Part:BBa_K1033926
asPink, pink chromoprotein (incl RBS, J23110)
This chromoprotein from the coral Anemonia sulcata, asPink (also known as asCP or asFP595), naturally exhibits strong color when expressed. The protein has an absorption maximum at 572 nm giving it a pink/purple color visible to the naked eye. The strong color is readily observed in both LB or on agar plates after less than 24 hours of incubation. The protein asPink has significant sequence homologies with proteins in the GFP family.
Characterisation
The iGEM team of Rotterdam 2019 characterized this part more as part of the bronze criteria. [1]An addition to the characterization tests is to see whether there will be a change in the absorbance spectrum when the proteins are suspended in acidic or basic environments.
First, full-spectrum analysis with a Synergy™ LX Multi-Mode Microplate Reader (300-1000 nm) was performed to what iGEM Upsala 2013 has done, which is 300-800 nm (Figure 1-3).
The second characterization experiment (figure 4 and 5) was to test the effect of pH: 0.3, 4.3, 7.3, 10.3 and 14. The tests have been performed twice in different wells of a 96-wells plate with a Synergy™ LX Multi-Mode Microplate Reader, 100 uL of each chromoprotein sample was mixed with 100 uL of different pH-samples. Data of the Microplate Reader: https://2019.igem.org/wiki/images/1/18/T--Rotterdam_HR--excelfilepH.xlsx
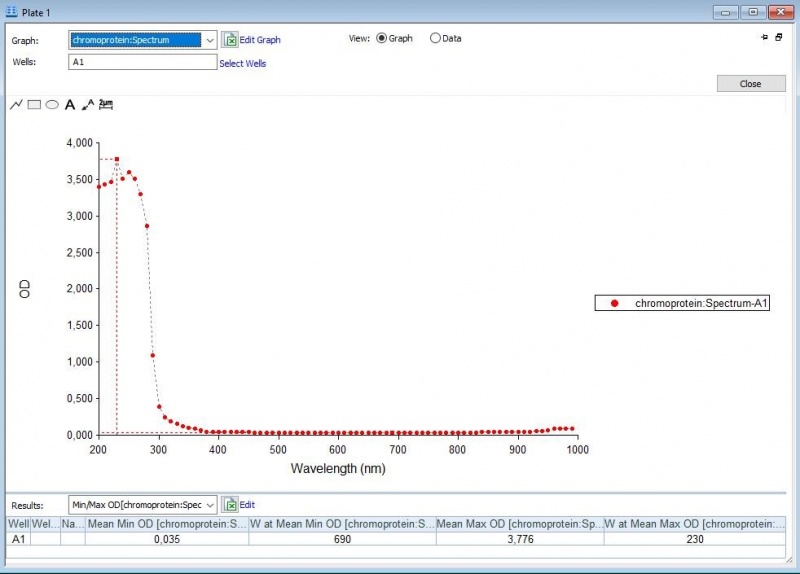
Figure 1: Absorbance spectrum of saline.
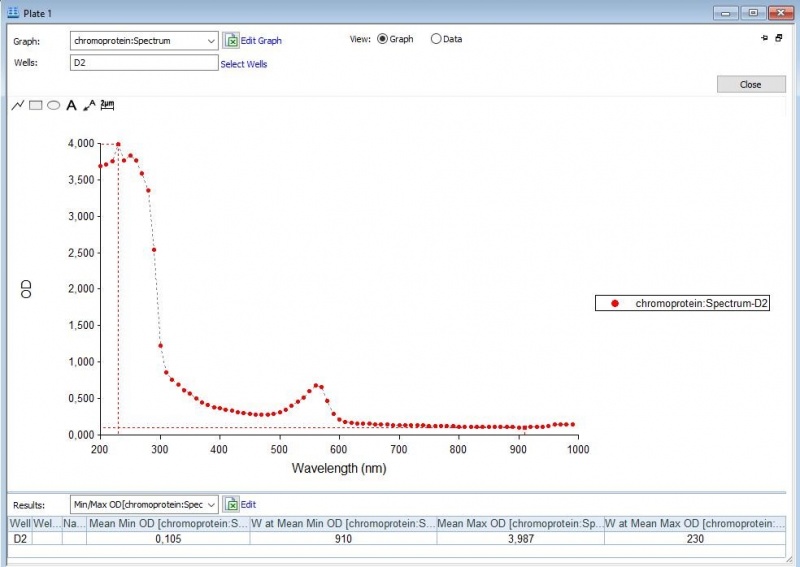
Figure 2: Full spectrum analysis of asPink.
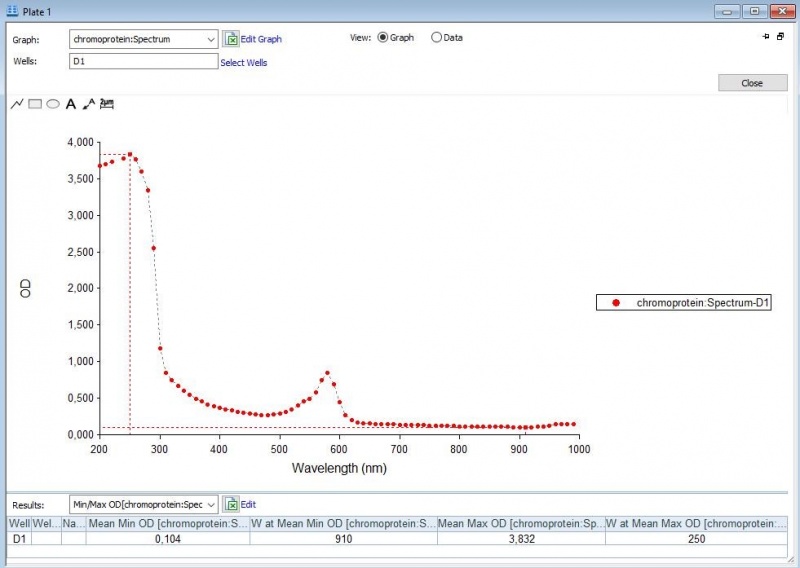
Figure 3: Duplicate of the full spectrum analysis of asPink.
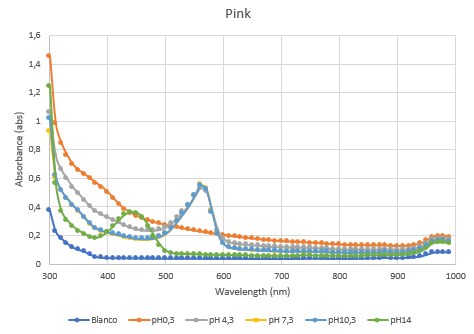
Figure 4: Full spectrum pH-analysis of asPink.
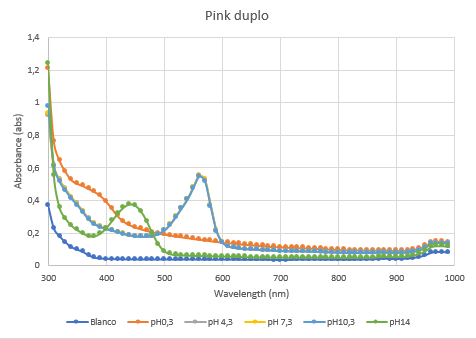
Figure 5: Duplicate of the full spectrum pH-analysis of asPink.
Usage and Biology
This part is useful as a reporter.
iGEM2013 Uppsala: Expression of asPink in E. coli DH5alpha by promoter J23110 from medium copy plasmid pSB3K3 (left) or high copy plasmid pSB1K3 (right).
Source
The protein was first extracted and characterized by Lukyanov et. al. 2000 under the name asFP595 (GenBank: AAG02385.1). This version is codon optimized for E coli by Genscript.
References
[http://www.jbc.org/content/275/34/25879.short]Lukyanov, Konstantin A., et al. "Natural animal coloration can be determined by a nonfluorescent green fluorescent protein homolog." Journal of Biological Chemistry 275.34 (2000): 25879-25882.
[http://www.jbc.org/content/280/4/2401.short]Wilmann, Pascal G., et al. "Variations on the GFP Chromophore - A Polypeptide Fragmentation Within The Chromophore Revealed In The 2.1-Å Crystal Structure Of A Nonfluorescent Chromoprotein From Anemonia Sulcata." Journal of Biological Chemistry 280.4 (2005): 2401-2404.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
| None |
