Part:BBa_K1033901
meffBlue, blue chromoprotein (incl RBS)
This chromoprotein from the coral Montipora efflorescens, meffBlue (also known as Rtms5), naturally exhibits strong color when expressed. The protein has an absorption maximum at 592 nm giving it a blue color visible to the naked eye. Compared to many other chromoproteins, such as amilCP (BBa_K592009), amilGFP (BBa_K592010), spisPink (BBa_K1033932), asPink (BBa_K1033933) and aeBlue (BBa_K864401), the color development is slower. The color is readily observed in both LB or on agar plates after 24-64 hours of incubation. The protein meffBlue has significant sequence homologies with proteins in the GFP family.
Usage and Biology
This part is useful as a reporter.
Source
Montipora efflorescens. The protein was first extracted and characterized by Beddoe et. al. under the name Rtms5 (UniProtKB/Swiss-Prot: P83690.2). This version is codon optimized for E coli by Genscript.
References
[http://scripts.iucr.org/cgi-bin/paper?cy0089] Beddoe, Travis, et al. "The production, purification and crystallization of a pocilloporin pigment from a reef-forming coral." Acta Crystallographica Section D: Biological Crystallography 59.3 (2003): 597-599.
[http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0969212603000285] Prescott, Mark, et al. "The 2.2 Å crystal structure of a pocilloporin pigment reveals a nonplanar chromophore conformation." Structure 11.3 (2003): 275-284.
Characterization
Team:NJTech_China 2022
Hoping to make a useful contribution for future iGEM teams,we completed the experimental characterization of existing parts tsPurple, purple chromoprotein(incl RBS) and meffBlue, blue chromoprotein and provided new documents for both of them.
The meffBlue sequence (Part:BBa_K1033901) optimized for E. coli was incorporated into plasmid pET-29a(+), transformed into E. coli BL21 for characterization and measurement. We provided meffBlue with results and data based on protein expression and purification, TOF-Mass spectrometry, and Swiss-model.
Methods: SDS-PAGE, ultramicro spectrophotometer ,TOF-Mass Spectrometry, and Swiss-Model.
Results:
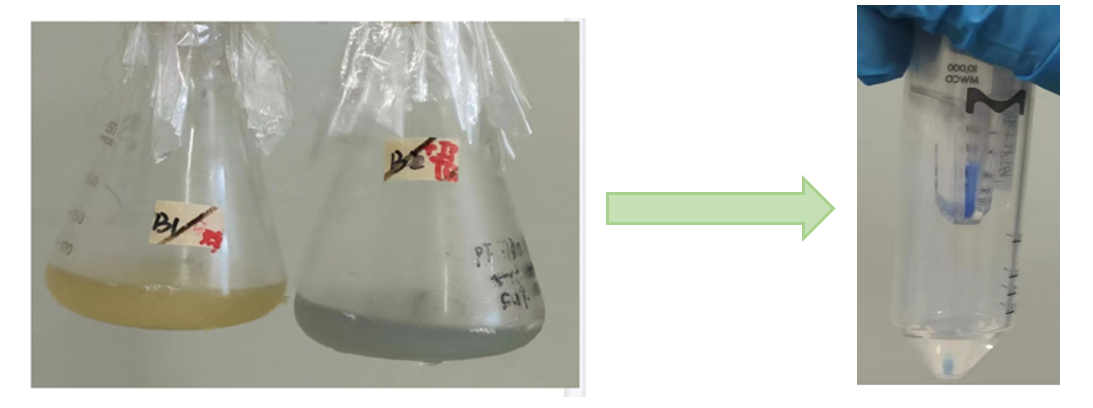
Fig.1 The fermentation broth of meffBlue Fig.2 Proteins after secondary ultrafiltration
Conclusion: The cell pellet was collected by harvesting 50mL culture after 24h of induction followed by centrifugation at 4 degrees and 6000 rpm for 10min. Then, we performed ultrasonic disruption and collected the supernatant after centrifugation. The protein was purified and collected through ultrafiltration and affinity chromatography.
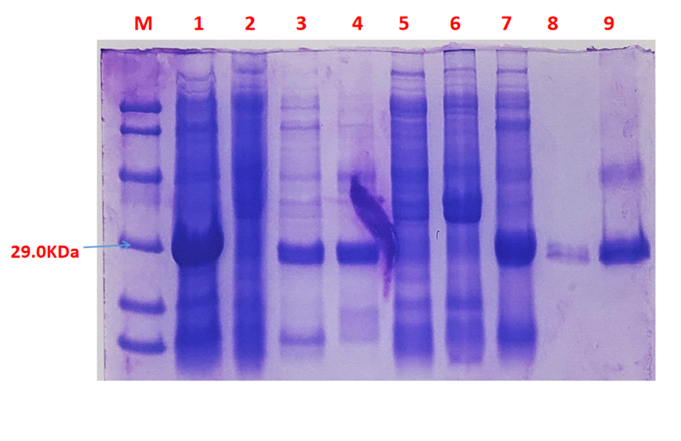
Fig.3 SDS-PAGE of the chromoprotein meffBlue
1· meffBlue- The culture without IPTG induction.
2· meffBlue- Supernatant without IPTG induction after sonication.
3· meffBlue- The sedimentation without IPTG induction and after sonication.
4· meffBlue- Supernatant sample without IPTG induction after sonication.
5· meffBlue- The sedimentation after IPTG induction and ultrasound.
6· meffBlue- The culture after IPTG induction.
7· meffBlue- Protein sample after the ultrafiltration (diluted 5 times).
8. meffBlue- Protein after GST affinity chromatography.
9· meffBlue- Purified protein sample.
Conclusion: The protein gel preliminarily proved that the molecular mass of the meffBlue protein was correct, which is consistent with the expected molecular mass of meffBlue protein (the molecular mass of amajLime protein is about 26.3 kDa). Compared with lane 5, 6 and 7, lane 1, 2,3 and 4 indicate that more meffBlue protein can be obtained with IPTG induction. As is shown in lane 8, the concentration of protein was increased after ultrafiltration concentration. Lane 9 shows that the purification effect of protein after nickel affinity chromatography was better, and the impurity protein was less than before affinity chromatography. In conclusion, it can be seen that our expression and purification strategy is effective.
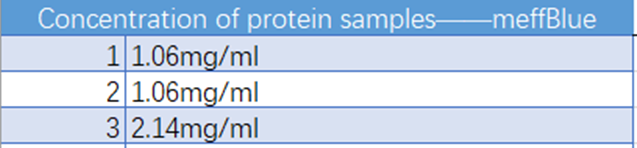
Fig. 4 concentration of the meffBlue protein samples
Conclusion:We used the ultramicro spectrophotometer to measure the concentration of meffBlue protein. The concentration of meffBlue samples was 1.42mg/ml.
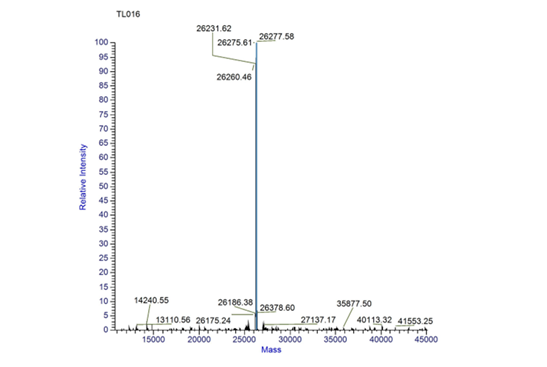
Fig.5 TOF MS of meffBlue.
Conclusion: We performed a Time of Flight Mass Spectrometer on the purified HIS-tagged meffBlue protein. The predicted molecular mass of this protein is about 26.3KDa. The result of TOF-Mass Spectrometry showed that the specific molecular mass of meffBlue protein is 26.27Da (the value of the sharpest peak is shown as the molecular mass of meffBlue protein).
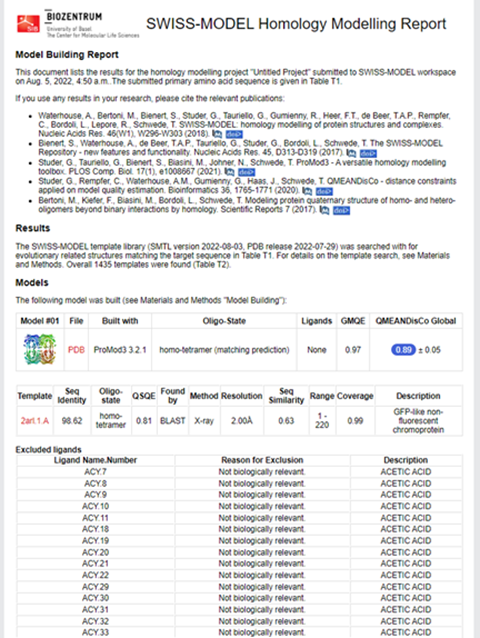
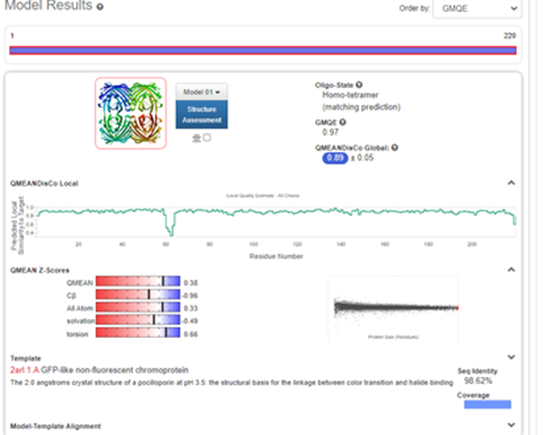
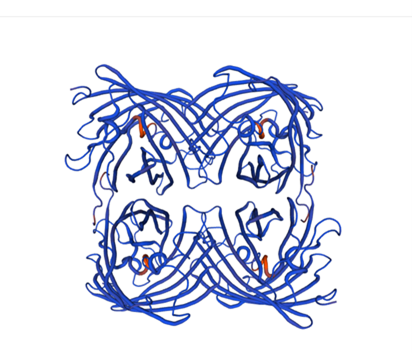
Structural modeling results of the meffBlue protein based on Swiss-Model
Fig.6-1 The results of the homology and structural modelling protein meffBlue.
Fig.6-2 The 3D model of the homology and structural modelling protein meffBlue.
Conclusion: We used Swiss-Model to simulate the three-dimensional structure of meffBlue protein. The above figures showed the modeling result of Swiss-Model.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
//function/reporter
//function/reporter/color
| abs | 592 nm |