Part:BBa_K4182007:Design
Lysis-phi X174
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Profile
Base Pairs
273
Design Notes
The gene was optimized by E. coli codon
Source
Shigella flexneri 2a str. 301 (strain: 301, serotype: 2a)
Usage&Biology
Source and Principle
Biosafety is an important consideration when designing engineered bacteria. From the beginning, we designed the bacteria on the premise that it would work in the field soil, so we first needed to consider whether our product could be easily controlled for the time of its operation and whether there were potential risks to soil structure, crop growth, and the balance of soil microbiota. So we designed a "suicide system" at the genetic level to ensure that our engineered bacteria would not pose a potential biosecurity risk to the ecological environment.
The suicidal behavior of bacteria is a common phenomenon in nature, which is a programmed death mechanism of prokaryotes. quorum sensing (QS) is a form of communication between bacterial cells. Cells synthesize and secrete signal molecules. When the concentration of signal molecules in the environment reaches a certain threshold, a series of genes are activated, and the bacterial population synchronously realizes certain functional and behavioral changes. A quorum-sensing suicide gene circuit has been constructed, and the systematic study and precise regulation of this gene circuit are of great significance both in theory and application [1].
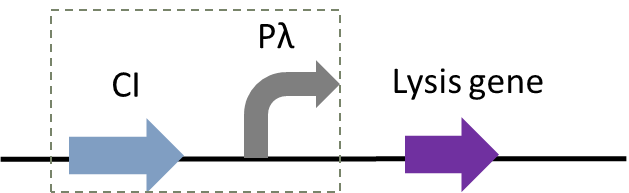
In addition to population-responsive suicide mechanisms, suicide systems with other regulatory modes can also be designed through synthetic biology. Here, we designed a temperature-responsive cleavage system to achieve temperature-controlled cleavage, that is, cleavage of thermoregulated lysis genes (Gene ID: IF654_RS00240) (Figure 1).
Figure 1: Circuit diagram of plasmid 5: Where CI is the C1857 suppression subsystem, Pλ is the promoter, and the temperature control system is in the dashed box.
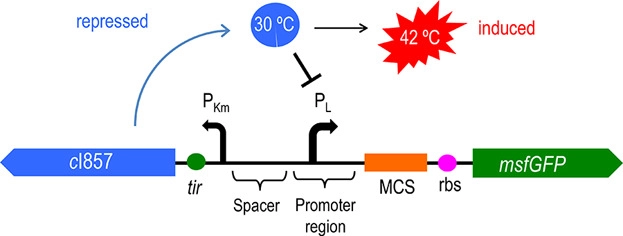
Figure 2 shows the principle of the temperature control system [4]. When bacteria are at a low temperature, the c1857 gene expression protein binds to the Pλ promoter, making downstream genes unable to be translated. At 42℃, the protein will be cleaved, leading to the expression of downstream genes.
In conclusion, we wanted to take advantage of temperature changes as a variable environmental signal, allowing our engineered bacteria to function at lower temperatures and Lysis proteins to lysis the engineered E. coli cells at higher temperatures, resulting in control of the engineered bacteria and release of the product.
Codon improvement and optimization
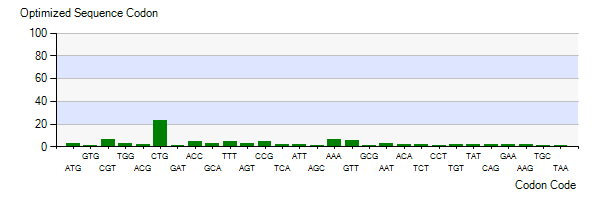
The Lysis gene we used was expressed in Pseudomonas lundensis. To better express the Lysis gene in engineered bacteria, we optimized the codon of the Lysis gene according to the codon preference of Escherichia coli. Figure 5-3 shows the number of codons we optimized to make our codons more in line with Escherichia coli preference. The modified Lysis gene is shown in BBa No.K4182007.
Figure 3: Optimized Sequence Codon in plasmid Ⅴ
References
1. Din, M.O., et al., Synchronized cycles of bacterial lysis for in vivo delivery. Nature, 2016. 536(7614): p. 81-85.
2. Saeidi, N., et al., Engineering microbes to sense and eradicate Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a human pathogen. Mol Syst Biol, 2011. 7: p. 521.
3. Restrepo-Pineda, S., et al., Thermoinducible expression system for producing recombinant proteins in Escherichia coli: advances and insights. FEMS Microbiol Rev, 2021. 45(6).
4. Aparicio, T., V. de Lorenzo, and E. Martínez-García, Improved Thermotolerance of Genome-Reduced Pseudomonas putida EM42 Enables Effective Functioning of the PL/cI857 System. Biotechnology Journal, 2019. 14(1): p. 1800483.