Part:BBa_K3846511
CYP1A1-CPR fusion protein (10 aa rigid, MfeI/BamHI)
Linker Design V 1.0
To allow more variability and easier combination of CYP P450 enzymes and reductases with different linkers restriction enzymes sites for MfeI (CAATG) and BamHI (GGATCC) were introduced at the N-terminus and C-Terminus of CYP 450 enzymes and reductases respectively. Linkers were then created by annealing DNA oligos with AATG and GATC overhangs. Flexible linkers mainly containing Glycine (BBa_K3846500, BBa_K3846502) and rigid linkers mainly containing proline (BBa_K3846501, BBa_K3846503) of different length were created. Due to the introduced restriction sites, the linker sequence could not be chosen freely. Two amino acids at the N-Terminus (Glutamine + Leucine) and two amino acids at the C-terminus (Glycine + Serine) were fixed.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 1615
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
iGEM Hamburg 2021 part collection
Terpenoids are an important group of natural products used as biofuels, drugs or fragrances. Naturally occuring in plants it has been shown that microbial terpene production in microorganisms like yeast, E. coli or cyanobacteria is possible. Nevertheless iGEM projects seem to rarely focus on this interesting class of natural products which is correlated with a lack of useful parts inside the iGEM registry.
Fortunately we were able to change that and designed a novel golden gate based toolbox which allows.
- production of terpenoid precursors and simple terpenoids
- creation of CYP P450-reductase fusion enzymes to optimise processing of terpenoid precursors and production of bioactive target products
- modularity of the system to enable exchange of linker sequences/promoters/etc. (MoClo-compatible toolbox)
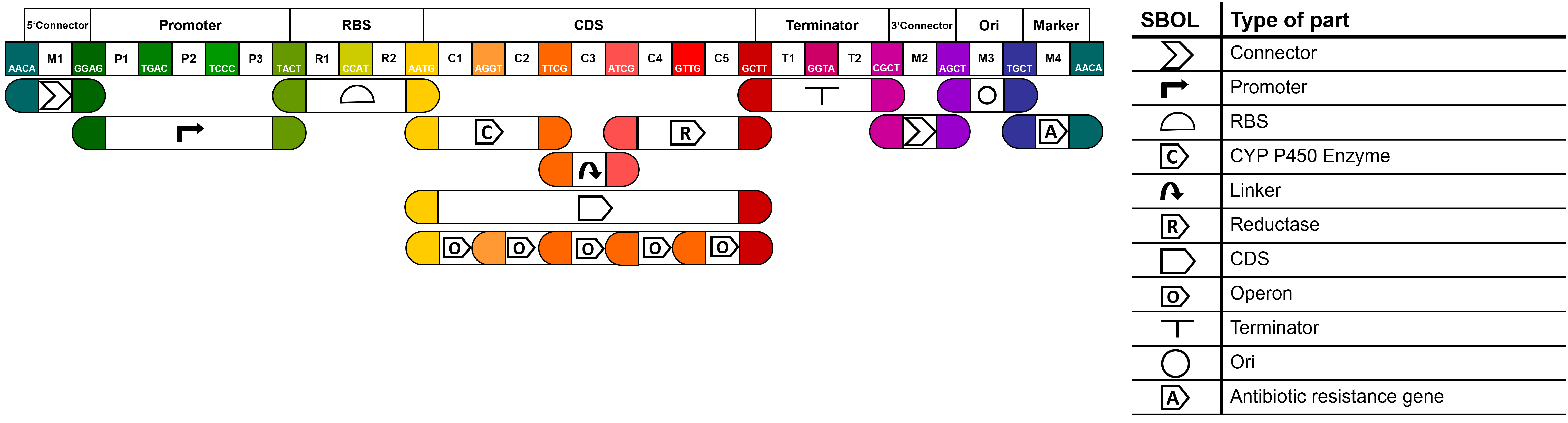
MoClo-based Part Design 2.0
To improve the usefulness of our parts, we then aimed to make our parts compatible with the MoClo standard of goten gate based IIS restriction enzyme assembly. Thereby we expanded the Common Genetic Syntax for fusion sites to allow the creation of a) fusion proteins connected by linker sequences and b) multiple CDS expressed in an operon. More useful information and an overview of all our parts can be found on our wiki.
| None |