Part:BBa_K3580101:Experience
This experience page is provided so that any user may enter their experience using this part.
Please enter
how you used this part and how it worked out.
Applications of BBa_K3580101
In our project, we inserted this parts into pBbe5a(AmpR colE1-ori high copy plasmid., BglBrick vectors) plasmid.
1. in vivo monoterpene synthesis
1.1 Introduction
Before monoterpene synthesis with cell-free system, we confirmed activity of the genes by monoterpene production with E.coli In this experiment, DH5-alpha transformed with a plasmid encoding enzymes of the mevalonate pathway (pBbA5c-MevT-MBI from addgene) and a plasmid encoding GPP synthetase and monoterpene synthase (BBa_K3580101 / BBa_K3580102) were used.
1.2 Materials and Methods
1.2.1 Growth condition
DH5-alpha transformed with pBbA5c-MevT-MBI and BBa_K3580101 / BBa_K3580102 were used in this experiment. DH5-alpha was selected as the strain used because it was based on the strain used in the 2019 XJTU-CHINA team's limonene production project. And DH5-alpha transformed with only pBbA5c-MevT-MBI was used as negative control. Strains of transformed DH5-alpha were grown in 2xYT media (16 g/L tryptone, 10 g/L yeast extract, 7 g/L NaCl. These components were purchased from Nakalai tesque) containing 25 ng/µl (Nakalai tesque) of chloramphenicol and 1 % in mass percent concentration of glucose (Wako). After culturing overnight (37℃, 180 rpm, 14 h) on 3 ml scales, 500 µM IPTG (Nacalai tesque) to induce expression and 500 µl dodecane overlay to capture monoterpene were added when OD600 exceeded 1.5. After induction by IPTG, strains were continuously cultured at 30 ℃ and 200 rpm for 2 days (48 h). After 2 days of culture, 300 µl dodecane overlays were collected, mixed with 700 µl ethyl acetate and analyzed by GC/MS.
1.2.2 Method of GC/MS analysis
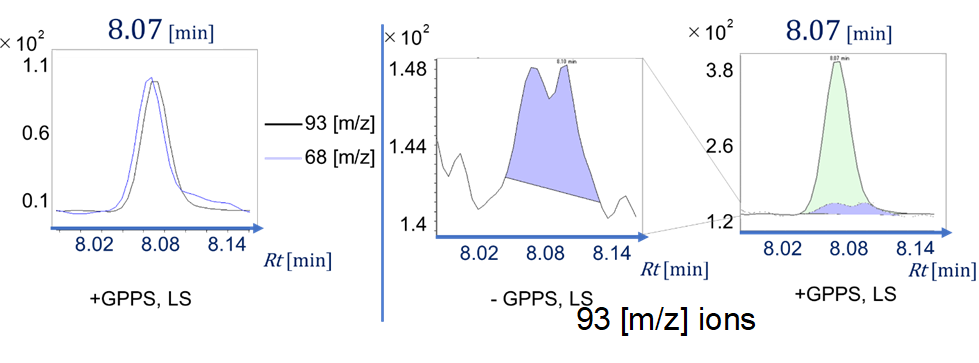
GC/MS analysis was performed on an Agilent 7890B GC with Agilent 5977B MS using a constant flow rate of 1.2 ml/min of helium carrier gas and using HP-5MS (30 m, 0.25 mm, 0.25 µm) column. The inlet temperature was 300 ℃ and initial column temperature was 40 ℃ for 1 min. The column was then heated to 300 ℃ at a rate of 15 ℃/min and held at 300 ℃ for 2 min. The Injection volume was 1 µl with the split ratio 10:1. In this experiment, SIM mode was used for the analysis. Ions with four m/z values characteristic of limonene (68 and 93) and sabinene (77 and 91, 93) were analyzed to confirm the presence of monoterpenes. And for quantitative analysis, 93 m/z was used in each monoterpene analyzes. The quantification of monoterpenes was performed by comparing the analysis results with the data of each monoterpene 100 µM standard product. These m/z values were selected by referring to the mass spectrum of each monoterpene present in NIST Standard Reference database. Preliminary experiments have confirmed that the retention time for the peaks of each monoterpene is 8.07 min for limonene and 8.45 min for sabinene (Figure. 1-2).
1.3 Results
From GC/MS analysis, we confirmed limonene from the introduced pathway. Ions with two characteristic m/z values (68, 93) in limonene were detected in the limonene synthesis system using BBa_K3580101. Also, GC chromatogram of the ion having 93 m/z from the complete limonene pathway shows a peak higher than that from a negative control (Figure. 1-3). Therefore, the yield of synthesized limonene per culture solution was calculated to be 0.161 µM.
2. Cell-free monoterpene synthesis
2.1 Introduction
In this cell-free monoterpene synthesis, we mixed two E. coli extracts each of which has either first 7 or last 2 enzymes of a pathway from Ac-CoA, which is a major intermediate of cell central metabolism. Through mevalonate pathway, the former extract one (derived from E. coli into which pBbA5c-MevT-MBI has been introduced) can provide IPP and DMAPP, which can also be used as intermediates for other important biosynthesis. Here we indeed supplemented only glucose and acetate as carbon sources. We obtained expression system for those seven genes from addgene and have converted this into Biobrick RFC 1000 format by synonymous replacement (BBa_K3580103). In order to take advantage of an engineering principle of synthetic biology we provided two biobrick parts ( BBa_K3580101, BBa_K3580102) for the source for the latter extract. BBa_K3580101 has GPP synthase (GPPS) and limonene synthase. Although GPP synthase is shared with BBa_K3580101, BBa_K3580102 has sabinene synthase, which has one point mutation in limonene synthase (Srividya Narayanan et al 2015) and a new coding sequence for Parts registry of iGEM (See here for more details on this experiments).
2.2 Materials and Methods
2.2.1 Cell growth and extract preparation
User Reviews
UNIQe19bf14f06a47154-partinfo-00000000-QINU UNIQe19bf14f06a47154-partinfo-00000001-QINU