Part:BBa_K346001
RBS (B0034) + MerR (mercury-responsive transcription factor)
This part was designed as a translational unit for MerR expression.
The mercury resistance operon, mer, enables bacteria to avoid and remove toxic metal Hg, under the regulation of the MerR family transcriptional factor MerR. MerR acts as an activator of mer genes in response to the presence of Hg (II), while it will turn into a weak repressor in the absence of Hg (II), to maintain its own expression at certain level.
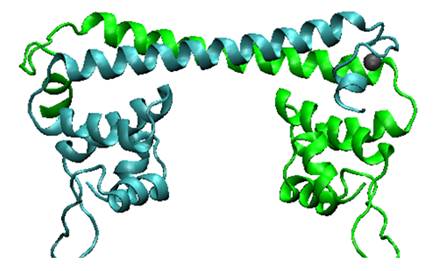
Fig.1. Predicted MerR dimer structure. The predicted three dimensional conformation of Hg (II) bound MerR structure by our 3D modeling. Two monomers are indicated in green and cyan, respectively. MerR can be divided into two modular domains: the metal binding domain at the C-terminal and DNA binding domain at the N-terminal. The signature of MerR family is a helix-turn-helix (HTH) motif followed by a coiled-coil region, namely, a similar N-terminal helix-turn-helix DNA binding domains and a C-terminal effector binding domains that are specific to the effector (eg. metal ions)to be recognized
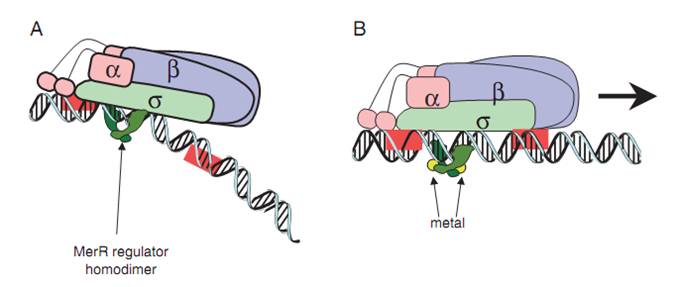
The MerR protein, in the form of homodimer, binds to the mer operon between the RNA polymerase binding sites of the promoter region. The attachment is independent on the presence of Hg(II). When the apo-MerR dimer bind to the dyad symmetrical operator DNA between the -35 and – 10 elements of mercury inducible promoter, PmerT, which has a unusually long spacer of 19 bp for MerR to bind on, the binding of RNA polymerase is inhibited. When Hg(II) is available in the environment, the ion binds to merR between the two subunits. The Hg-bound MerR can result in an a structural distortion of PmerT, allowing the RNA polymerase contacts to be made, leading to the expression of down-stream genes(Fig.2).
Fig.2. A generalized mechanism of MerR family regulator transcriptional activation. A: The dimeric MerR regulator binds to the operator region of the promoter and recruits RNA polymerase, forming a ternary complex. Transcription is slightly repressed because the apo-MerR regulator dimer has bent the promoter DNA such that RNA polymerase does not contact it properly. B: Upon binding the cognate metal ions (shown as cyan circles) the metallated MerR homodimer causes a realignment of the promoter such that RNA polymerase contacts the -35 and -10 sequences leading to open complex formation and transcription. Modified from Brown et al.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
//cds/transcriptionalregulator
| chassis | Device has been shown to work in DH5α. |
| n/a | RBS (B0034) + MerR (mercury-responsive transcription factor) |