Part:BBa_K316002
dif excision site from B. subtilis
B. subtilis dif: sequence-specific recombinase recognition site
In cells with circular chromosomes, recombinatorial repair and homologous recombination can generate multimeric chromosomes 1. ‘’Dif’’ sites are part of a system to ensure that multimeric chromosomes can be separated to monomers, which is required for proper sharing of genetic material between daughter cells. In ‘’B. subtilis’’ the tyrosine family recombinases such as RipX and CodV mediate the separation at 28-bp sequence Bs’’dif’’ 1. The site-specific recombinases are able to recognize two directly repeated ’’dif’’ sites and excise the fragment flanked by the two sites 2.
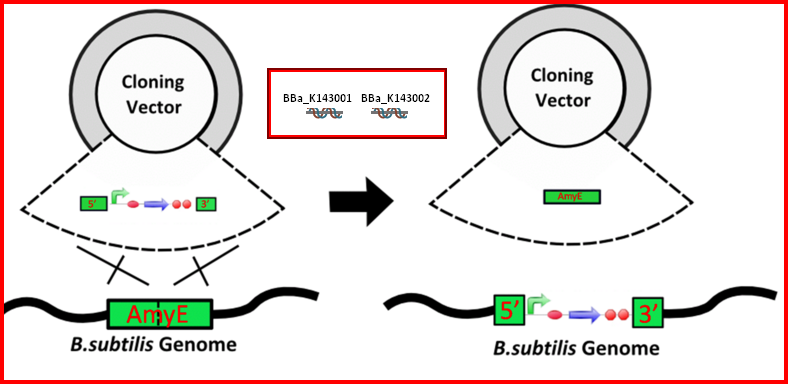
Figure 1. Removal of a specific gene from a genome integrated construct.
The site-specific recombinases, endogenous to ‘’B. subtilis’’ strains are able to recognise Bs’’dif’’ sites and recombine out the strand of DNA directly flanked by the two sites. Recombination leaves a single dif site.
The construct was previously engineered to homologously recobine into the genome of ‘’B. subtilis’’. Integration sequences such as amyE BBa_J143001, BBa_J143002 can be used to achieve this.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
References
<biblio>
- 1 http://2010.igem.org/Team:Imperial_College_London
- 2 pmid=14597697
</biblio>
| None |