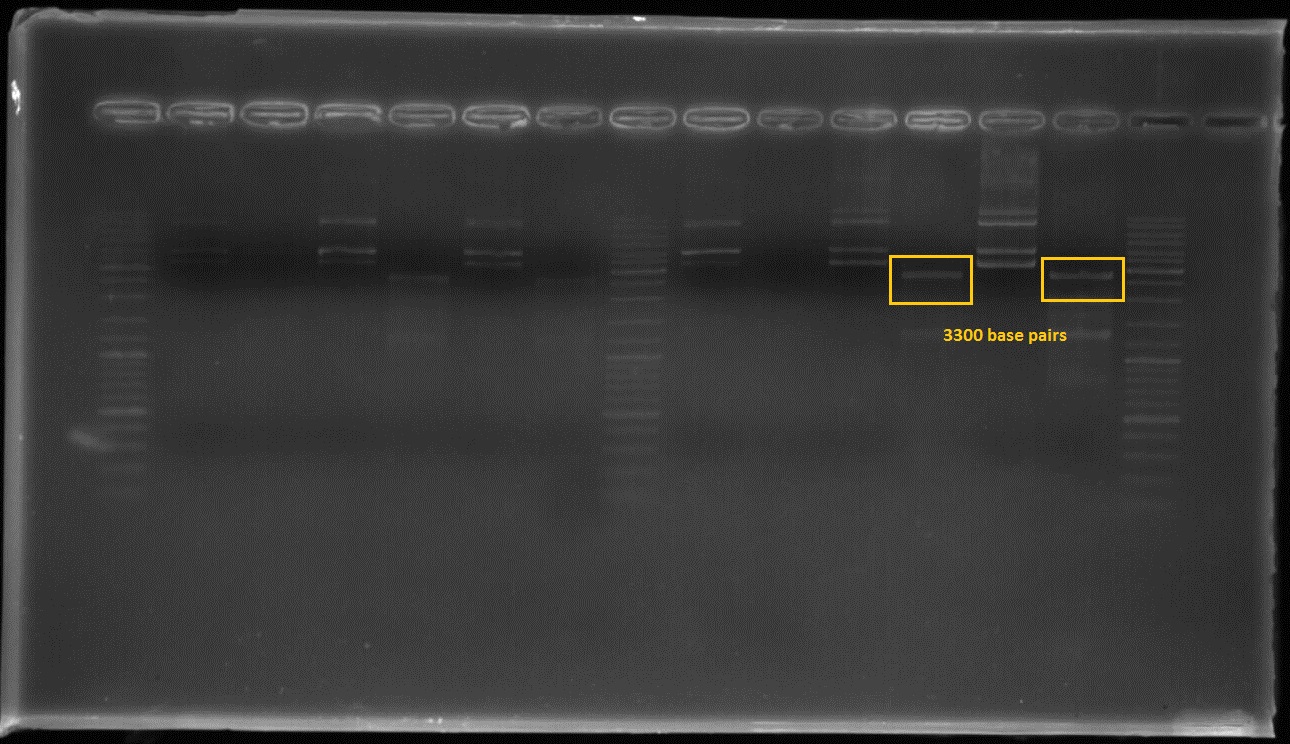
Figure2:The first and third lanes before last ladder well shows that the composite part which includes constitutive promoter(j23100), Ribosome binding side(B0034), CAD1 enzyme coding gene and Terminator(B0010) in order at 3300 basepairs after double digestion.
This enzyme belongs to the family of oxidoreductases, specifically those acting on the CH-OH group of donor with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor. The systematic name of this enzyme class is cinnamyl-alcohol:NADP+ oxidoreductase. Other names in common use include cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase, and CAD. This enzyme participates in phenylpropanoid biosynthesis.
Chemical Reaction of CAD: Cinnamyl alcohol + NADP+ = cinnamaldehyde + NADPH.
Cofactor :Zn2+ Note: Binds 2 Zn2+ ions per subunit.
Involved in lignin biosynthesis. Catalyzes the final step specific for the production of lignin monomers. Catalyzes the NADPH-dependent reduction of coniferaldehyde, 5-hydroxyconiferaldehyde, sinapaldehyde, 4-coumaraldehyde, caffeyl aldehyde and cinnaml alcohol to their respective alcohols
Functional expression of the Ocimum CAD1in E.coli PCR was used to introduce EcoRI , Xbal, Spel, Notl and Pstl at side ends of CAD1 coding region. The amplified product was single and double digested with EcoRl and Notl and the resultant fragment was cloned into the same sides ofthe puC57 vector. The engineered plasmid was transformed into E.coli BL 2l (DE3) cells which has lack of nudeases and proteinoses and ideal for expression.


Characterization
Fehling's solution is actually a mixture of two solution that are kept apart until needed. These are called Fehling's A and Fehling's B solutions.
Fehling's A is a solution of copper(II) sulphate and Fehling's B is a mixture of sodium hydroxide and potassium sodium tartrate (2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate).
When these two solutions are mixed together they form a copper(II) complex ion with the 2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate ligand. [Cu(tartrate)2]2+.
When the suspected aldehyde is warmed with a sample of this mixture, a red precipitate of copper(I) oxide is indicative of an aldehyde.
The copper(II) complex is reduced by the aldehyde to copper(I) oxide.
We used this technique to show that our CAD1 enzyme works and converts cinnamon alcohol to cinamaldehyde.
Since aldehyde is form, copper(II) complexes could be observed.
Source
Ocimum basilicum is sweet basil (Eukaryota, Viridiplantae, Streptophyta, Embryophyta, Tracheophyta, Spermatophyta, Magnoliophyta, eudicotyledons, Gunneridae, Pentapetalae, asterids, lamiids, Lamiales, Lamiaceae,Nepetoideae, Ocimeae, Ocimum)
Since the sequence obtained as mRNA of Ocimum Basilicum, we have obey the codon bias rule in order to express the enzyme in Escherichia Coli BL21(DE3) properly.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
References
Iijima, Yoko, and Guodong Wang. "Analysis of the Enzymatic Formation of Citral in the Glands of Sweet Basil." Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 21 July 2005: 145. Print
Ma, Q.(2010). Functional analysis of a cinnamyl alcohol dehydrogenase involved in biosynthesis in wheat. Journal of Experiment Botany, 2735-2744.
| None |